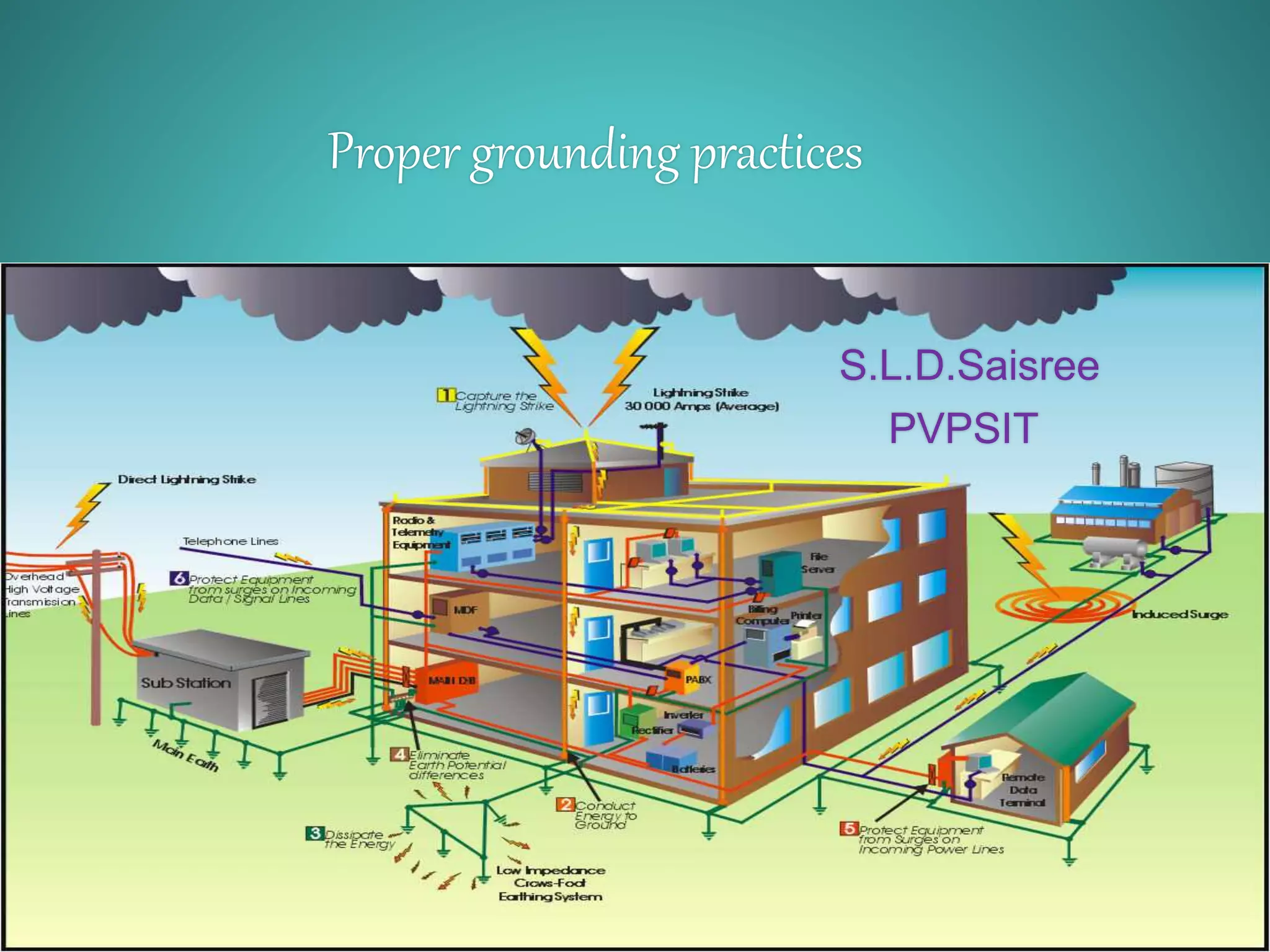
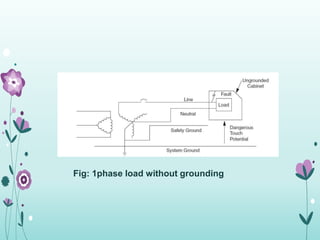
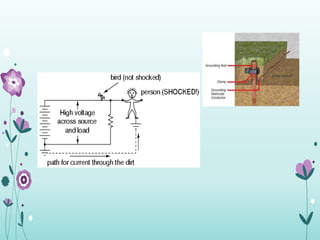
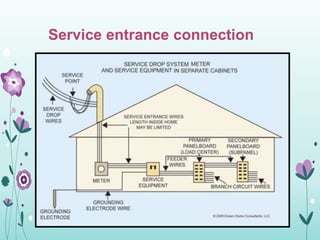
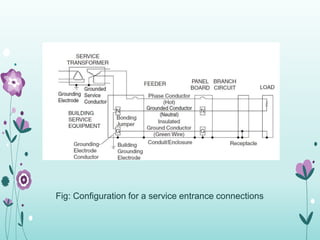
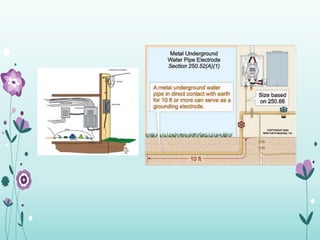
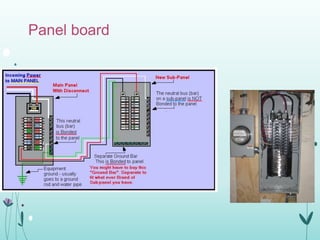
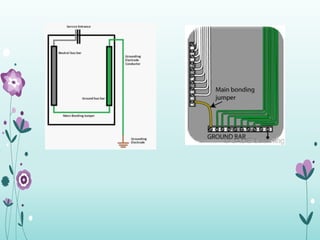
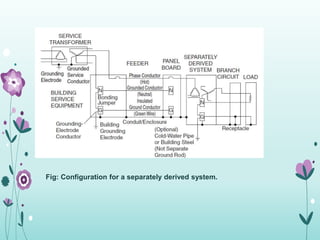
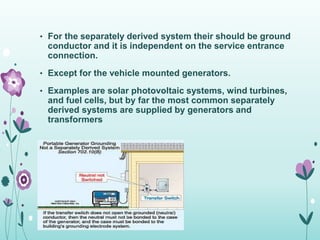
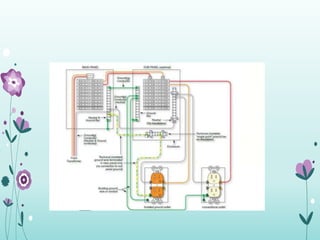
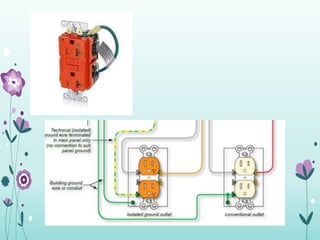
The document discusses the importance of proper grounding practices in electrical systems, highlighting that 80% of power quality issues stem from wiring and grounding problems. Key reasons for grounding include personnel safety, noise reduction in sensitive loads, and ensuring low impedance to limit voltage to ground. It also covers configurations for service entrance connections and the benefits of isolated grounds for sensitive loads.