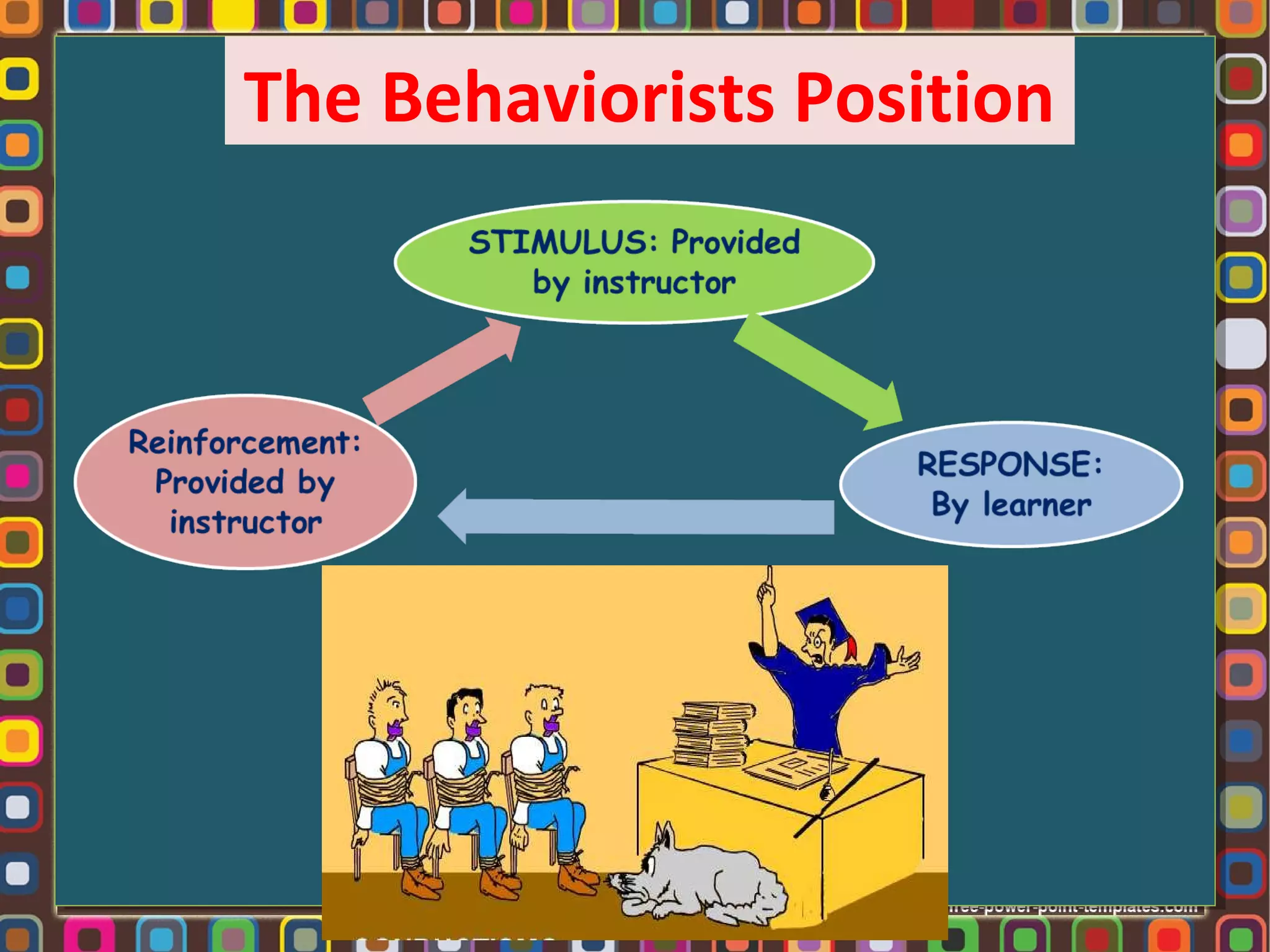
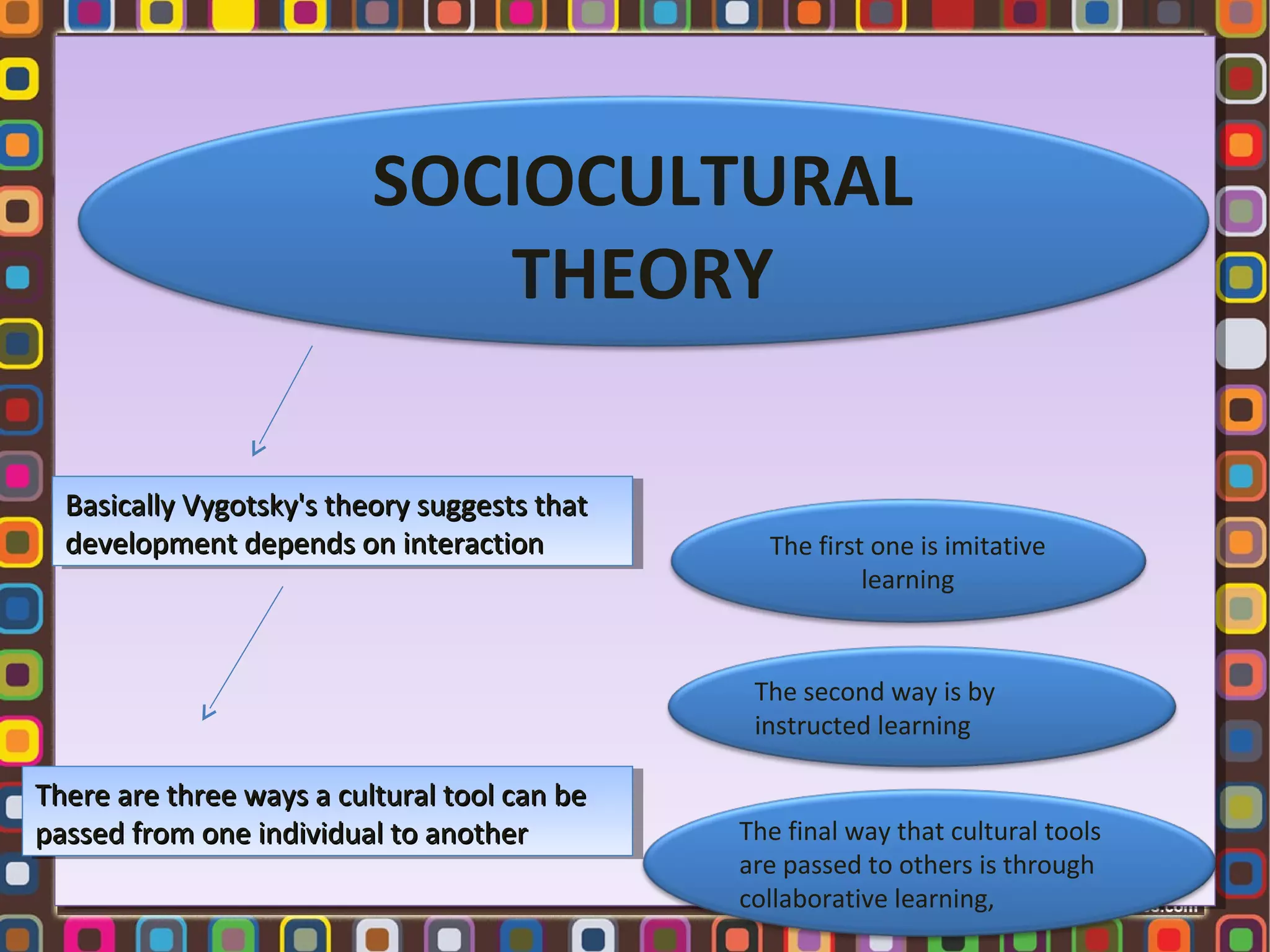
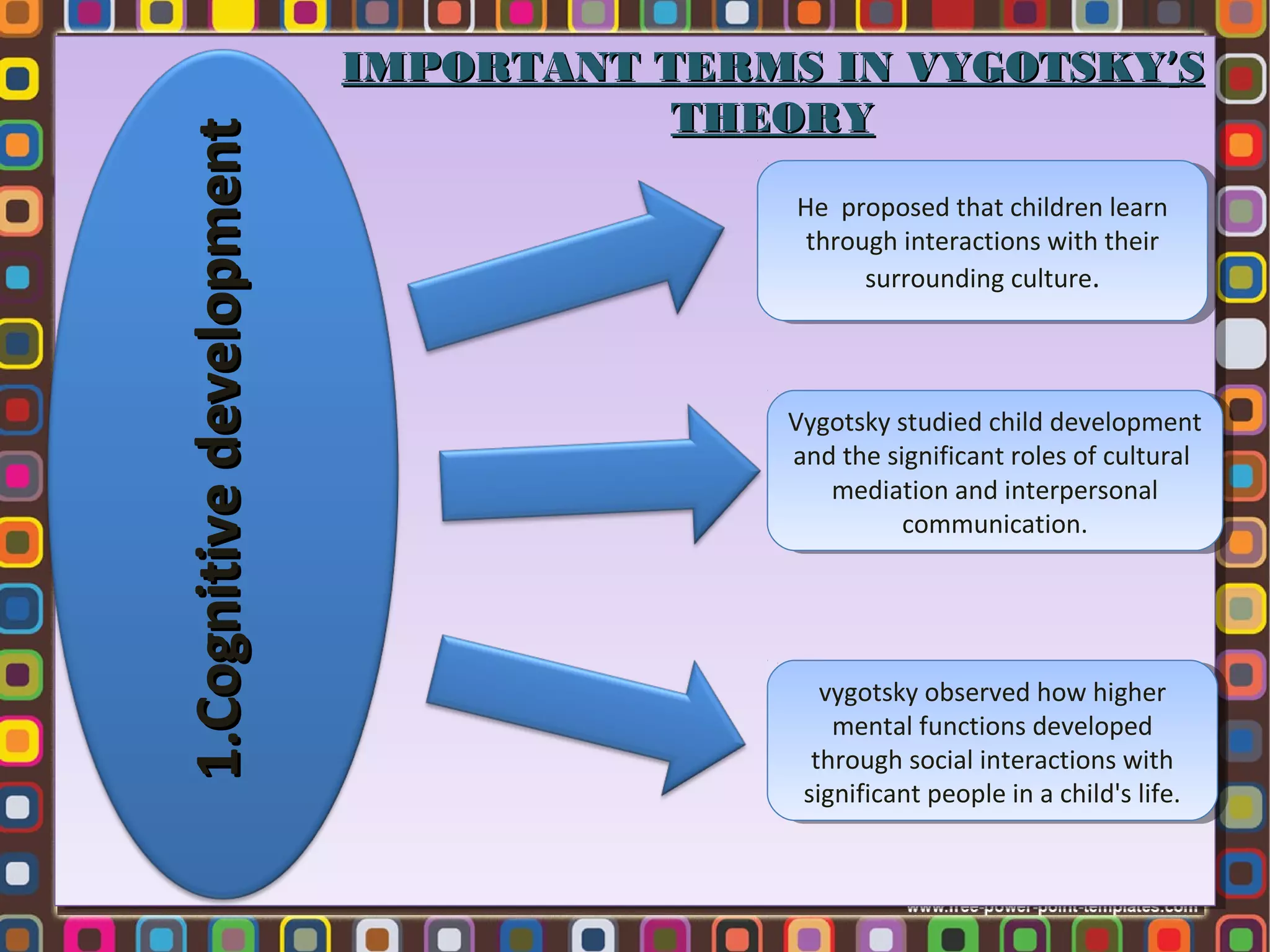
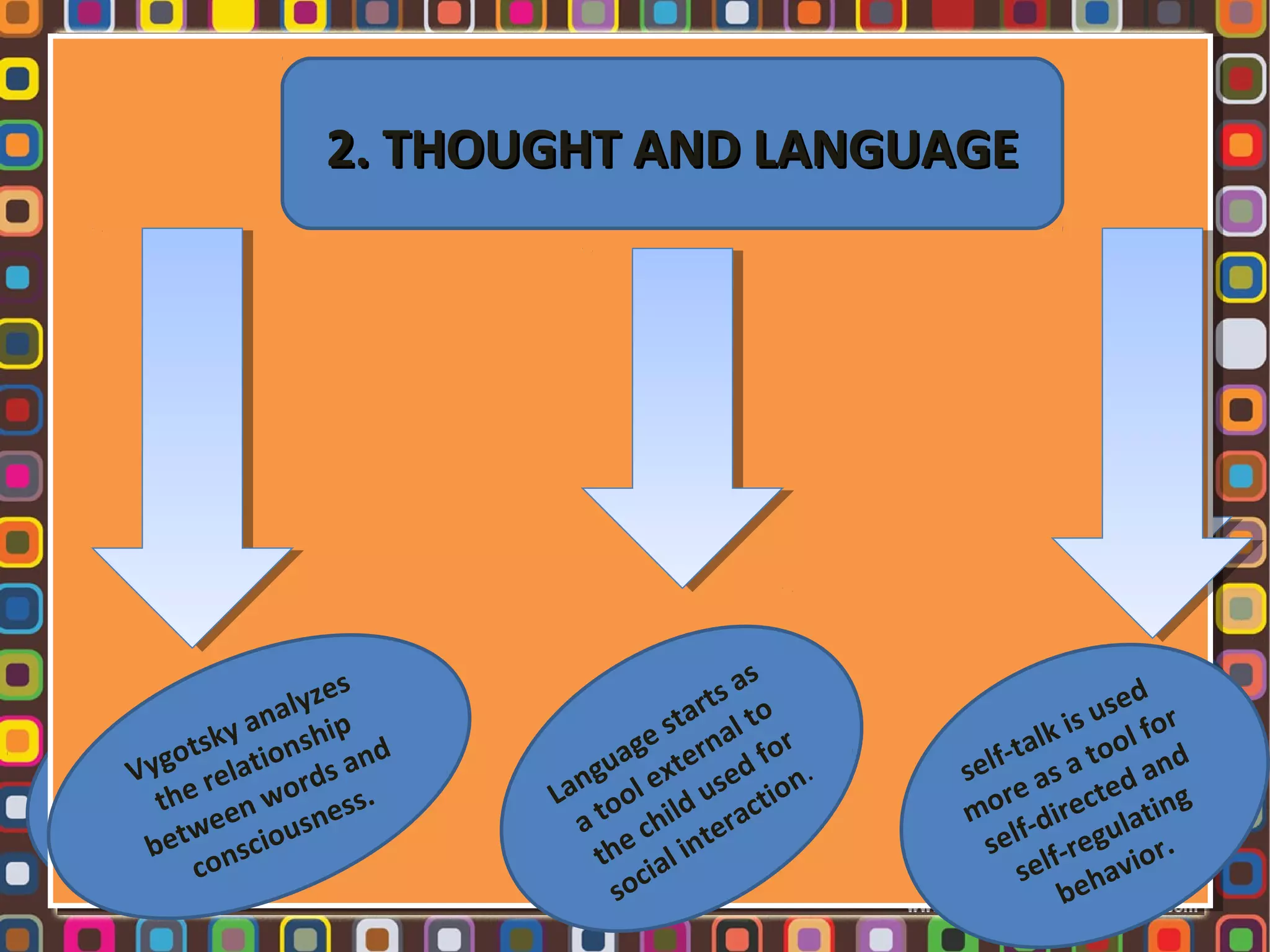
1. Lev Vygotsky was a Russian psychologist who developed the sociocultural theory of cognitive development, which posits that social interaction precedes development and that cognitive development occurs through socialization.
2. According to Vygotsky, learning awakens a variety of internal developmental processes that are able to operate only when the child interacts with people in his environment and in cooperation with his peers.
