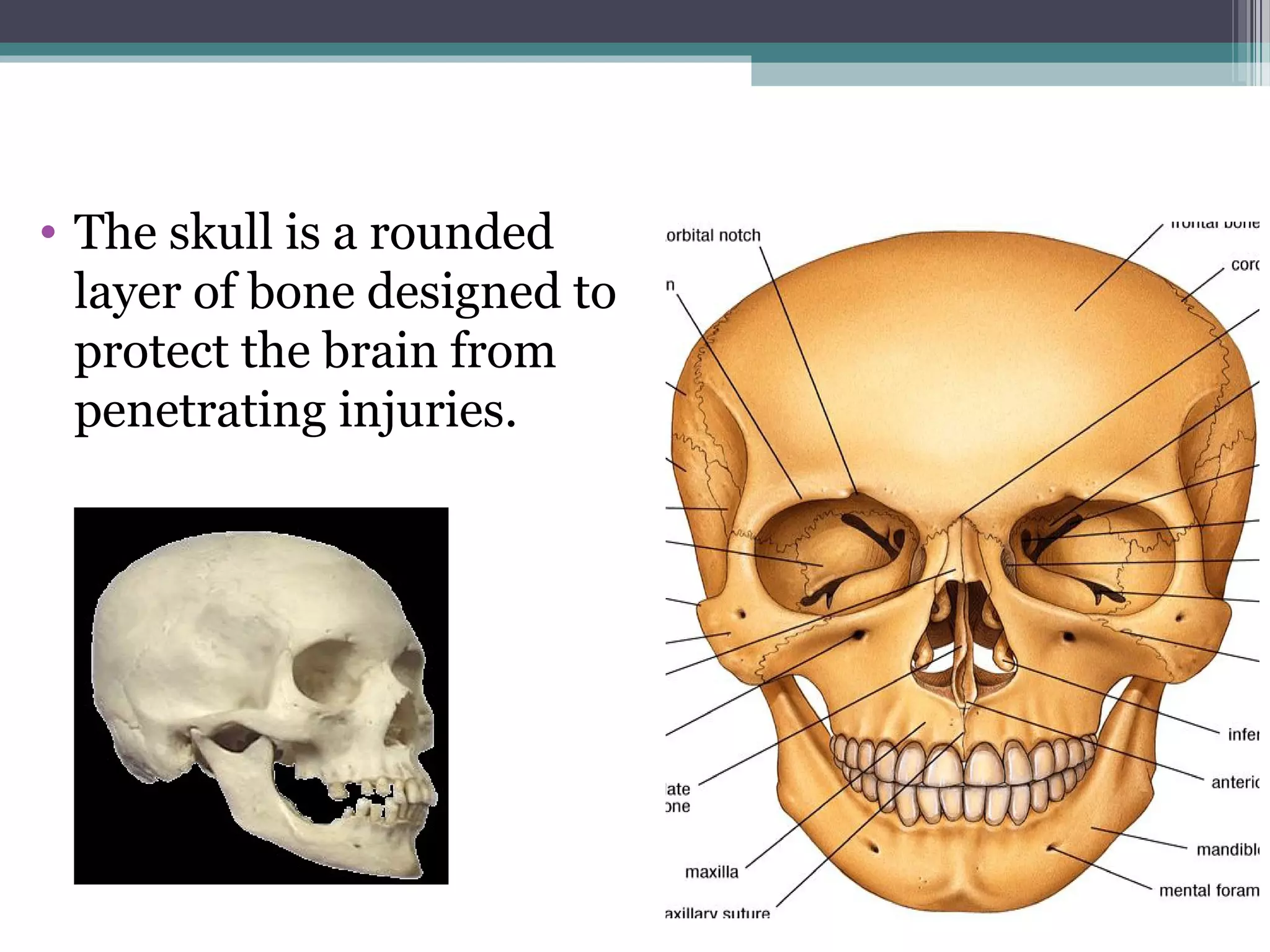
