Embed presentation
Download to read offline






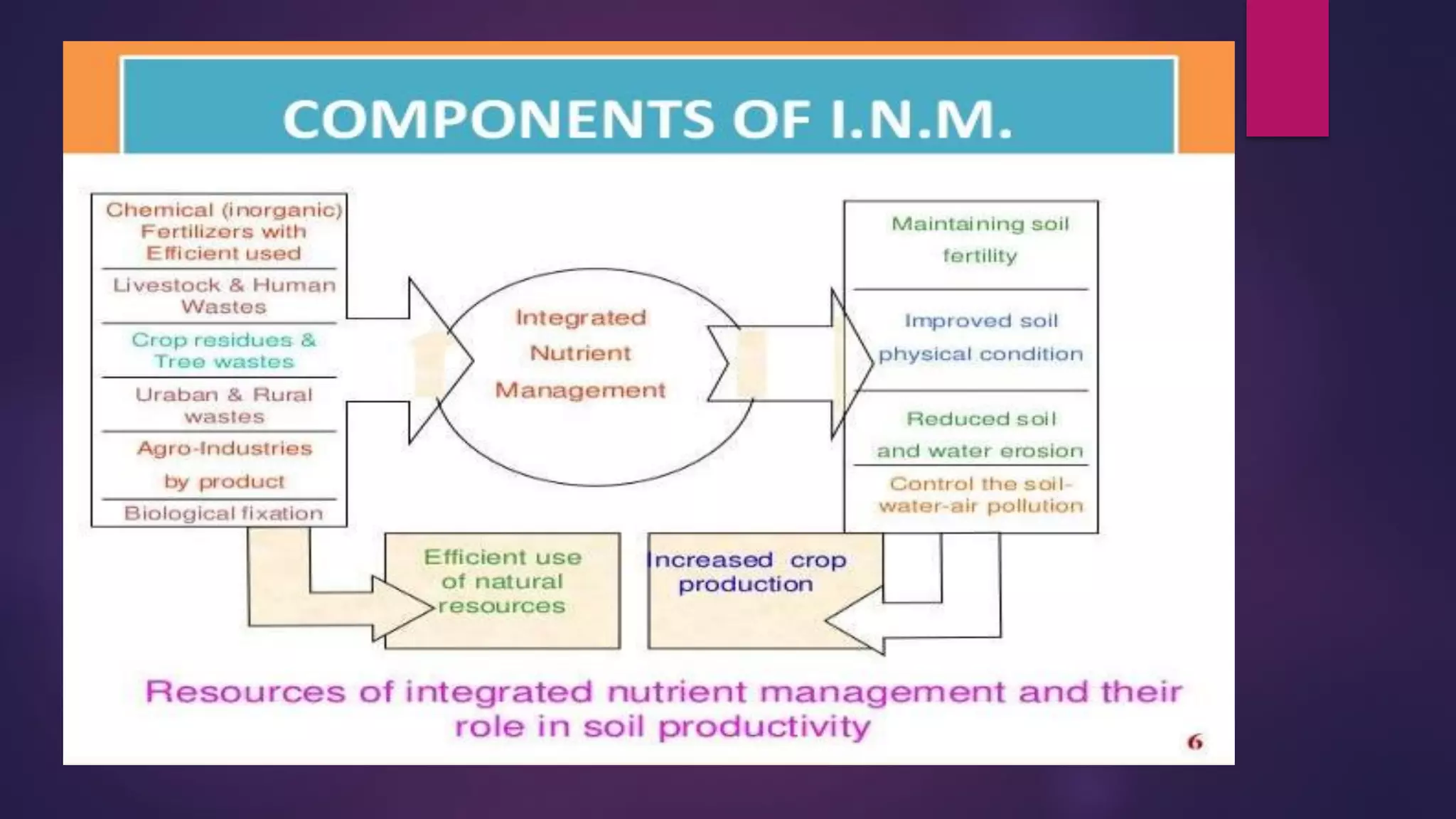







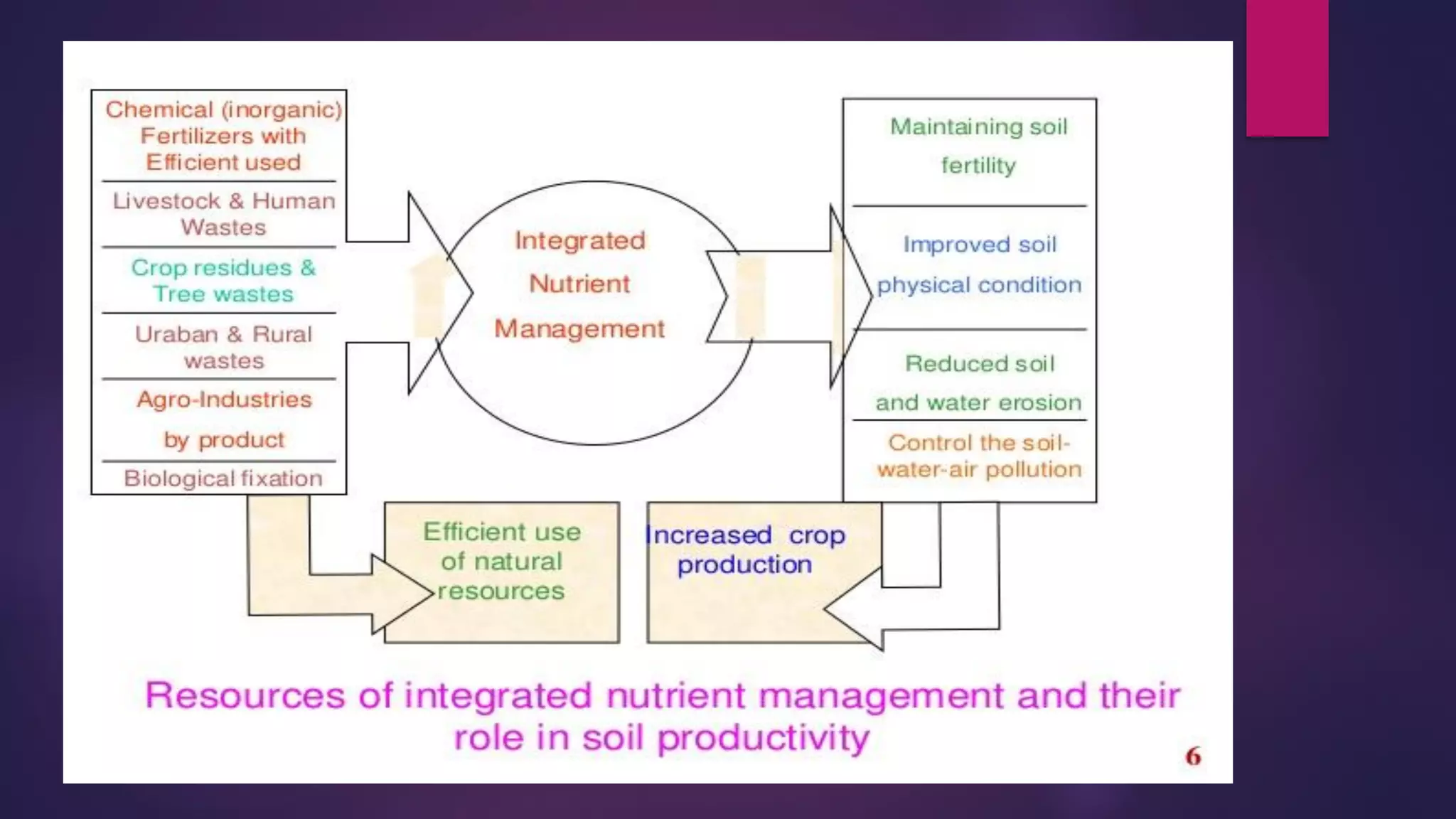
Integrated nutrient management is the balanced use of mineral fertilizers, organic sources, and biological sources to maintain soil productivity and improve nutrient levels. It aims to improve nutrient efficiency while limiting losses to the environment. The four components of integrated nutrient management are soil sources, organic sources like manure, biological sources like inoculants, and mineral fertilizers. An important part of integrated nutrient management is a nutrient management plan that analyzes each field to improve nutrient efficiency for crops.
Integrated Nutrient Management (INM) aims to optimize soil fertility using diverse nutrient sources.
INM objectives include enhancing soil productivity, improving nutrient efficiency, and soil physical conditions.
INM components focus on soil sources, organic and biological inputs, and mineral fertilizers.
Balanced fertilizer application is essential; it identifies sources like inorganic, organic, and biofertilizers.
A Crop Nutrient Management Plan enhances nutrient efficiency and includes field maps, soil tests, and reviews.
INM benefits include enhanced nutrient availability, synchronizing crop demands, and minimizing soil degradation.














