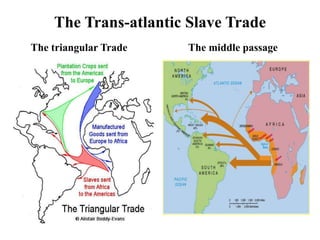
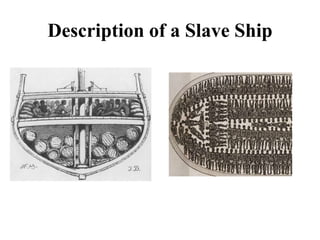
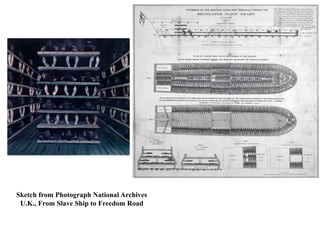
This document provides an outline for a research project on slavery in America. It begins with an introduction that establishes the aims of examining how slavery affected US history and hypotheses about its impact. Chapter 1 discusses the origins and foundations of slavery in America, including how it began in the US, the triangular slave trade, and the horrific conditions slaves faced. It also covers slave codes, resistance methods like revolts and the Underground Railroad. Chapter 2 will examine the Civil War and emancipation, while Chapter 3 focuses on the Civil Rights movement. The conclusion will synthesize the information presented.