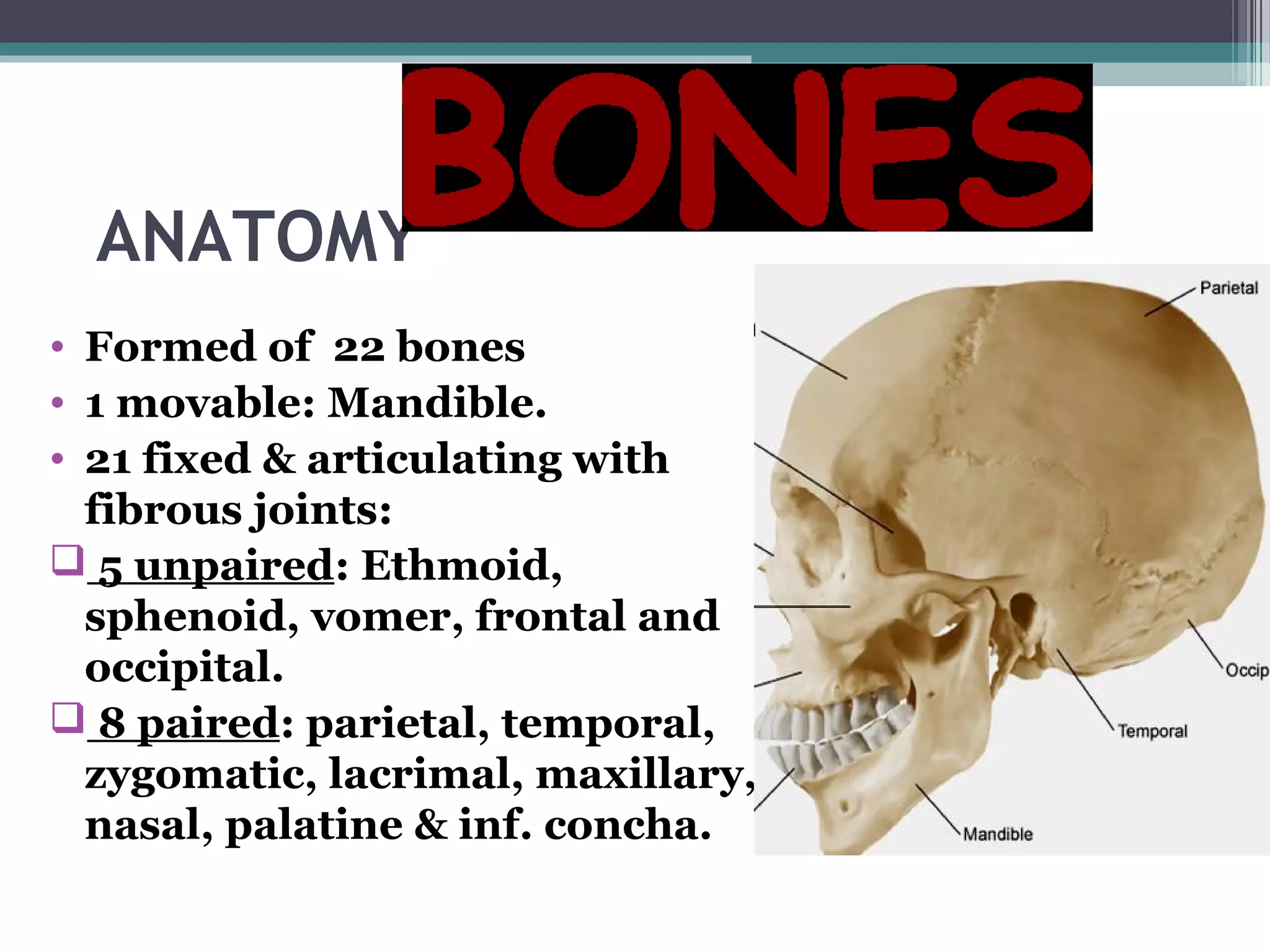
