Solar energy comes from nuclear fusion reactions in the sun. About 30% of the solar radiation that reaches Earth is absorbed by the Earth's surface, with the rest reflected or absorbed by the atmosphere. All life on Earth depends on solar energy through photosynthesis.
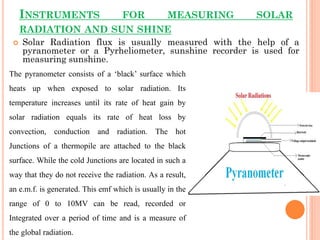
The rate at which solar energy reaches the top of the atmosphere is known as the solar constant, which NASA estimates to be about 1.353 kilowatts per square meter. Instruments like pyranometers and pyrheliometers are used to measure incoming solar radiation, while sunshine recorders measure the duration of bright sunshine.
Solar collectors, such as flat plate collectors and evacuated tube collectors, are devices that collect and concentrate solar radiation for uses like heating water