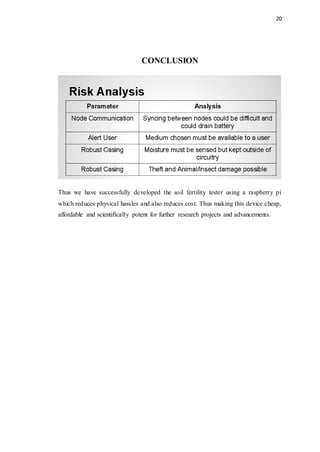
The document discusses the essential nutrient requirements for plant growth, highlighting the roles of primary, secondary, and micronutrients, as well as soil fertility and the impact of fertilizers. It elaborates on various types of fertilizers, their effects on soil life, and the importance of organic versus synthetic options. Additionally, the document introduces a soil fertility testing device utilizing a Raspberry Pi to measure soil temperature and nitrogen content, enhancing agricultural practices.
















![21
REFERENCES
[1].National Bureau of Statistics of China, China Statistical Yearbook 2006, Beijing
China, 2006.
[2]. Minzan Li. "Soil Parameters Sensing for Precision Farming": [Ph.D.
Dissertation].Tokyo: Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology, 2000.
[3]. Missouri Agricultural Experimental Station, Recommended chemical soil test
procedures, Columbia, US: North Central Regional Research Publication, University
of Missouri, 1998.
[4]. J. Ruzicka, E.H Hansen. and E.A. Zagatto, "Flow injection analysis. Part II: use
of ion-selective electrodes for rapid analysis of soil extracts and blood serum.
Determination of potassium sodium and nitrate", Analytica Chimica Acta, Vol. 88,
no. 1, pp. 1-16, 1977.
[CrossRef]
[5] C. Hongbo, E.H. Hansen and J. Ruzicka, "Evaluation of critical parameters for
measurement of pH by flow injection analysis", Analytica Chimica Acta, Vol. 169,
pp. 209-220, 1985.
[CrossRef]
[6]. F. AMR, L. JLC, and R. AOSS, "Potentiometric determination of total nitrogen in
soils by flow injection analysis with a gas-diffusion unit", Australian Journal of Soil
Research, Vol. 34, pp. 503, 1996.
[CrossRef]
[7].H.J. Kim, J.W. Hummel, and S.J. Birrell, "Evaluation of ion-selective membranes
for realtime soil nutrient sensing", Transactions of the ASAE, Vol. 46, no. 3, pp.
1075-1086, 2003.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/minorproject-160829133640/85/Soil-Fertility-Tester-Using-raspberry-Pi-Minor-project-21-320.jpg)