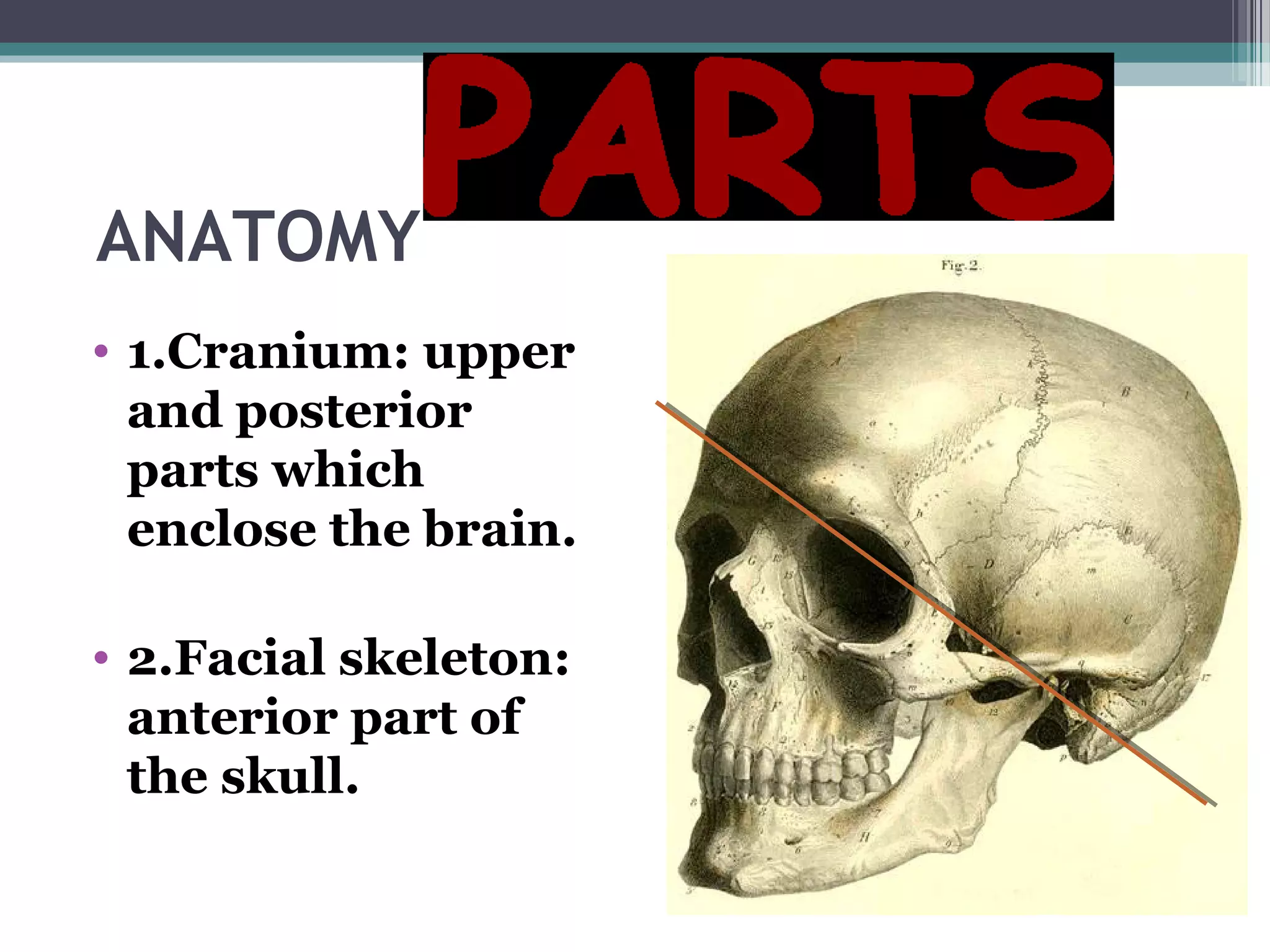
