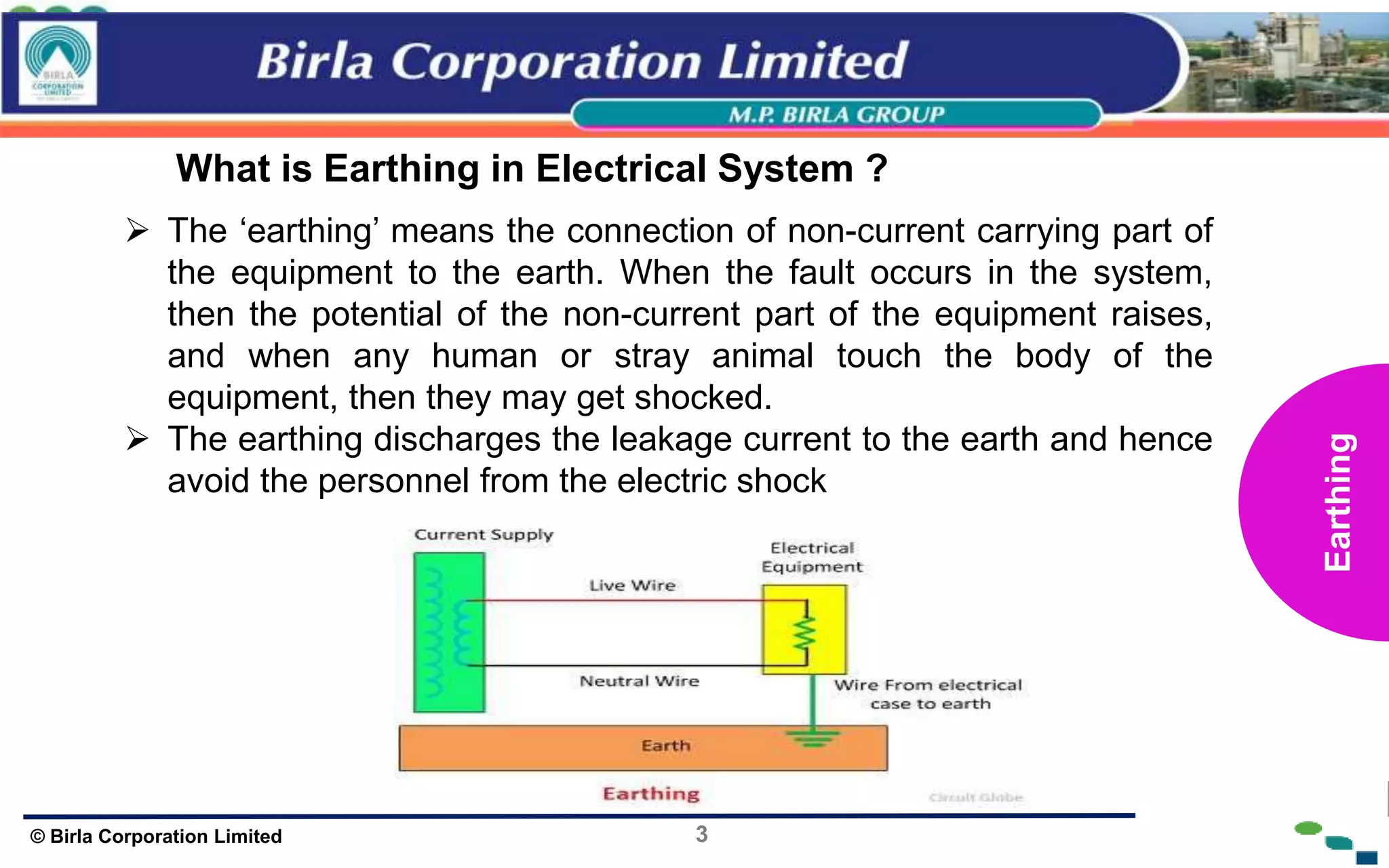
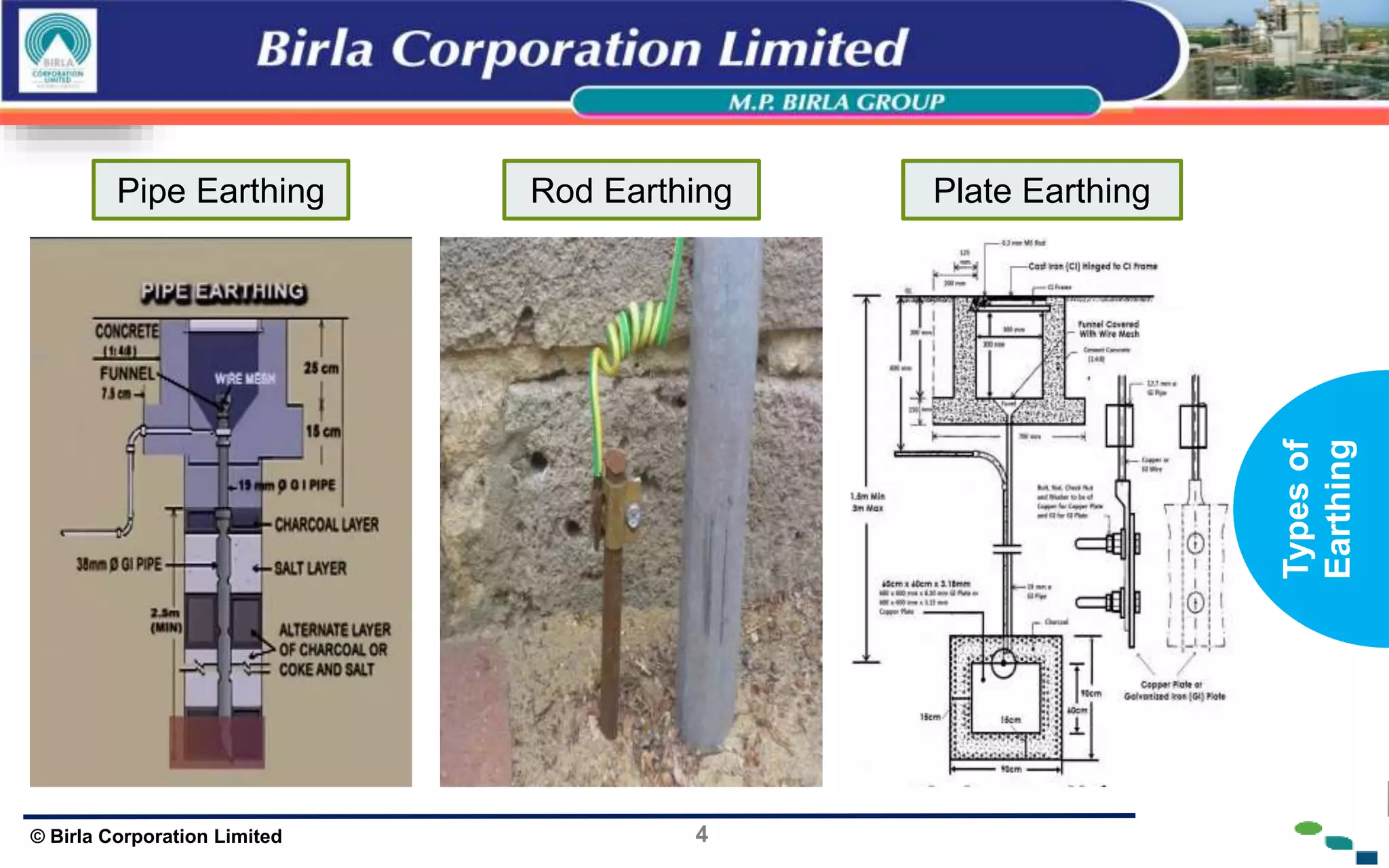
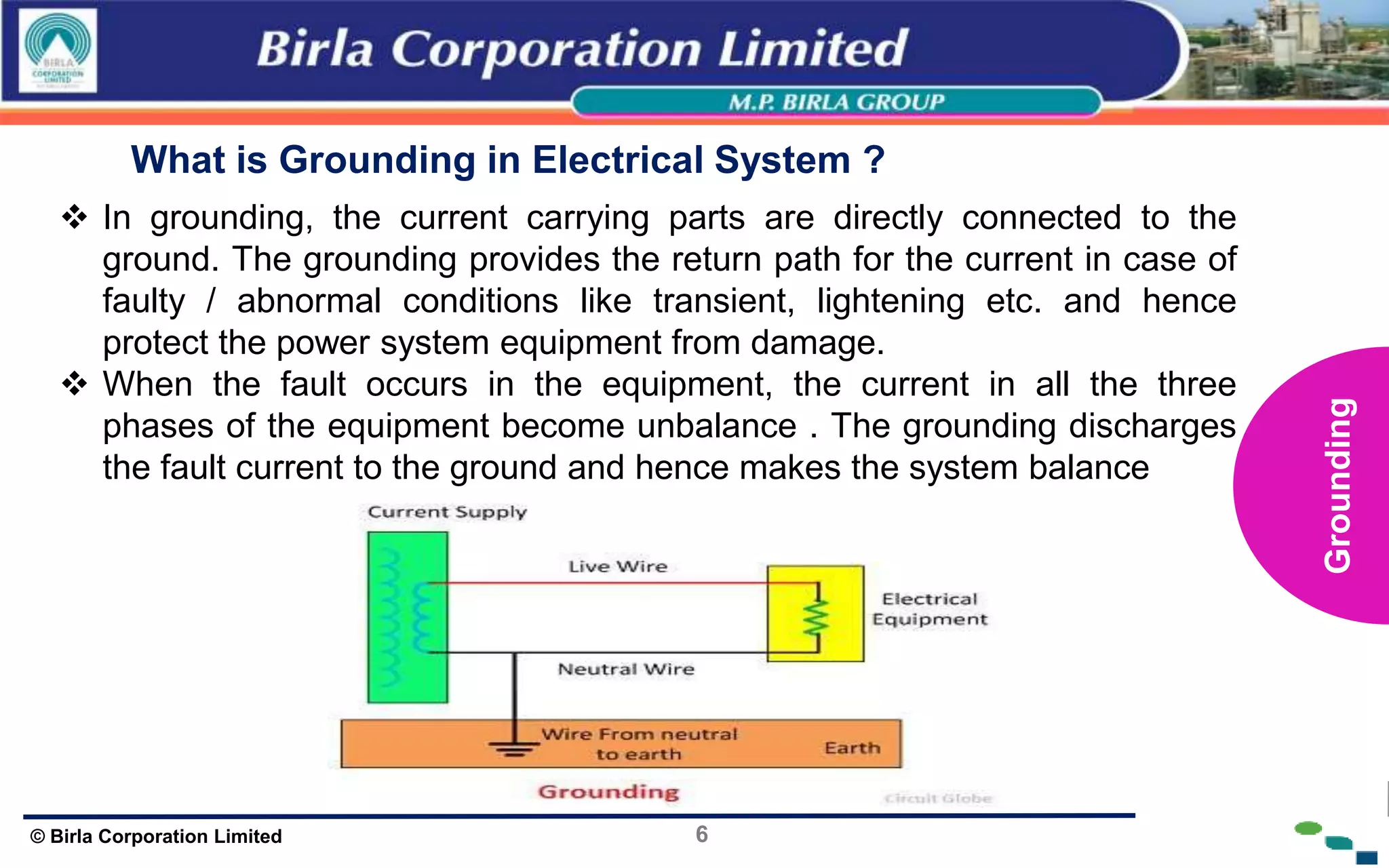
