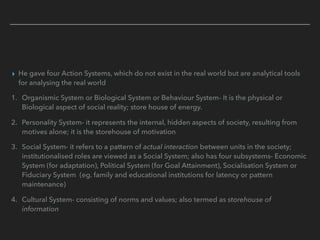
Parsons was a pioneer of functionalism in sociology. He introduced a grand theory of social action and social systems that aimed to provide a universal framework for understanding all human behavior. His theory of social action defined it as any consciously performed act. He also developed a systems approach, analyzing society as a system with four subsystems that perform the functions of adaptation, goal attainment, integration, and pattern maintenance. Parsons' theories were highly abstract and criticized for being difficult to empirically test.