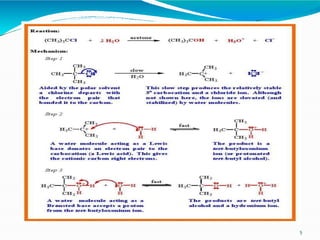
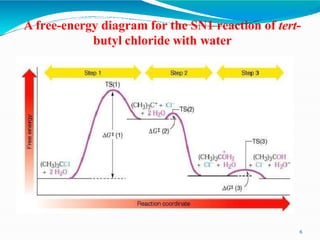
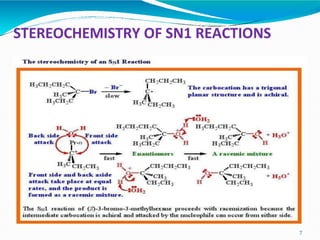
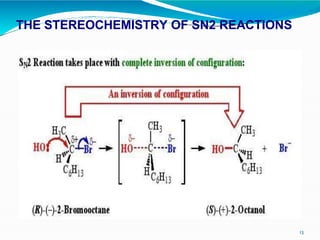
1. The document summarizes nucleophilic substitution reactions (SN1 and SN2). It defines nucleophiles as negatively charged or neutral species with a lone pair of electrons.
2. It describes the mechanism of the SN1 reaction, which is unimolecular and involves the rate being dependent only on the concentration of the substrate. It forms a carbocation intermediate.
3. It also describes the concerted bimolecular SN2 reaction mechanism where the nucleophile attacks the substrate from the backside in a single transition state, causing inversion of configuration. Factors favoring each reaction type are also discussed.