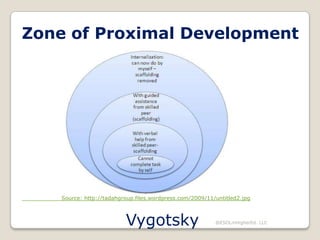
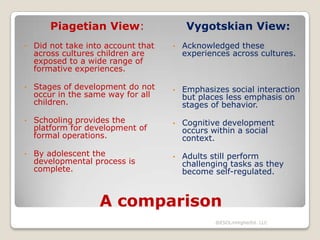
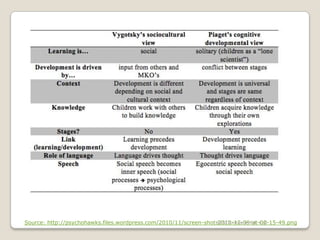
The document discusses several theories of second language acquisition, including Krashen's input hypothesis and the interaction hypothesis. According to Krashen, language acquisition occurs subconsciously when learners are exposed to comprehensible input at a level slightly above their current abilities. The interaction hypothesis posits that acquisition happens through negotiation of meaning between individuals. Piaget's theory of cognitive development includes stages that children progress through, while Vygotsky emphasized that social interaction and cultural experiences shape development within a zone of proximal development.





![
Culture is the primary determinant of
cognitive development.
Source: http://media.photobucket.com/user/startapper04/media/Random%20stuff/vygotsky.jpg.
html?filters[term]=vygotsky&filters[primary]=images&filters[secondary]=videos&sort=1&o=1
Lev S. Vygotsky (1896-1934)
@ESOLinHigherEd. LLC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sla-theorieschapter-6779-140209163437-phpapp02/85/SLA-Theories-Chapter-6-7-320.jpg)