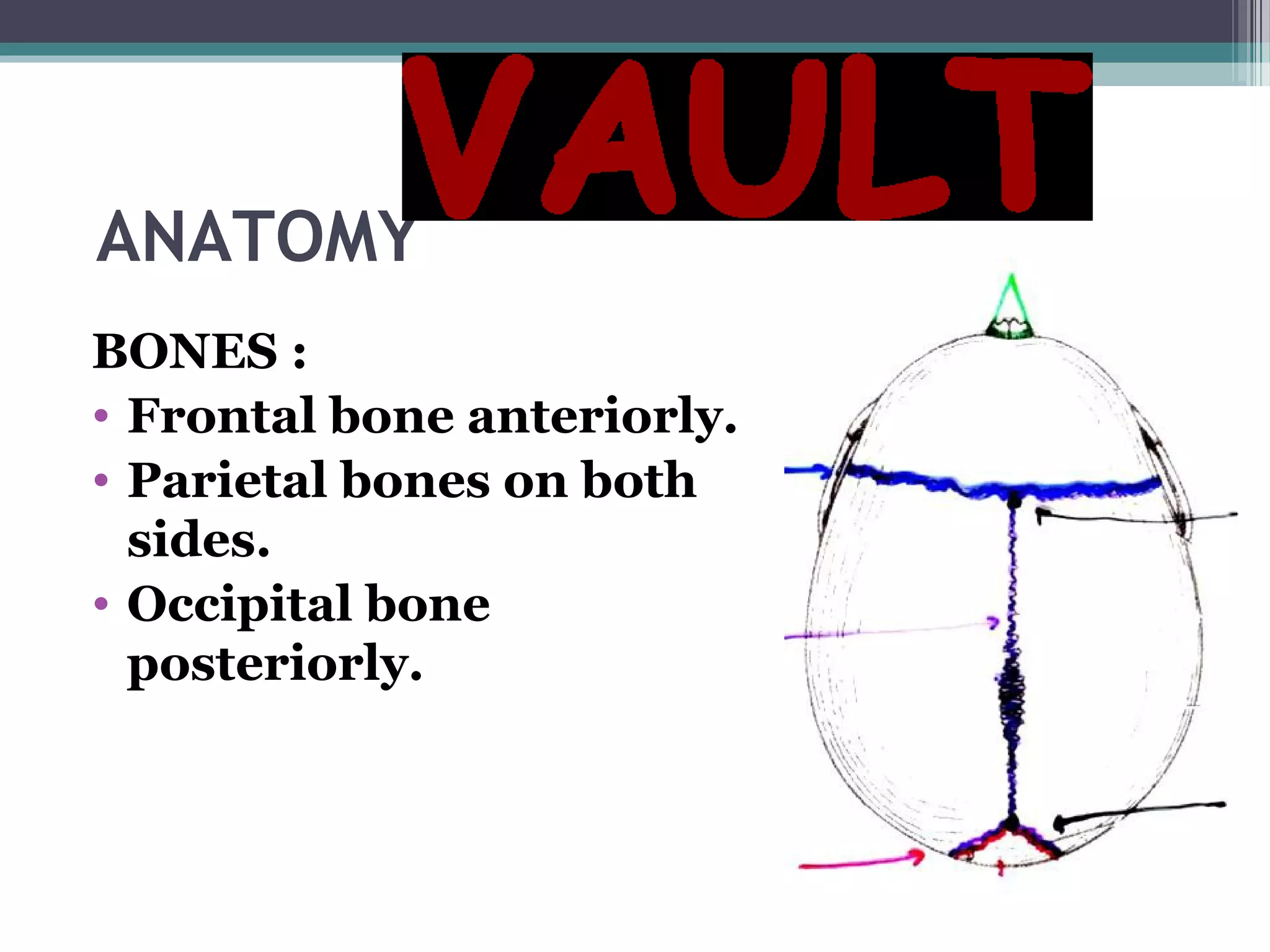
