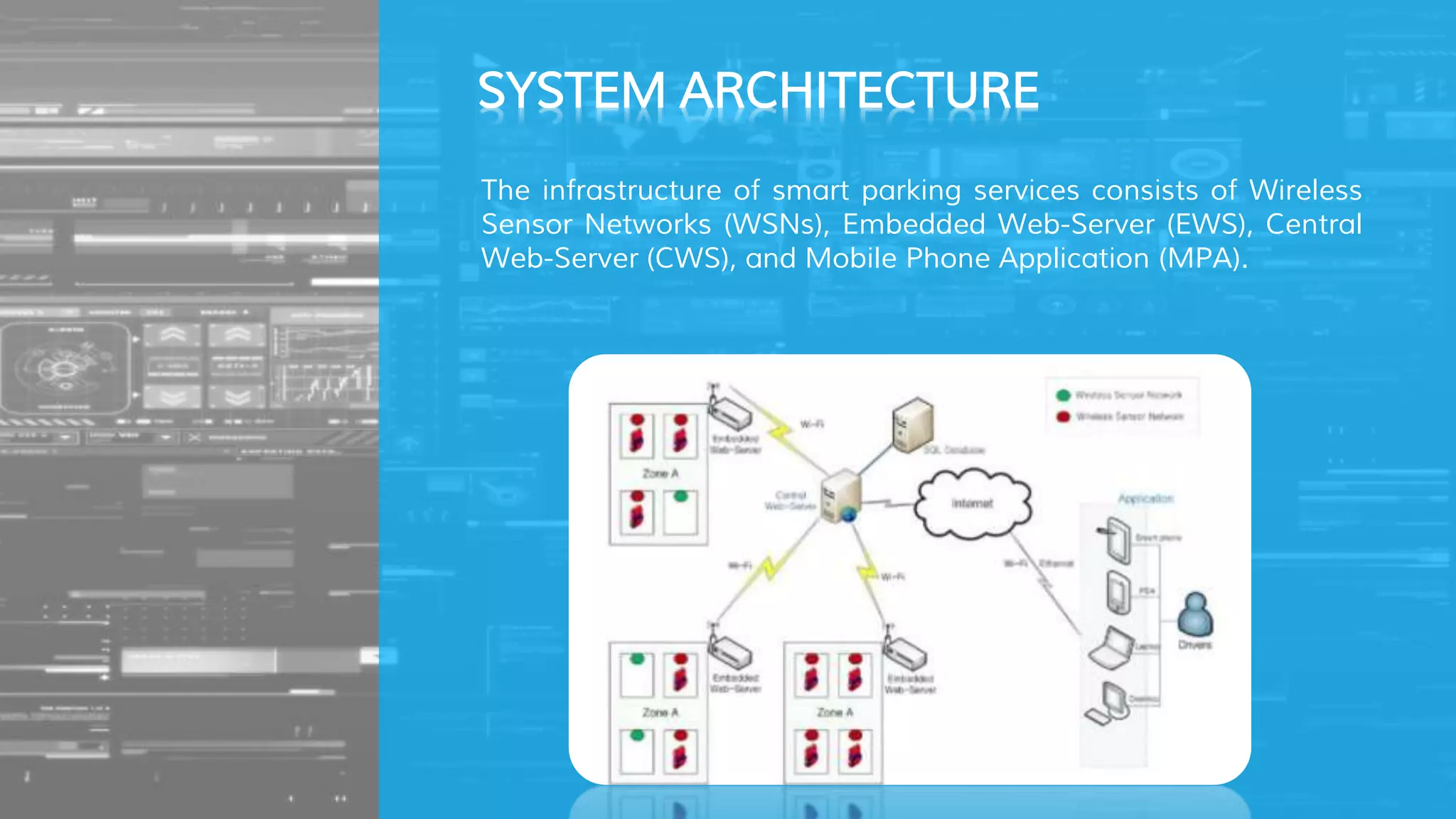
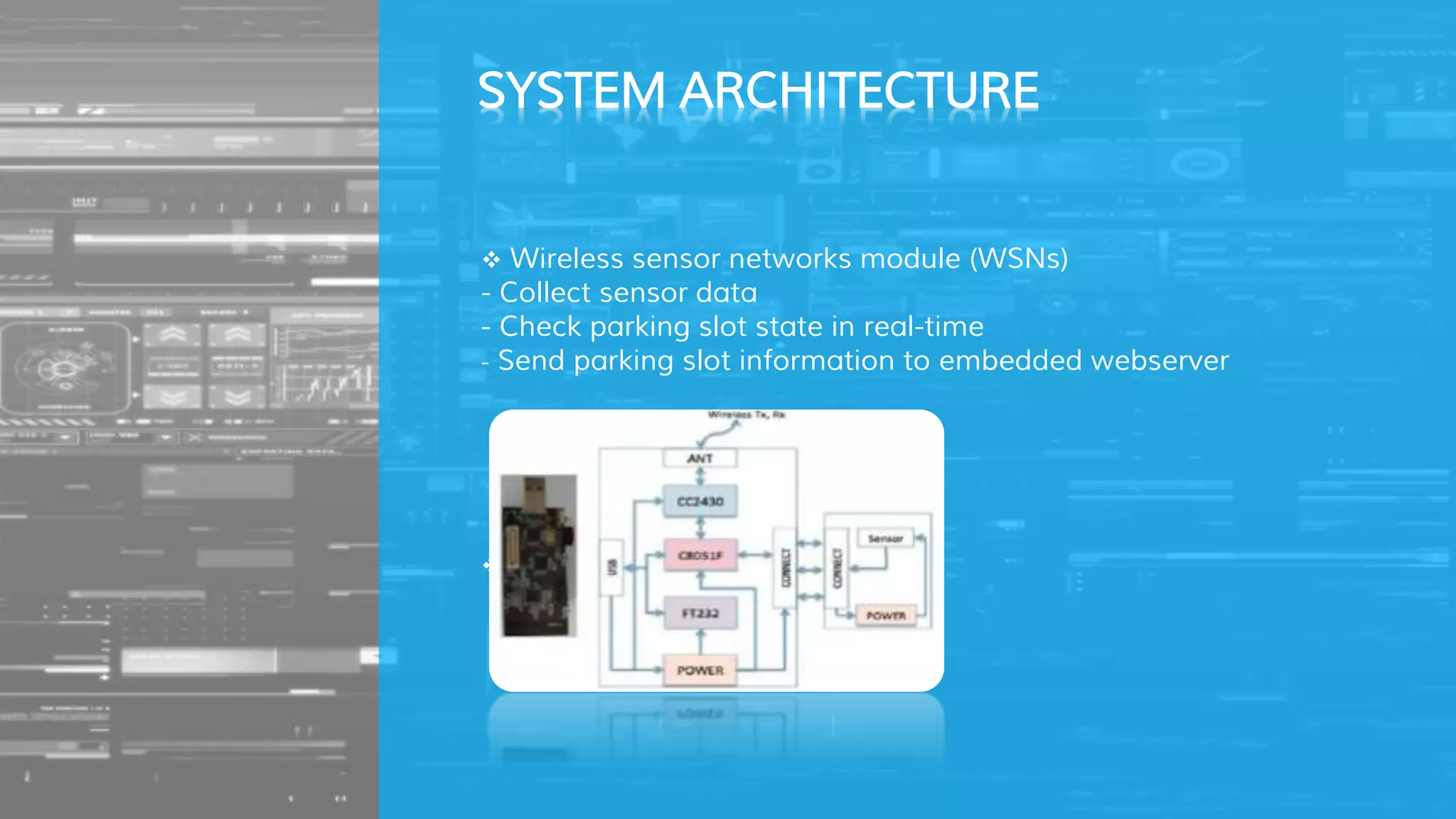
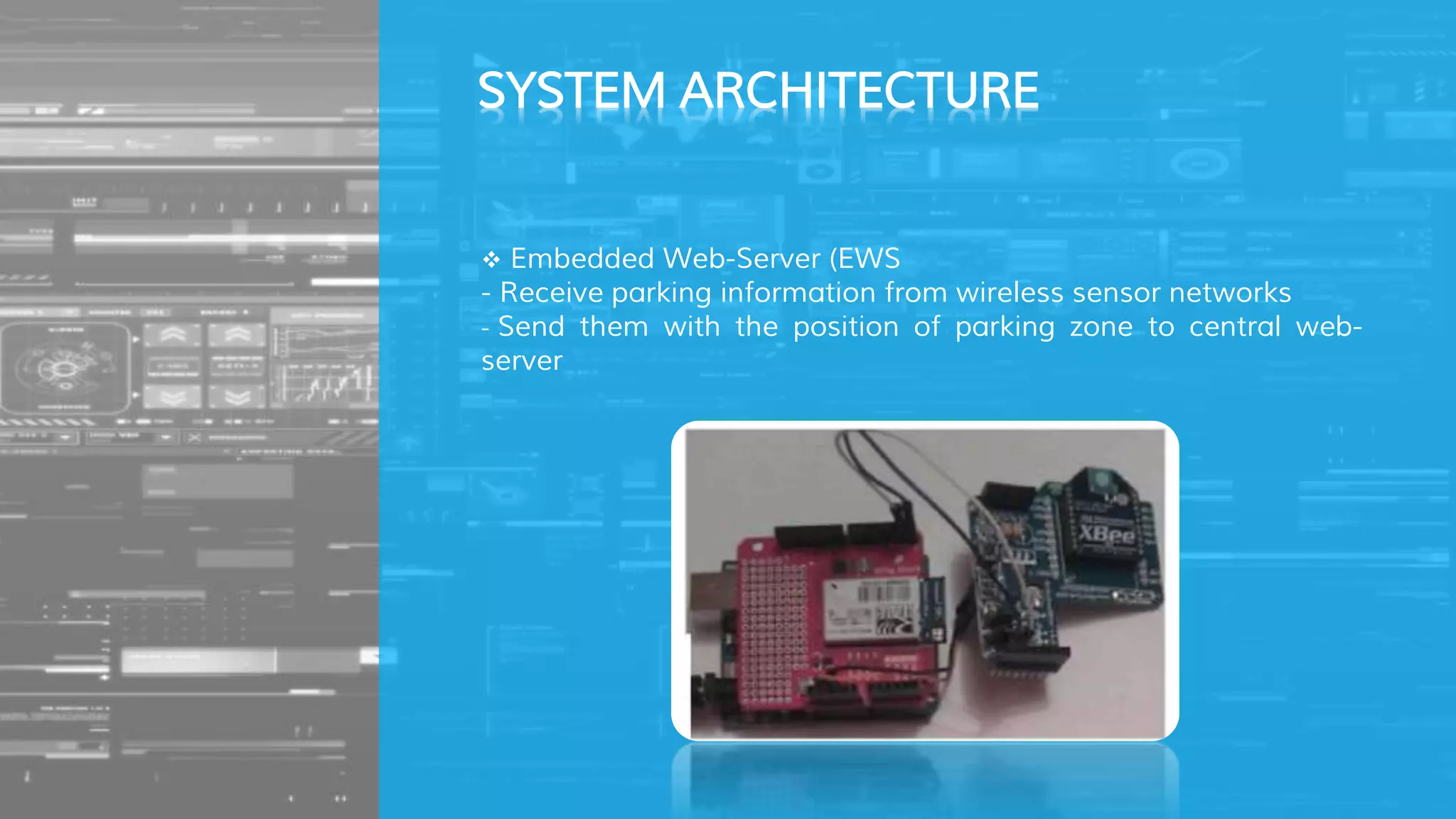
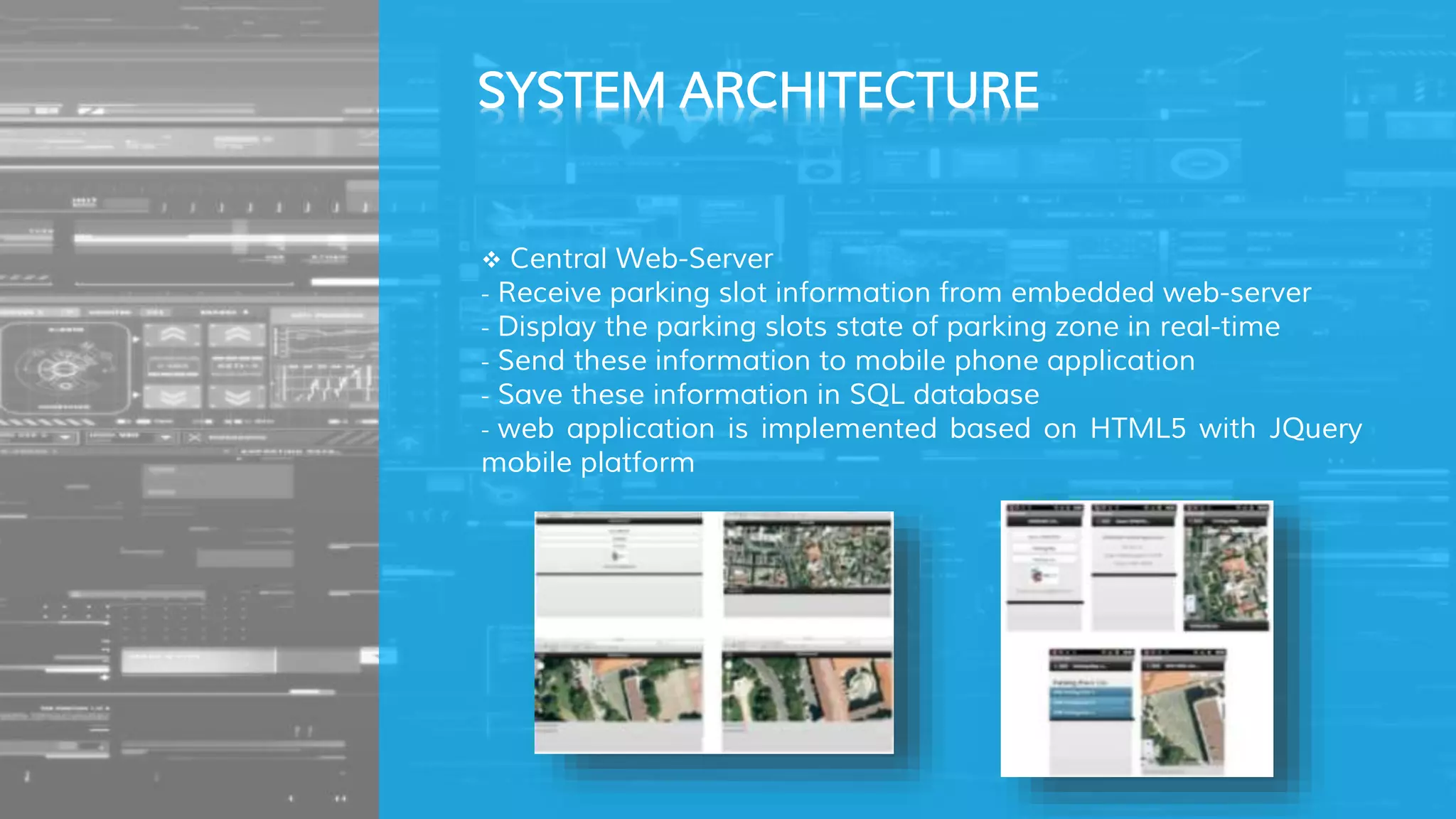
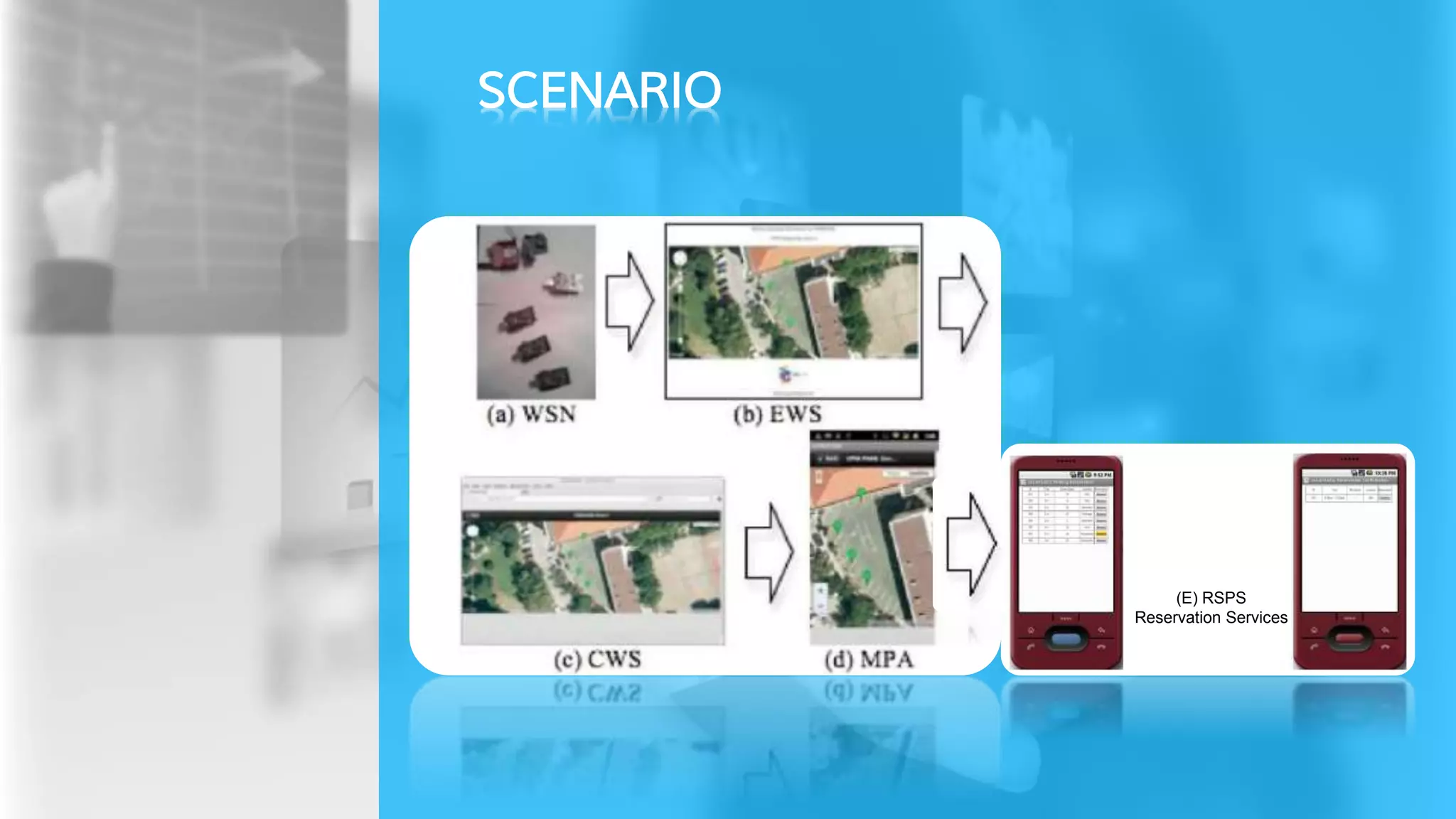
The document describes a proposed smart parking system that uses wireless sensor networks, embedded web servers, a central web server, and a mobile phone application to help drivers find available parking spaces. Wireless sensor nodes deployed in each parking spot detect occupancy and report it in real-time to embedded web servers. This data is then sent to a central web server which displays current availability and allows reservations via mobile apps. The system aims to more efficiently guide drivers to vacant spots and reduce traffic from drivers searching for parking.






![“Smart Parking Services based on Wireless Sensor Networks
(WSNs)”
Wireless sensor network mote [1] is a tiny device which
usually consists of a low cost-sensor module, a microprocessor
module and a communication module, and provides a powerful
consortium of distributed sensing, computing and
communication. These modules can rapidly and easily be
deployed to collect, process, and transmit information.
“Reservation-based Smart Parking System (RSPS)”
not only to broadcast real-time parking information to the drivers
as part of a communal application, but also to provide
reservation service as part of user-targeted service.
INTRODUCTION](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/smartparking-161007112007/75/Smart-Parking-7-2048.jpg)