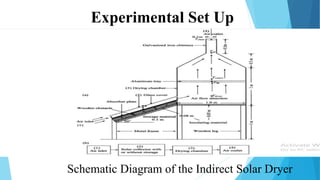
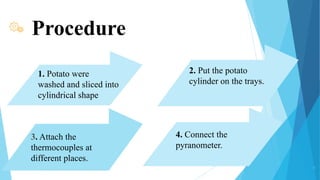
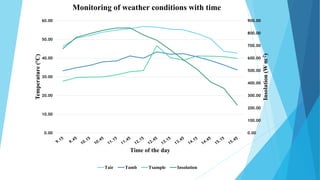
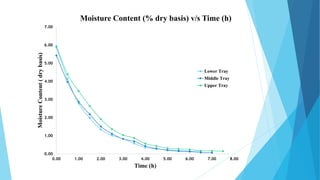
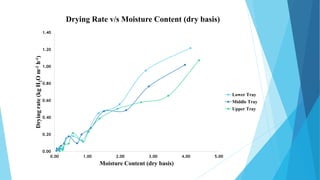
This document describes a solar dryer project to dry potato cylinders. It includes an introduction to drying and solar drying, descriptions of the experimental setup and procedures used, results of drying potato cylinders in an indirect solar dryer over 7 hours, and advantages and disadvantages of solar drying. Monitoring showed temperature increased with solar insolation and moisture content of potato cylinders decreased over time from 7% to 1% dry basis. Drying rates were highest for cylinders in the lower tray.