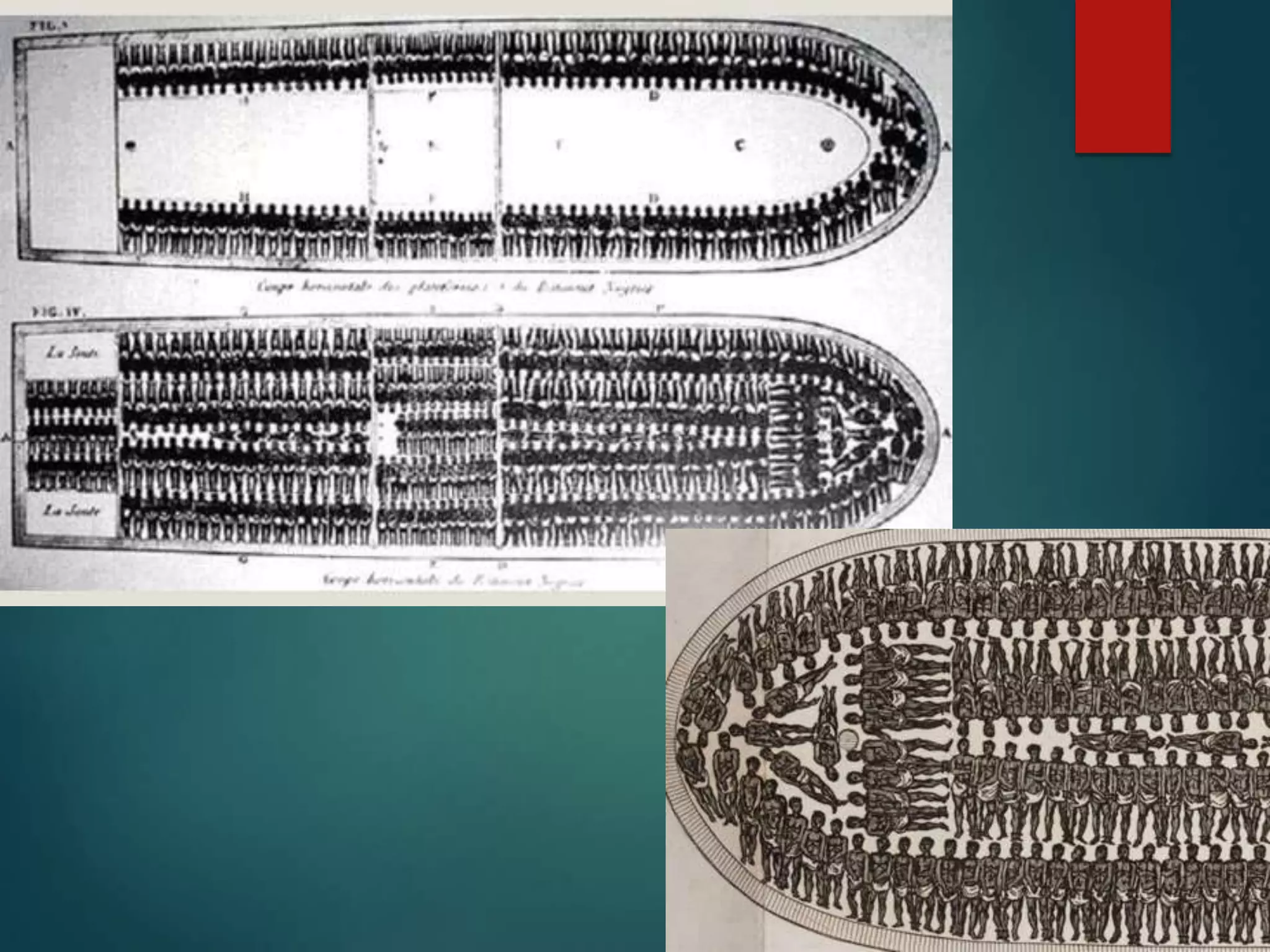
The document summarizes the triangular trade network that was central to the Atlantic slave trade between Africa, Europe, and the Americas. It describes the three legs of the triangular route: 1) Ships left Europe for Africa with goods and weapons to obtain slaves through attacks, debts or wars. 2) The middle passage involved transporting enslaved Africans in horrific conditions across the Atlantic to the Americas. 3) Ships then returned to Europe from the Americas loaded with raw goods to manufacture and sell. This network systematically exploited humans for profit through the dehumanizing capture and transport of millions of Africans.