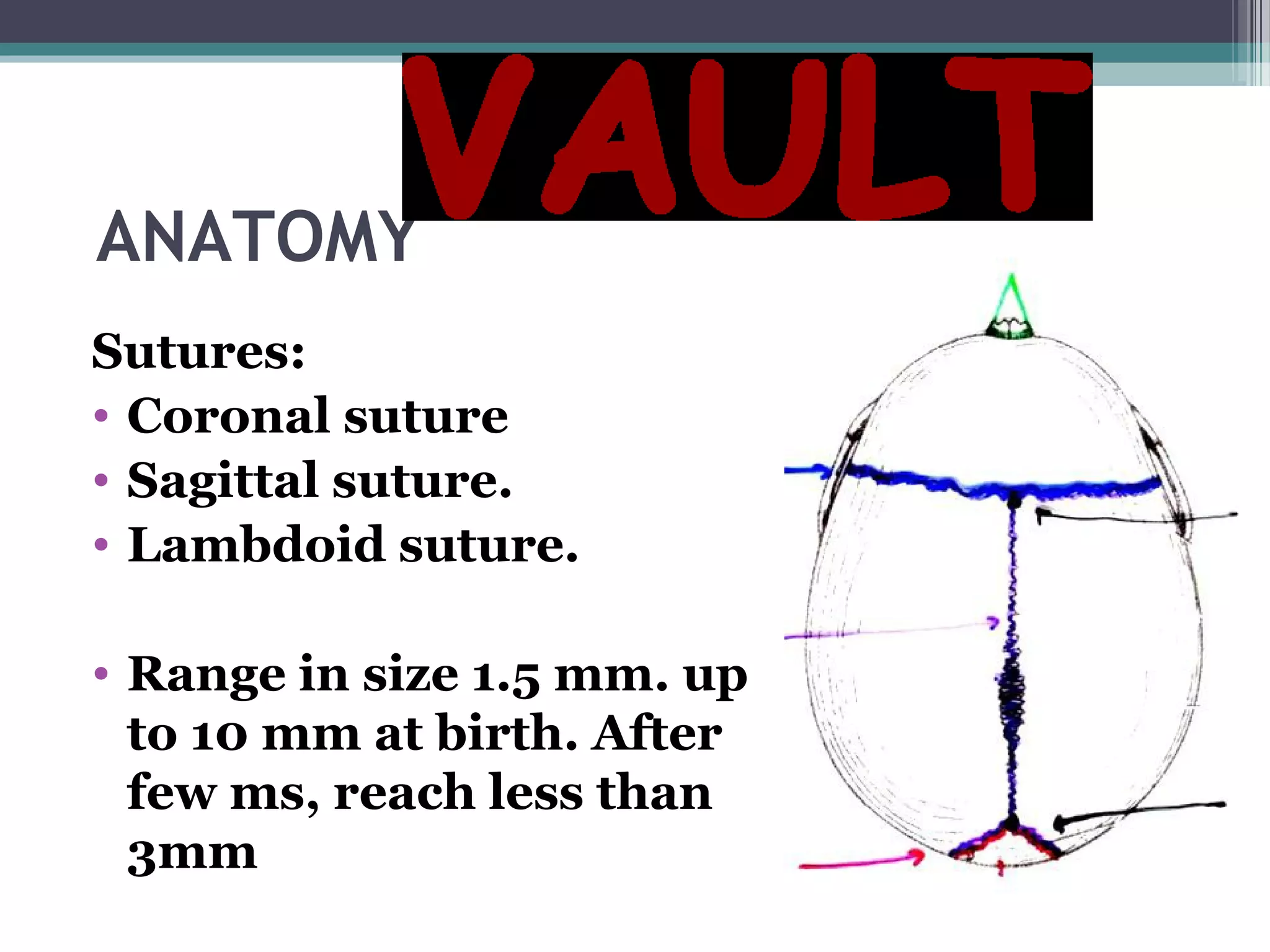
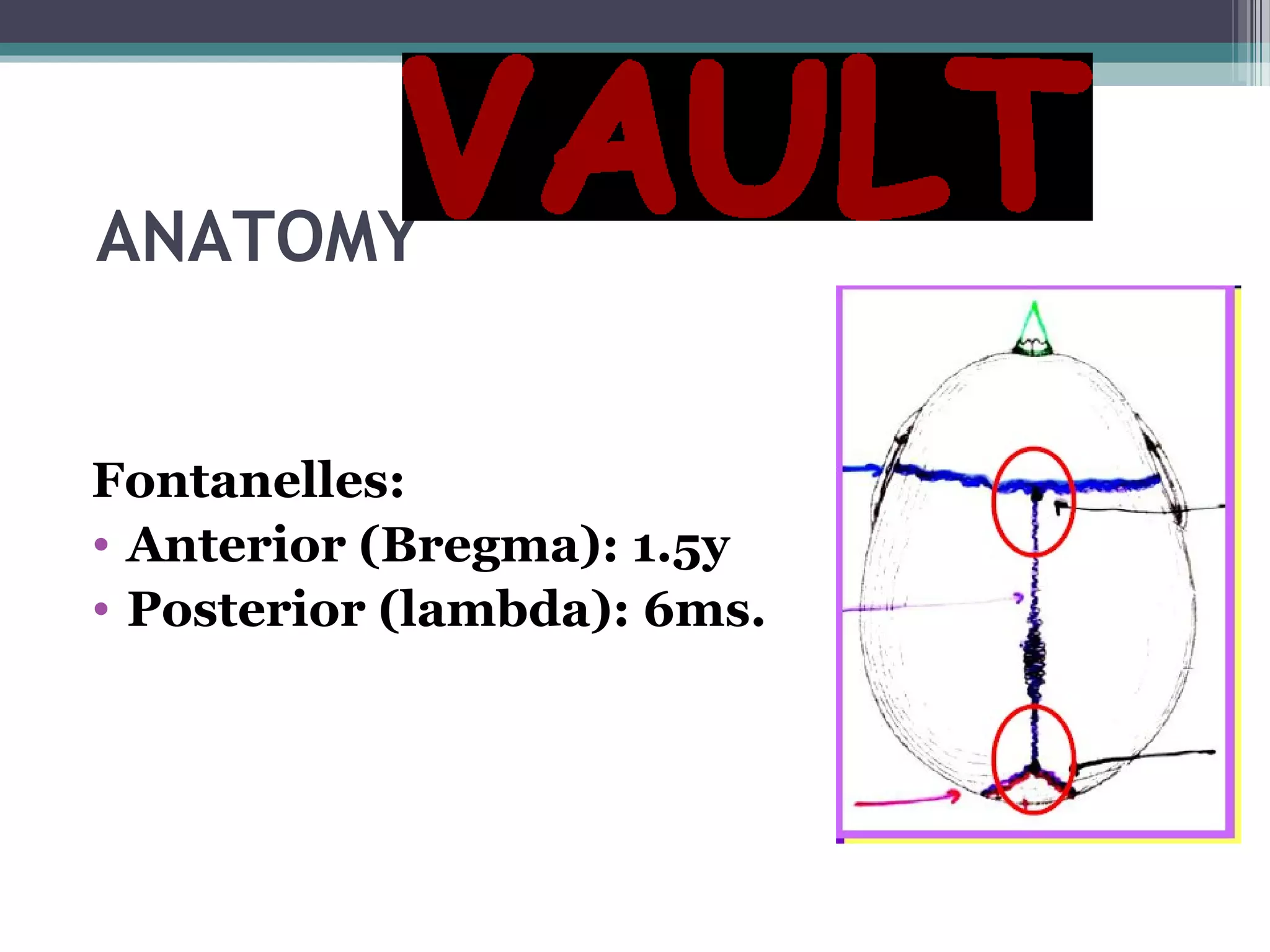
