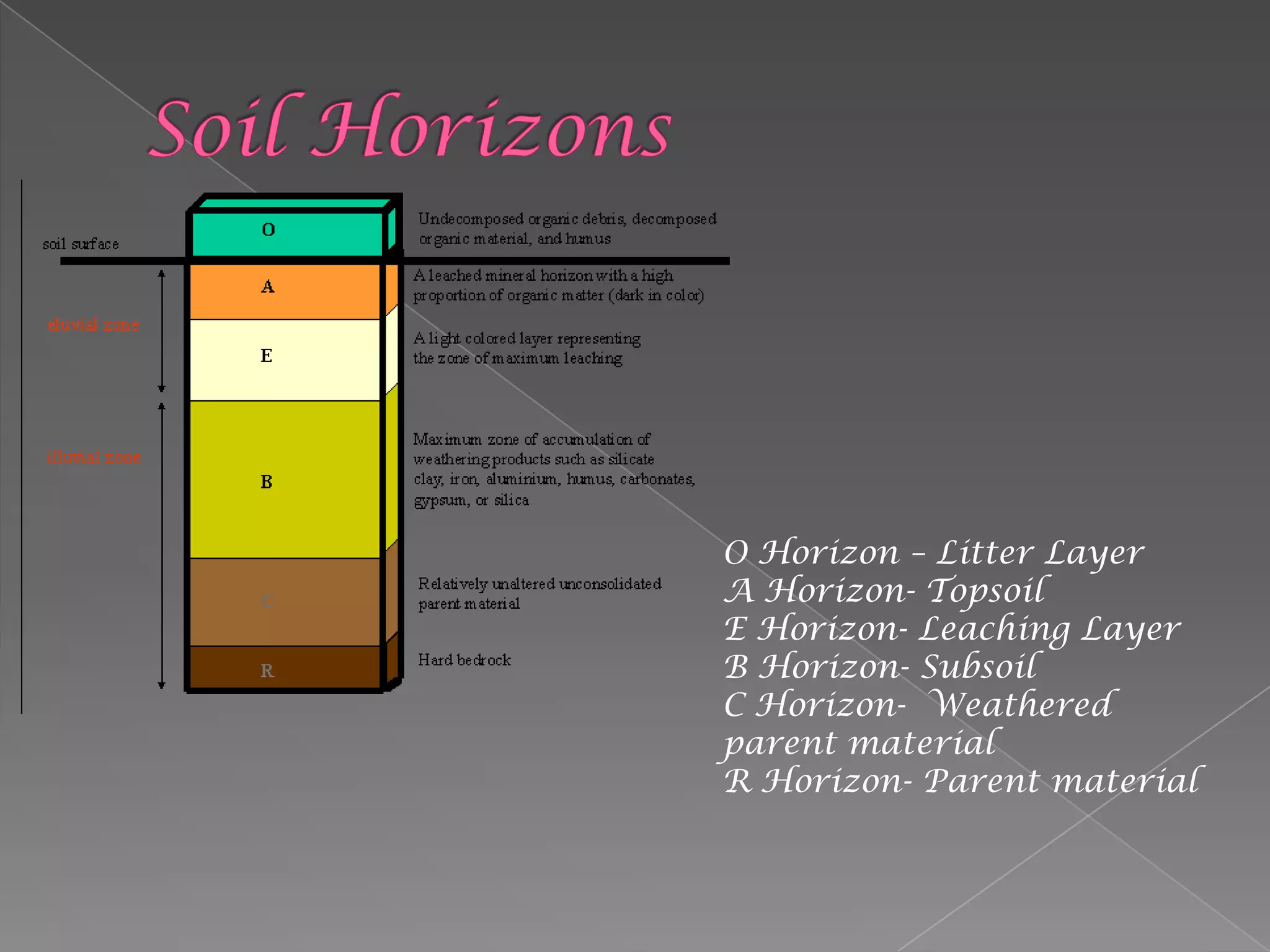
The document discusses soil horizons and properties including color, texture, structure, and pH. It notes that soil degradation in drylands is primarily caused by wind and water erosion. Desertification is defined as a loss of over 10% productivity due to various factors like erosion, overgrazing, drought, and climate change. The document also discusses irrigation, salinization, and pesticides and recommends soil conservation practices for farmers like crop rotation and reduced tillage to prevent degradation and build organic matter.