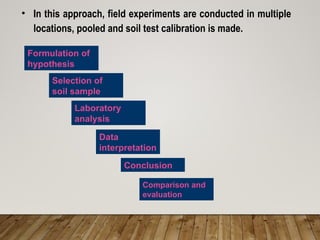
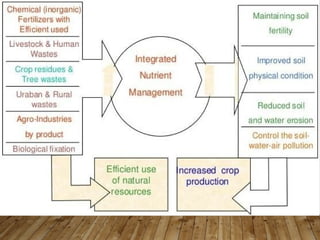
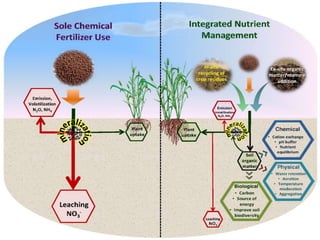
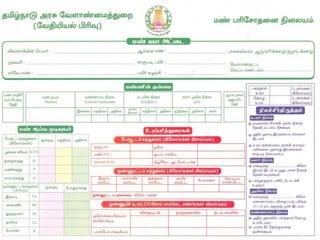
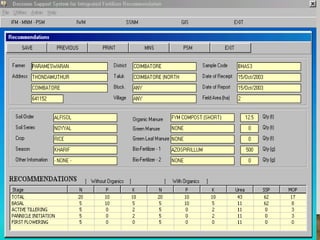
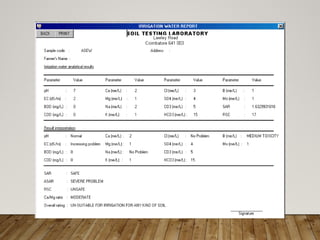
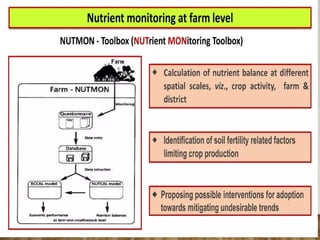
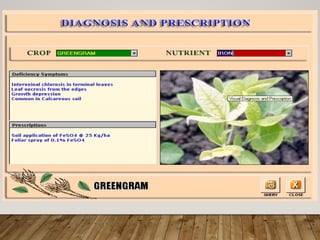
The document discusses integrated nutrient management (INM) and integrated plant nutrient system (IPNS) concepts, focusing on sustainable agriculture by combining organic, inorganic, and biological resources to enhance soil fertility and crop productivity. It outlines the principles of INM, which aims to optimize crop nutrition while considering ecological health, and explains decision support systems like DSSIFER and visual diagnostic kits for tailored fertilizer recommendations. The importance of calibration models for soil testing and the integration of various sources of nutrients are emphasized as key to maintaining long-term soil fertility and avoiding environmental degradation.