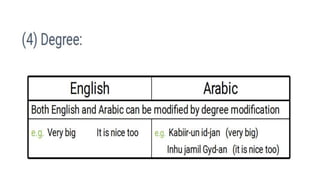
This document compares adjectives in English and Arabic. It outlines several key differences:
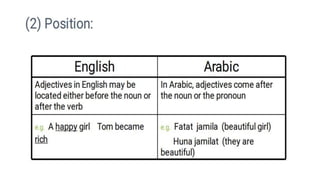
- In English, adjectives typically precede nouns, while in Arabic they follow nouns.
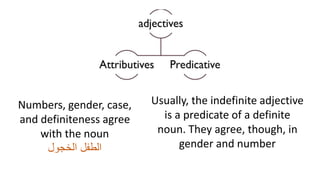
- English adjectives stay the same form regardless of the noun's properties, but in Arabic the adjective and noun must agree in gender, plurality, definiteness, and case.
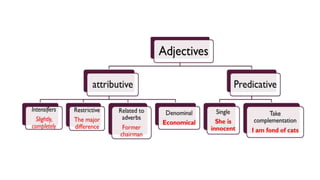
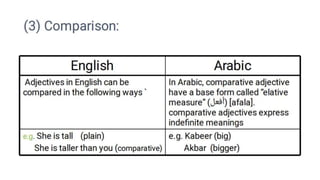
- English adjectives are distinguished from nouns by lacking number/case inflection and occurring attributively or predicatively. They have comparative/superlative forms.
The document then provides more details on the features and types of adjectives in each language.