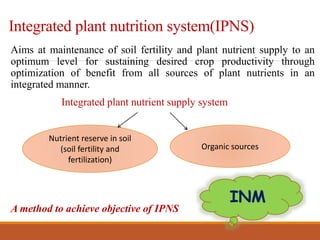
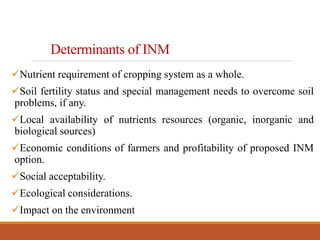
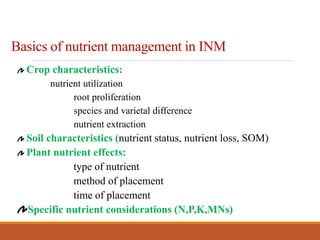
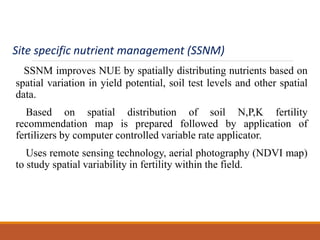
Integrated nutrient management (INM) aims to maintain soil fertility and provide optimal nutrient levels for crop productivity through an integrated approach using all sources of plant nutrients. The goals of INM include maintaining soil productivity, ensuring sustainable agriculture, and reducing input costs by using organic sources like farm manure, compost, and green manures. INM follows principles like being technically sound, economically viable, environmentally safe, and sustainable. Determinants of an INM plan include the nutrient needs of crops, soil fertility status, availability of nutrient sources, economic factors, and environmental impacts.