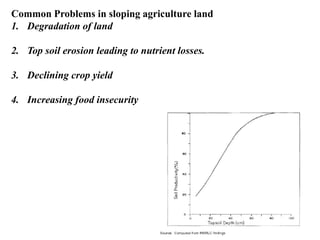
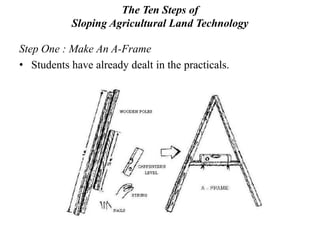
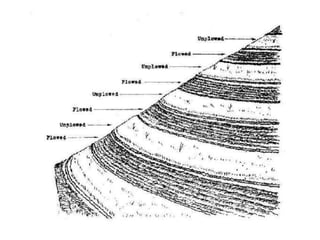
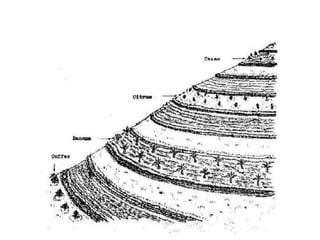
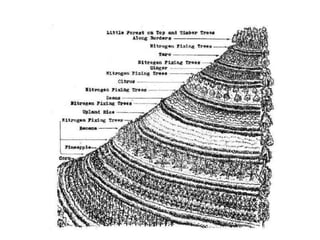
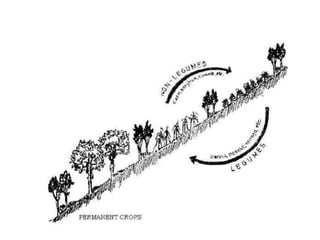
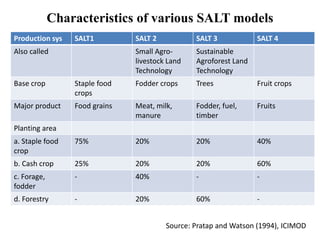
The document discusses Sloping Agriculture Land Technology (Salt), which addresses common issues in sloping agricultural land such as erosion and declining crop yields by integrating various soil conservation measures. It details the methods for implementing Salt, highlighting its benefits for small family farms, including increased productivity and low-cost implementation. Additionally, it provides a ten-step guide for farmers to establish and manage this farming system effectively.