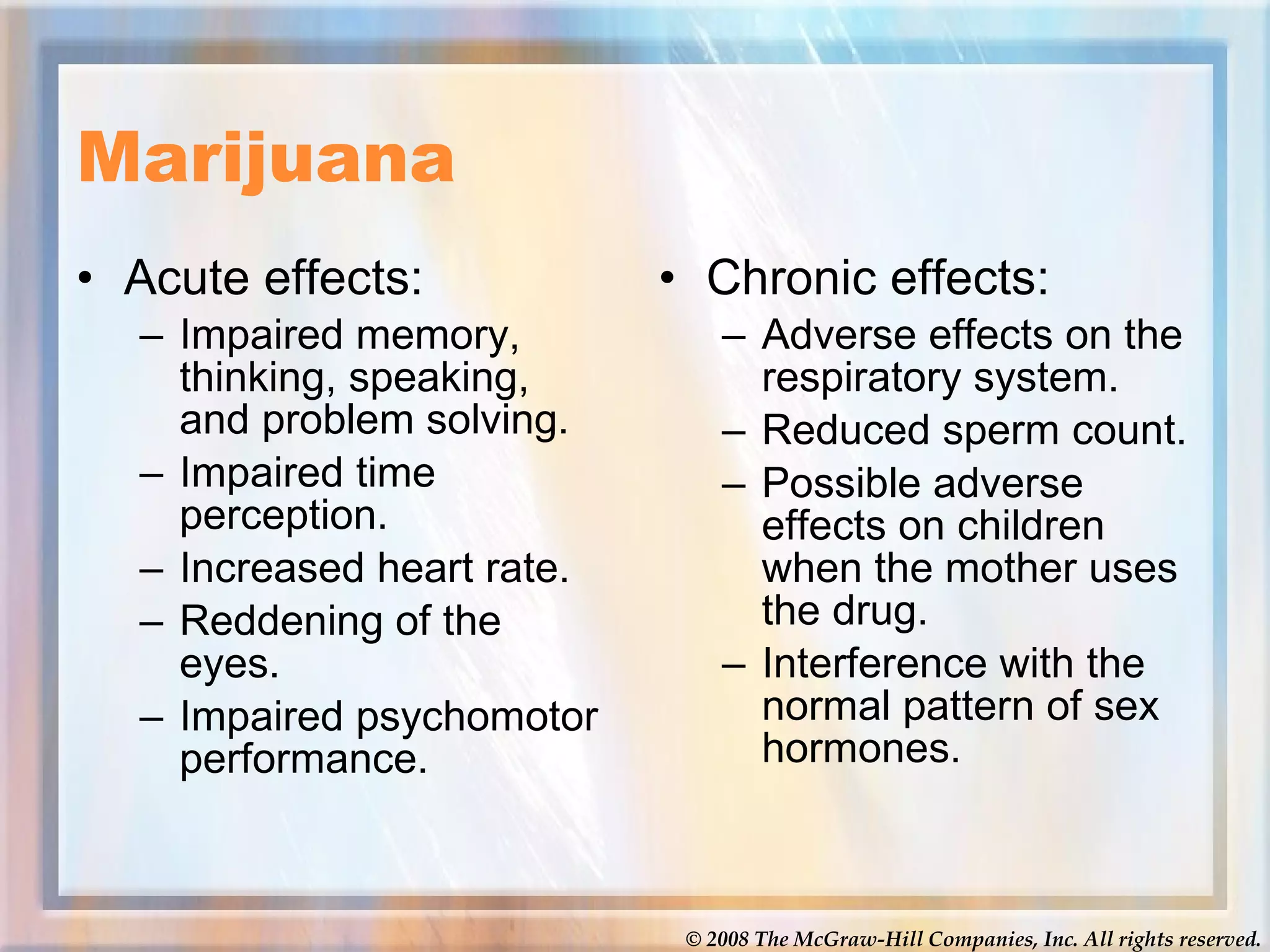
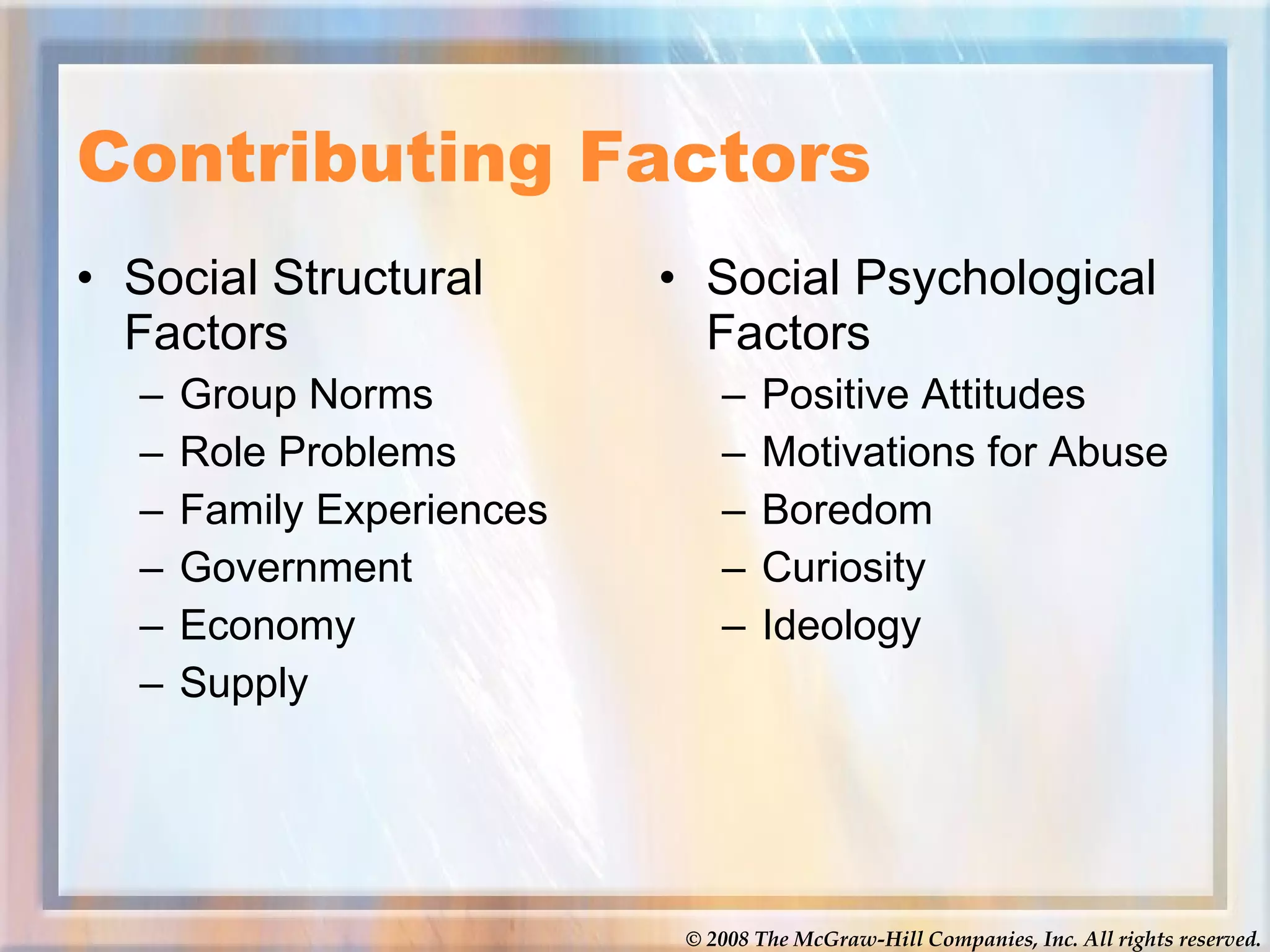
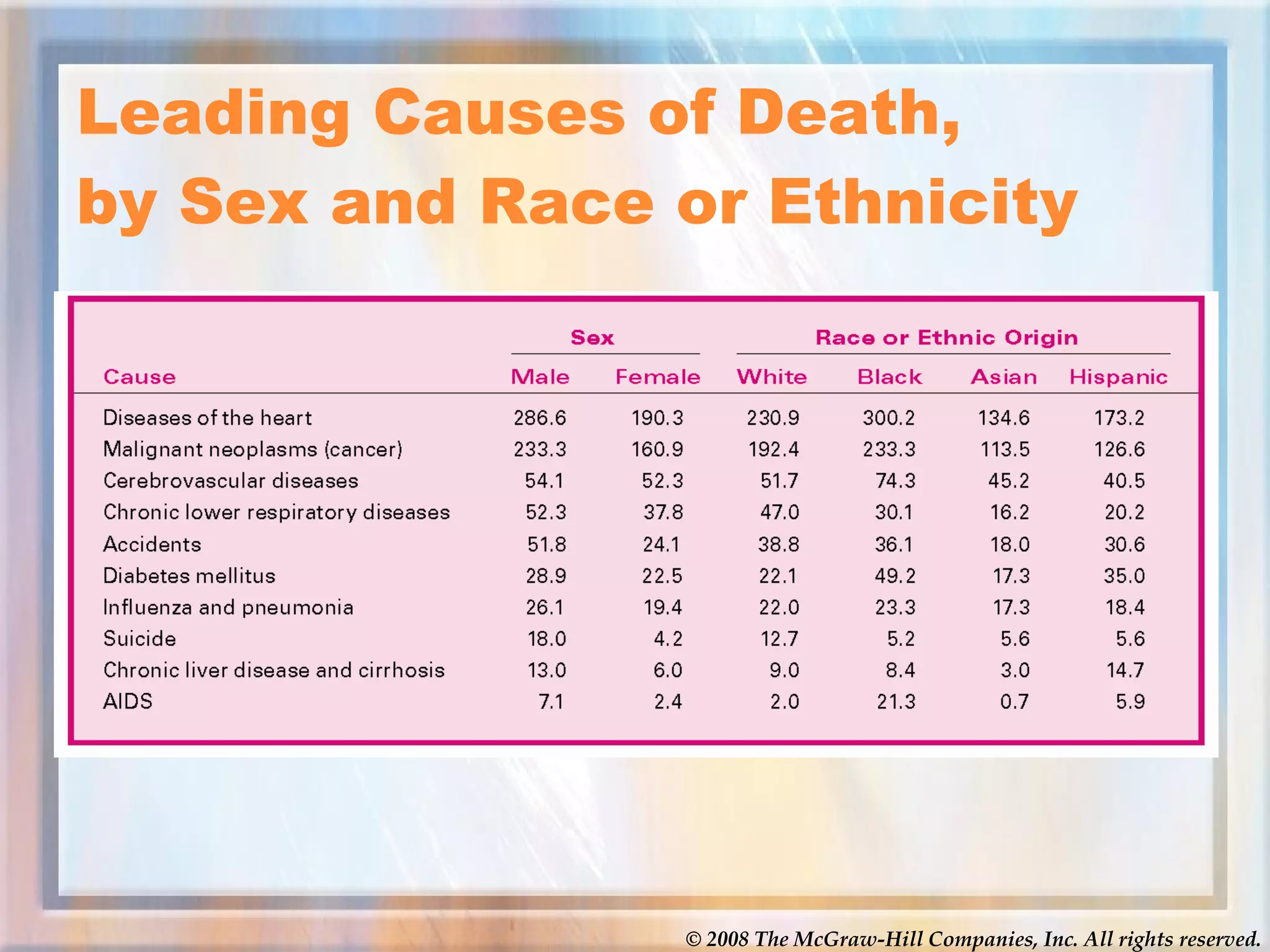
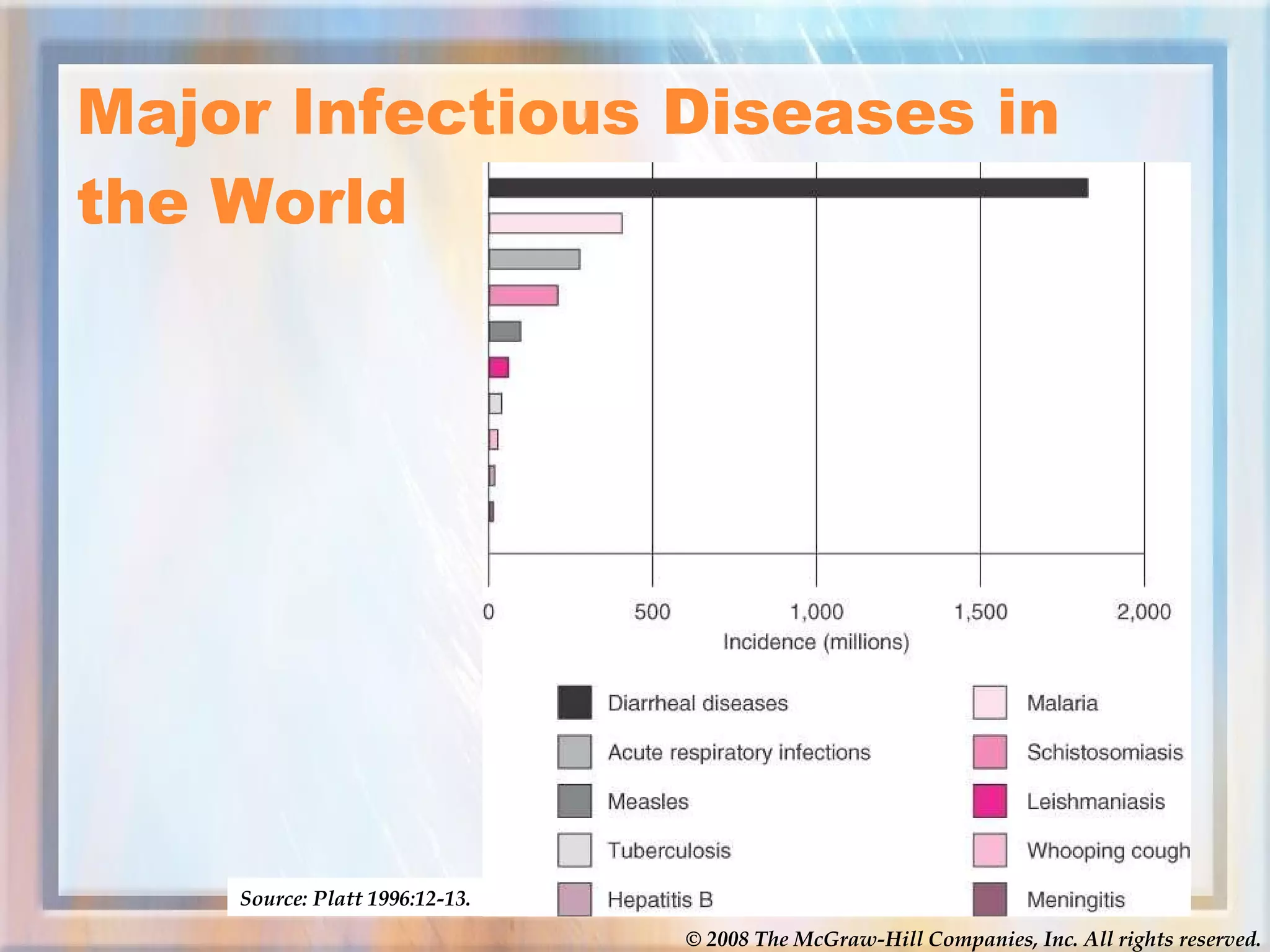
The document discusses various topics related to social problems involving alcohol, drugs, physical health, and mental health. It provides definitions and statistics on substance abuse and addiction, discusses the health effects of alcohol, tobacco, and various illegal drugs. It also covers leading causes of death in the US and worldwide, statistics on AIDS, and types of mental illness and factors influencing physical and mental health. Videos are linked on the meth epidemic and AIDS epidemic for students to watch.