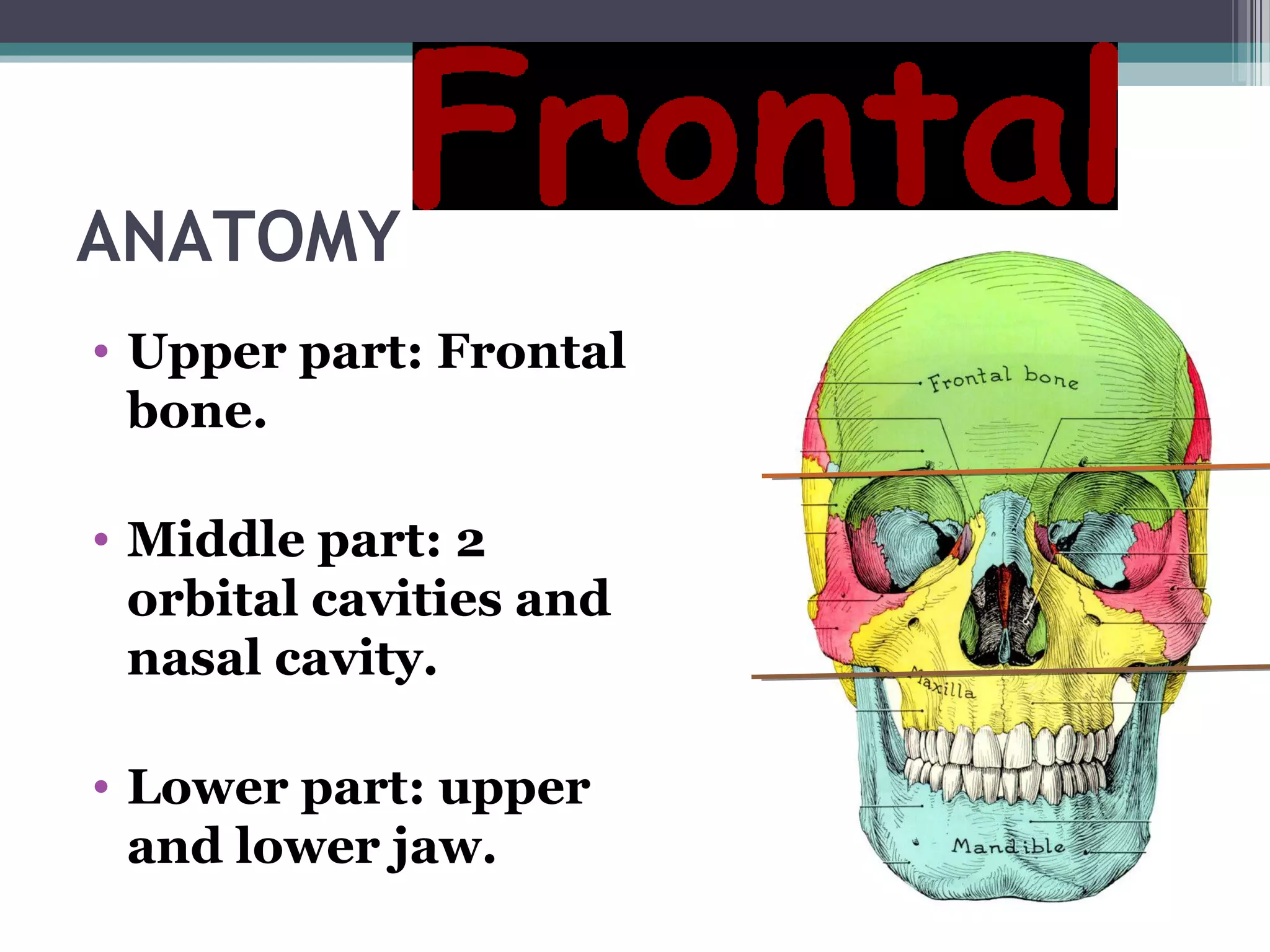