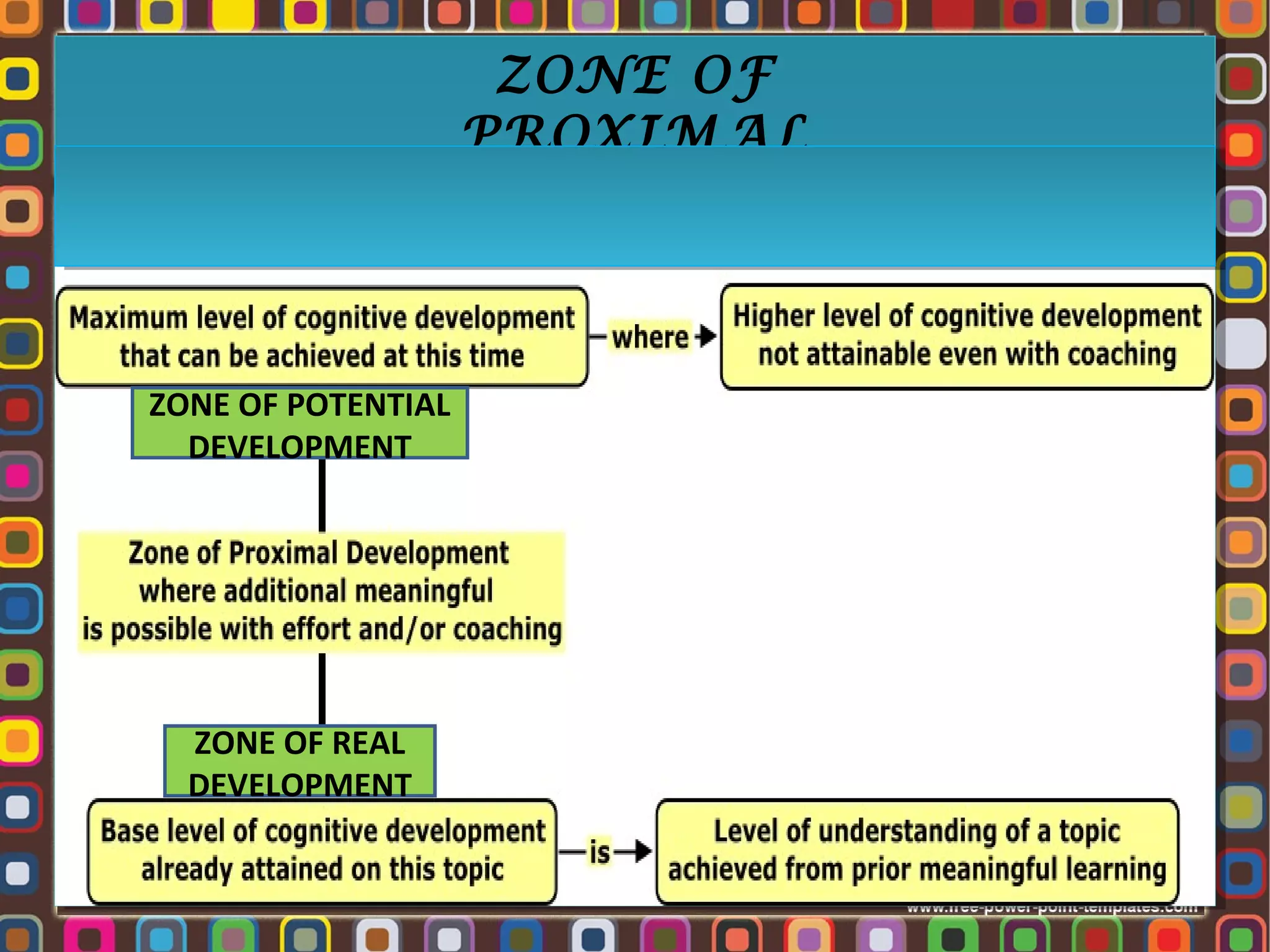
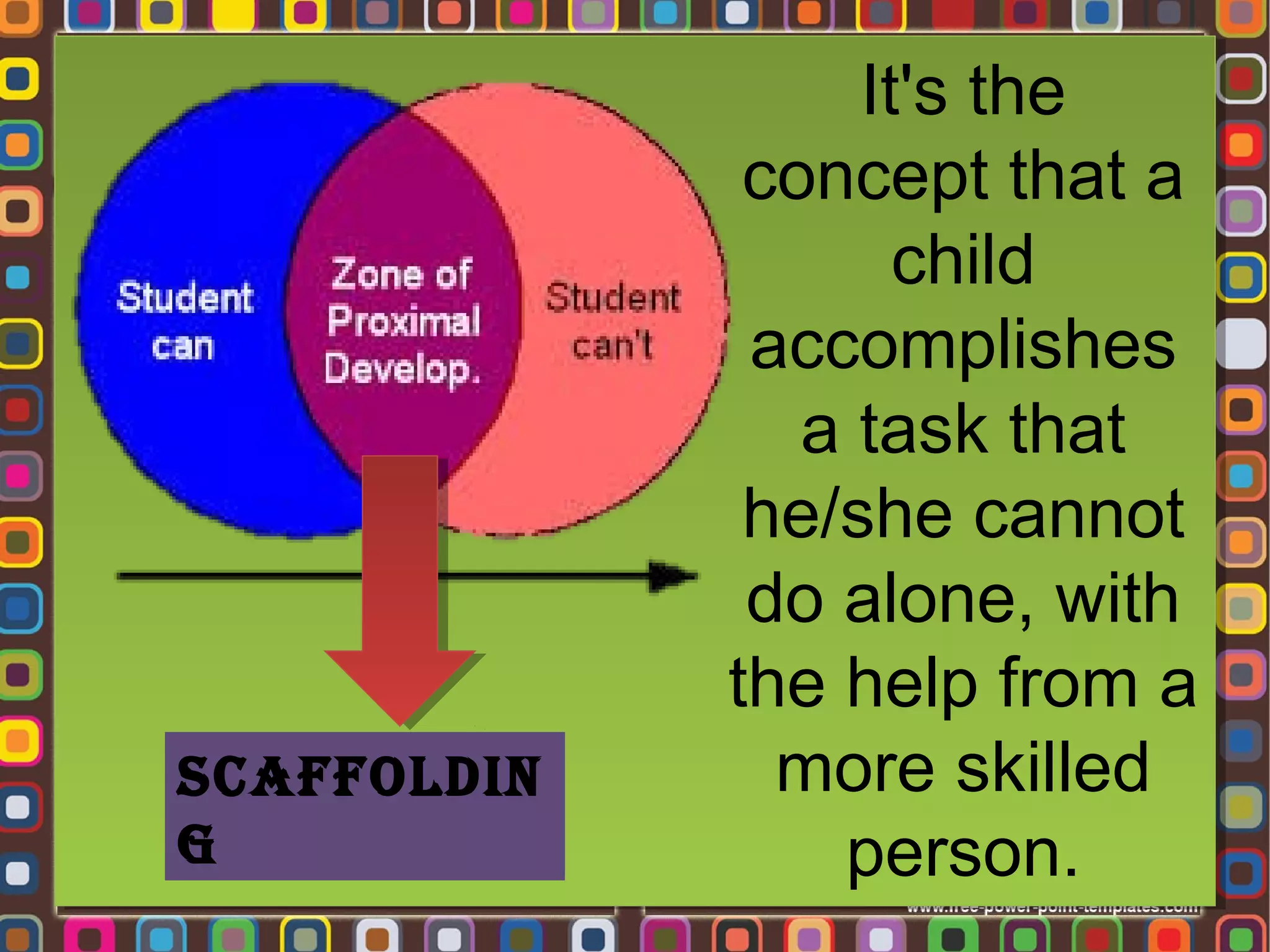
3. Key concepts in Vygotsky's theory include the zone of proximal development, more knowledgeable others, scaffolding, private speech, and the importance of social learning and cultural tools in cognitive development.