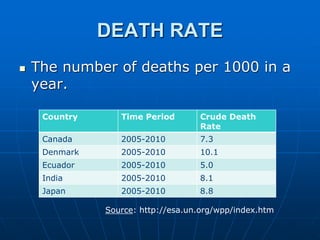
There are four main factors that affect population change: birth rate, death rate, immigration, and emigration. Birth rates are influenced by the number of women in the population, education levels, economic status, medical conditions, and culture/religion. Death rates are impacted by development of medicine, sanitation, education, economic development, and war or disasters. Immigration is influenced by pull factors in destinations while emigration stems from push factors in origins. Population growth depends on the rate of natural increase and total fertility rate.