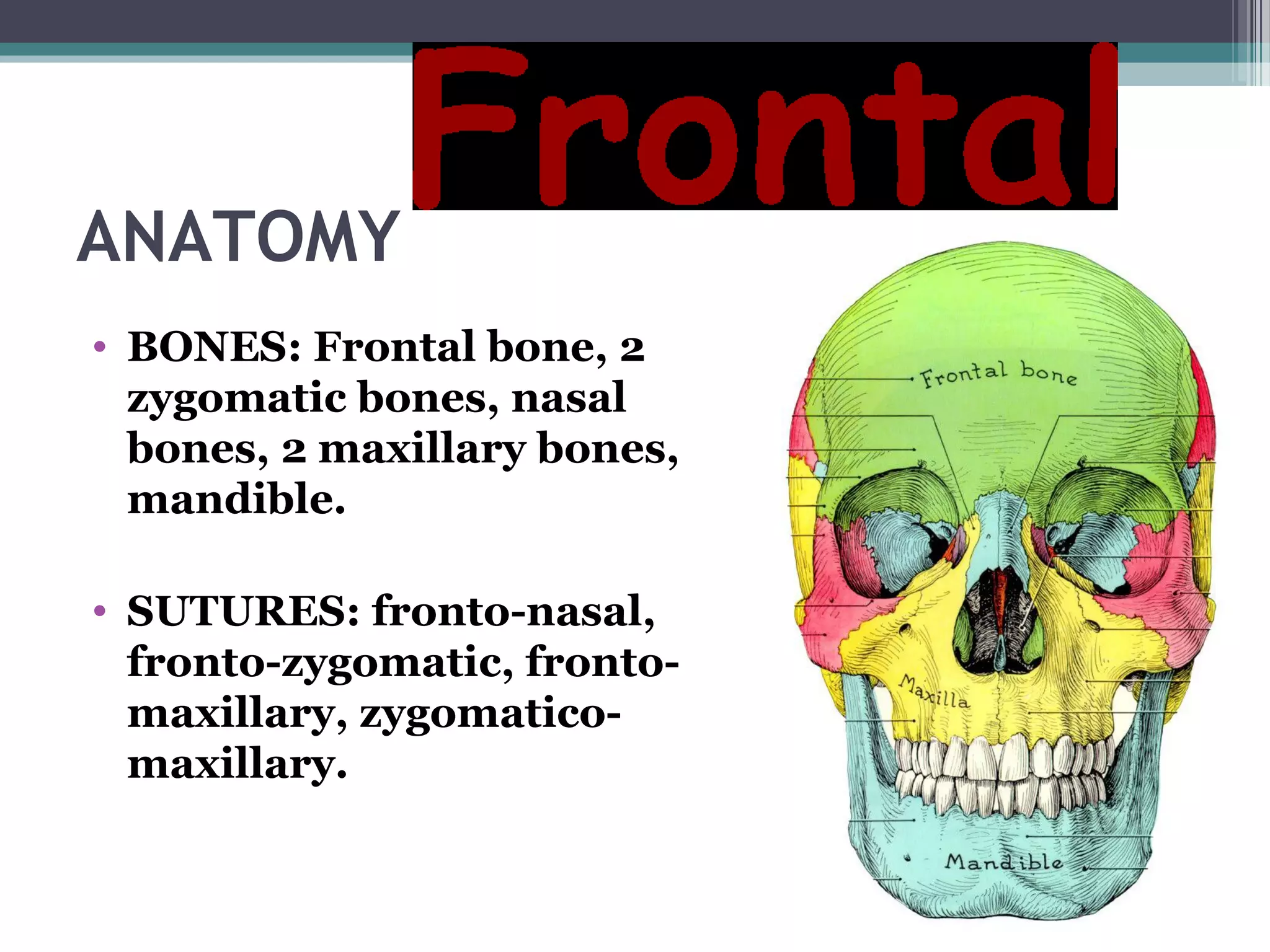
