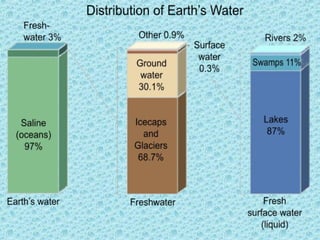
Water resources include sources of water that are useful for human purposes like agriculture, industry, households, recreation and the environment. Nearly all human uses require fresh water, but only 3% of the Earth's water is fresh, and over two-thirds of that is frozen in glaciers and polar ice caps. The remaining fresh water is found as groundwater or above ground. Increasing water scarcity is caused by overuse, population growth, industrialization, deforestation, and mismanagement of water resources. Multi-purpose river projects provide irrigation water while also generating hydropower, enabling navigation, and supporting fisheries to help address increasing scarcity. Rainwater harvesting and water conservation methods like reducing waste are important for preserving