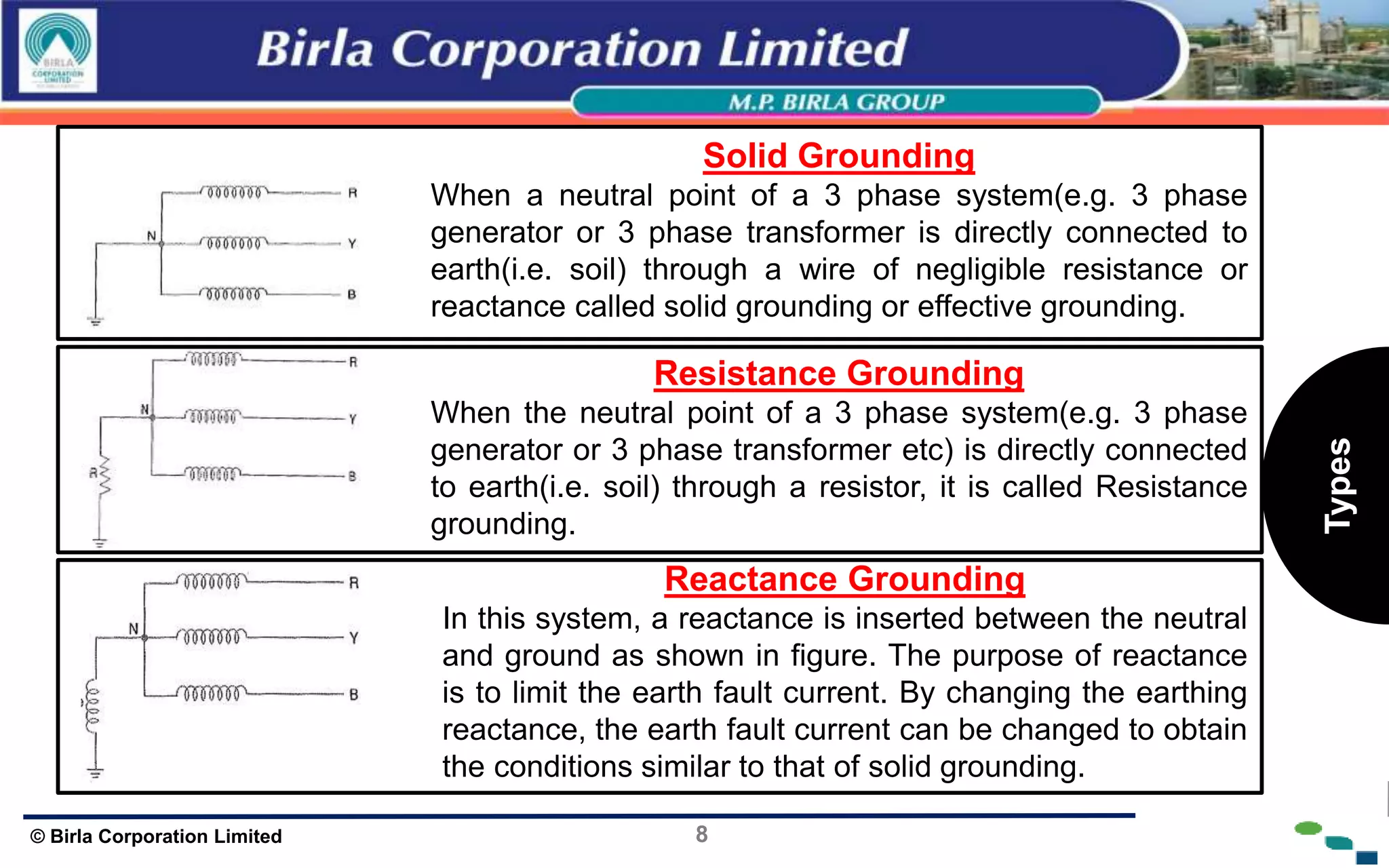
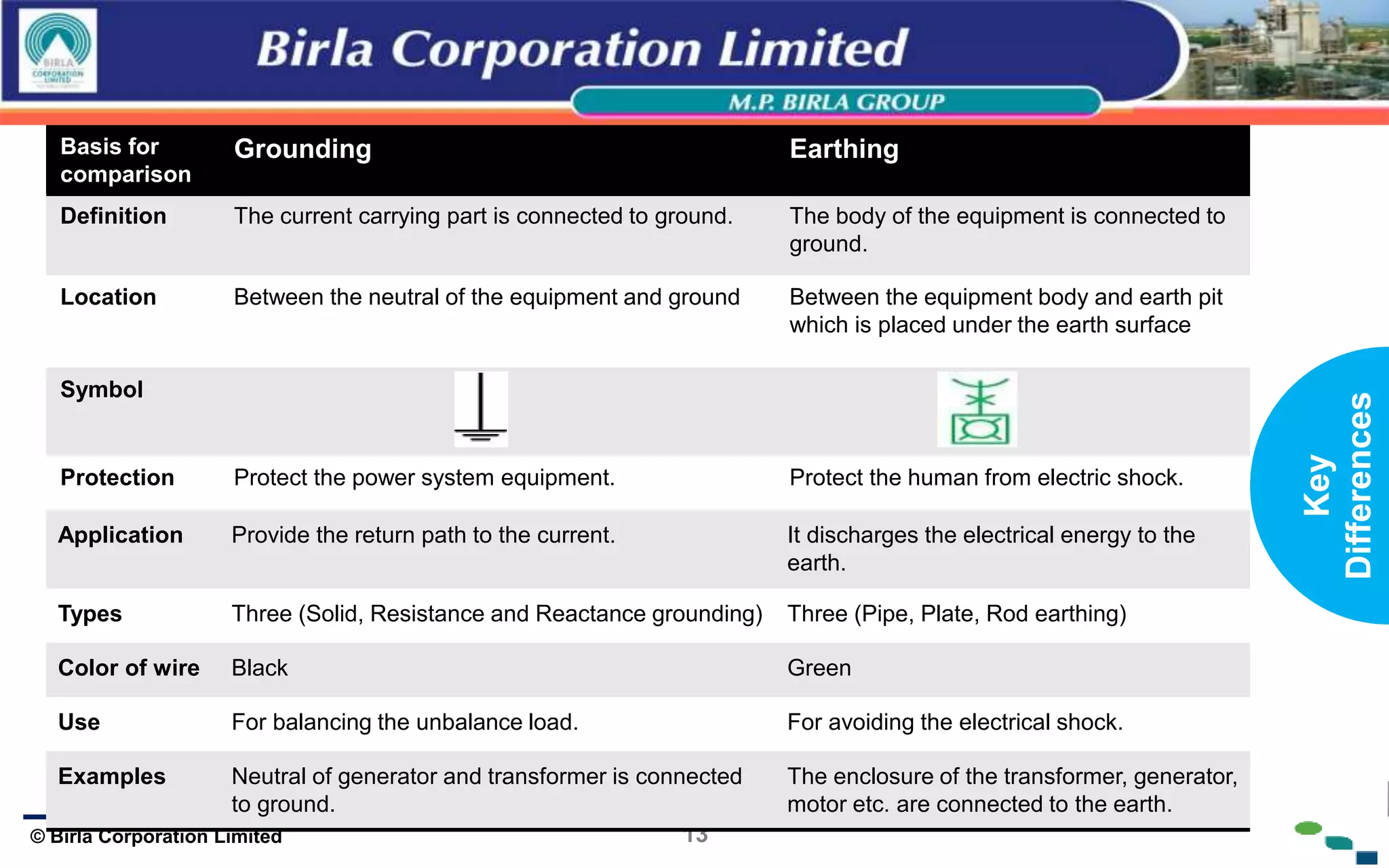
The document presents an overview of earthing and grounding in electrical systems, explaining their definitions, types, and importance for safety and equipment protection. Earthing minimizes electric shock risks and stabilizes voltage during surges, whereas grounding provides return paths for fault currents, ensuring equipment safety. Key differences between earthing and grounding are also highlighted, including their applications and symbols.