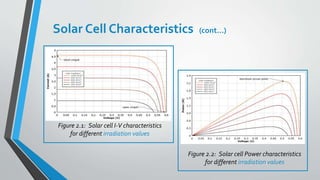
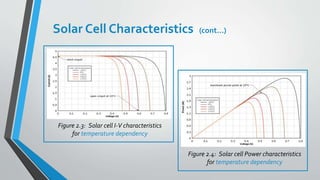
Solar cells convert sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. They are made from semiconducting materials like crystalline silicon that produce electricity when exposed to light. Maximum power point tracking (MPPT) is a technique used to extract the maximum possible power from solar panels by matching the panel voltage to the battery or load voltage. MPPT controllers sample the power output from solar panels and apply the proper resistance to obtain the maximum power point. Solar cell performance is affected by factors like irradiation levels and temperature, with characteristics like current, voltage, and power output varying under different conditions.