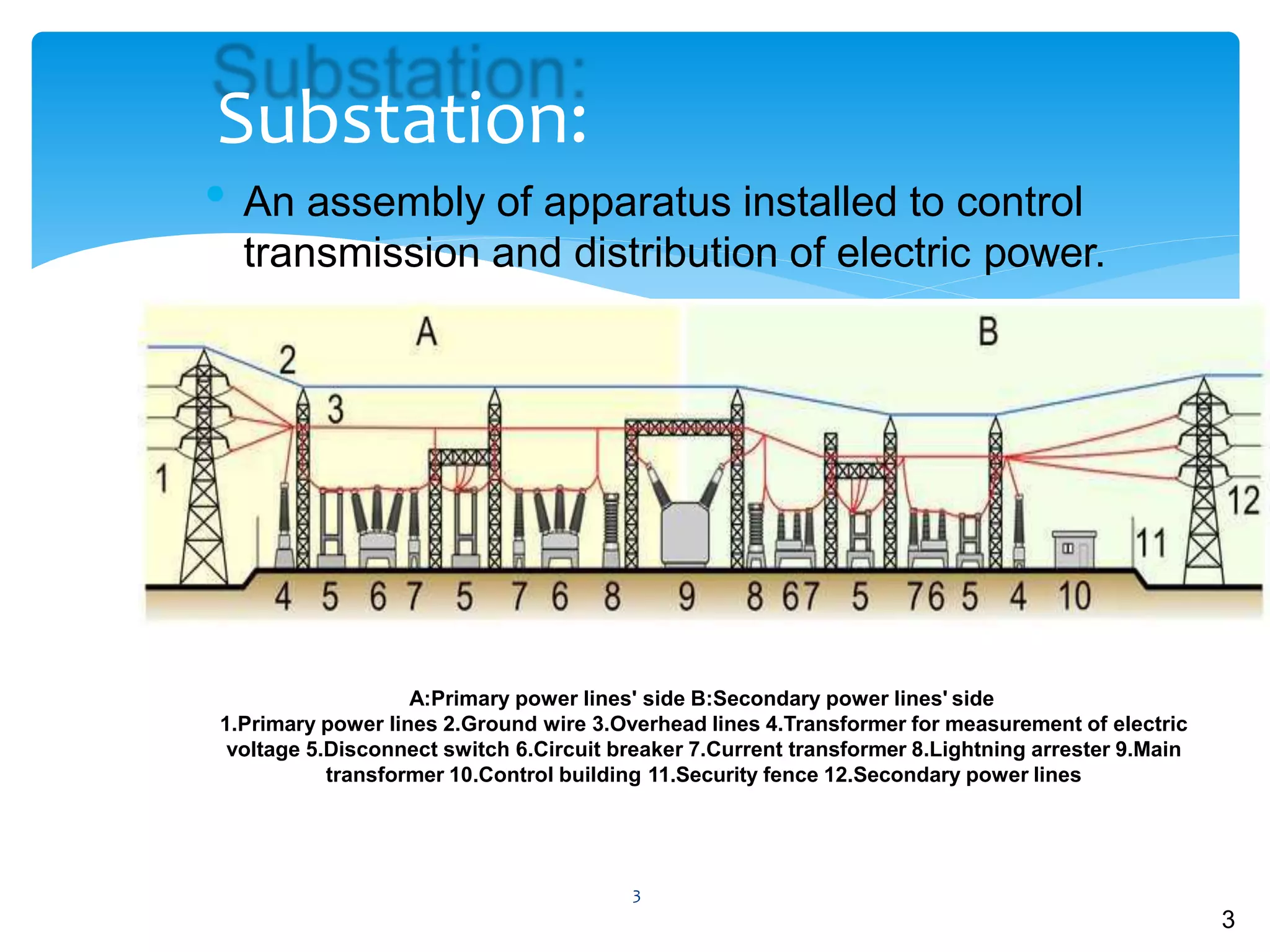
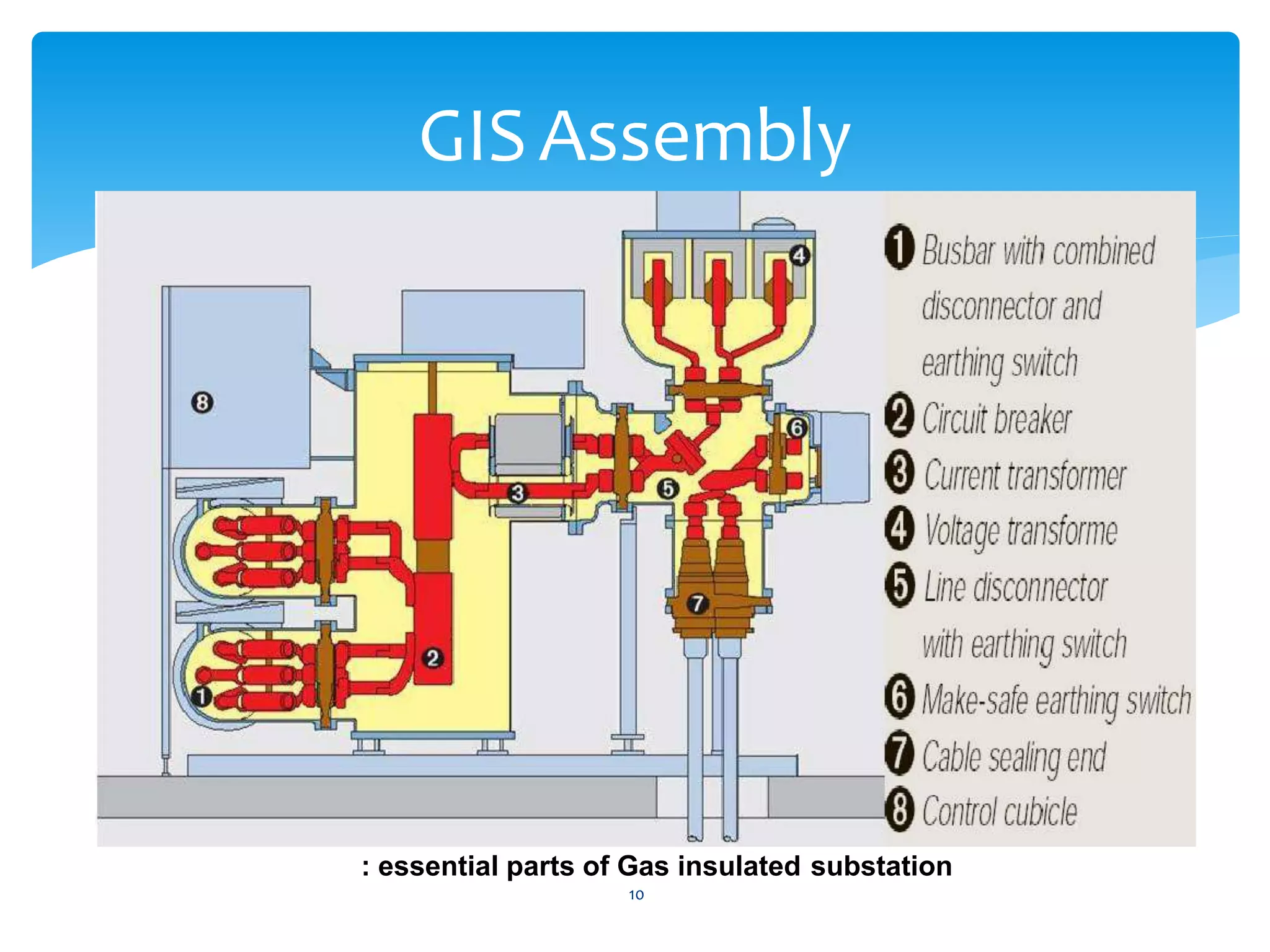
Gas insulated substations (GIS) provide a compact alternative to traditional air insulated substations. GIS assemblies contain various electrical components housed in metal enclosures filled with sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) gas, which serves as the primary insulating medium. SF6 has superior dielectric properties and allows GIS to operate at high voltages in a small footprint. While more expensive initially, GIS occupy one-tenth the space of air insulated substations, making them preferable for urban areas with limited space. However, SF6 is a potent greenhouse gas so future GIS may utilize alternative insulating gases or mixtures.