This document provides an overview of the first unit of a sociology course. It includes:
- An introduction to examining social life, including defining sociology and differentiating it from other social sciences.
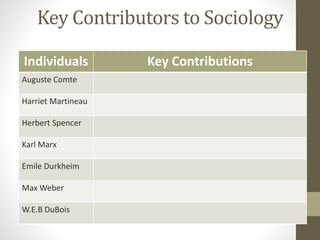
- An outline of the development of sociology from the 17th-19th centuries in Europe in response to industrialization and other social changes. Key early theorists who contributed to the field are identified.
- An introduction to the three major theoretical perspectives in sociology - functionalism, conflict theory, and symbolic interactionism - and how they differ in their levels of analysis.
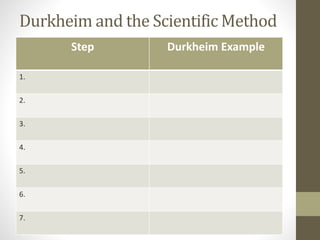
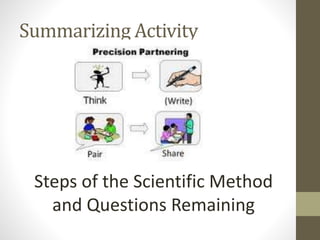
- An overview of how sociological research is conducted scientifically, using methods like surveys, observation, and experiments while following ethical standards













![Sociological Imagination
C. Wright Mills described the sociological
imagination as…
“the capacity to range from the most impersonal
and remote [topics] to the most intimate features
of the human self—and to see the relations
between the two.”
1) What does this mean?
2) Why would Mills think that all good sociologists
need to possess this?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sociologyunit1powerpoint-140222062627-phpapp01/85/Sociology-unit-1-power-point-15-320.jpg)