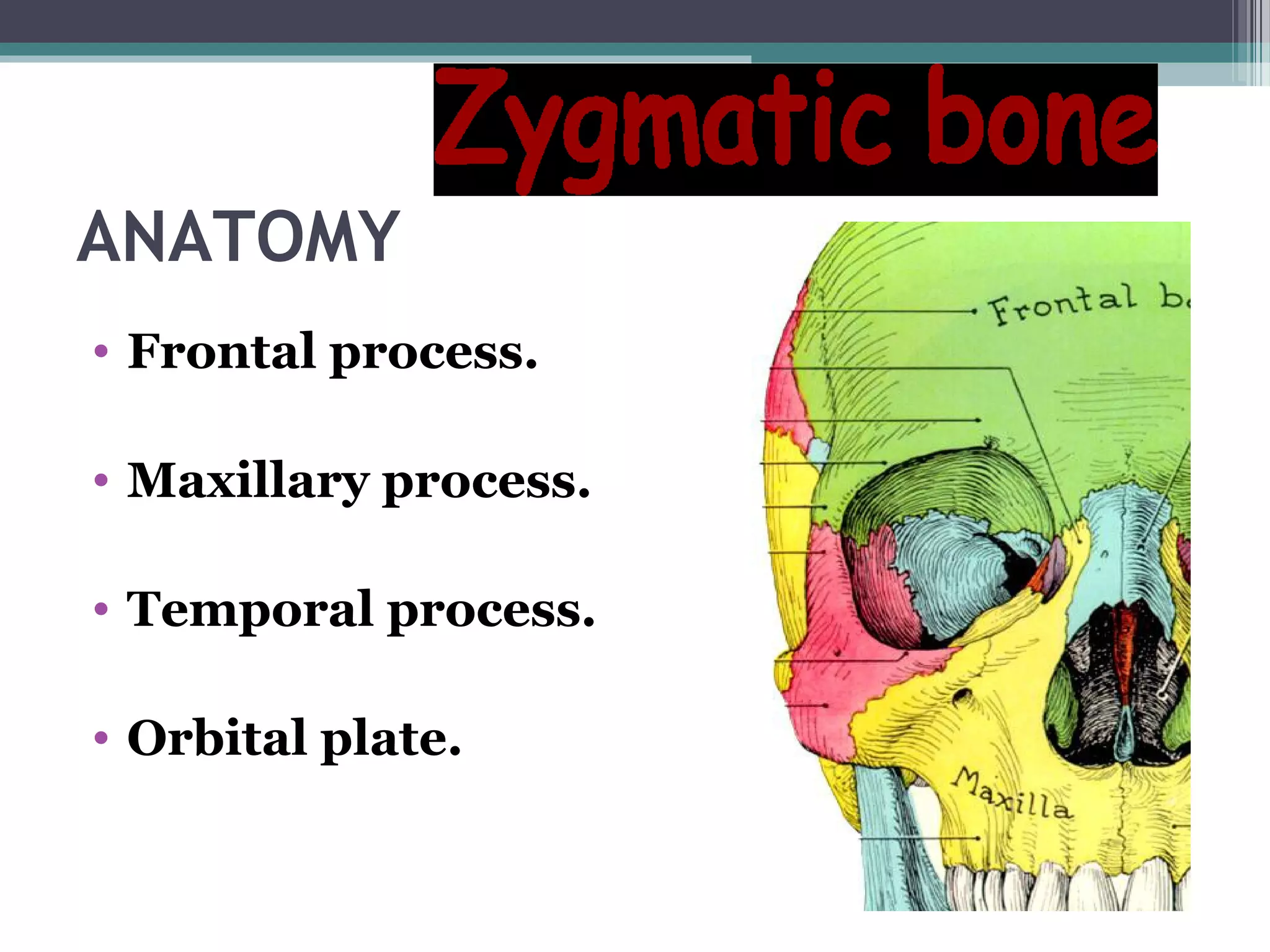
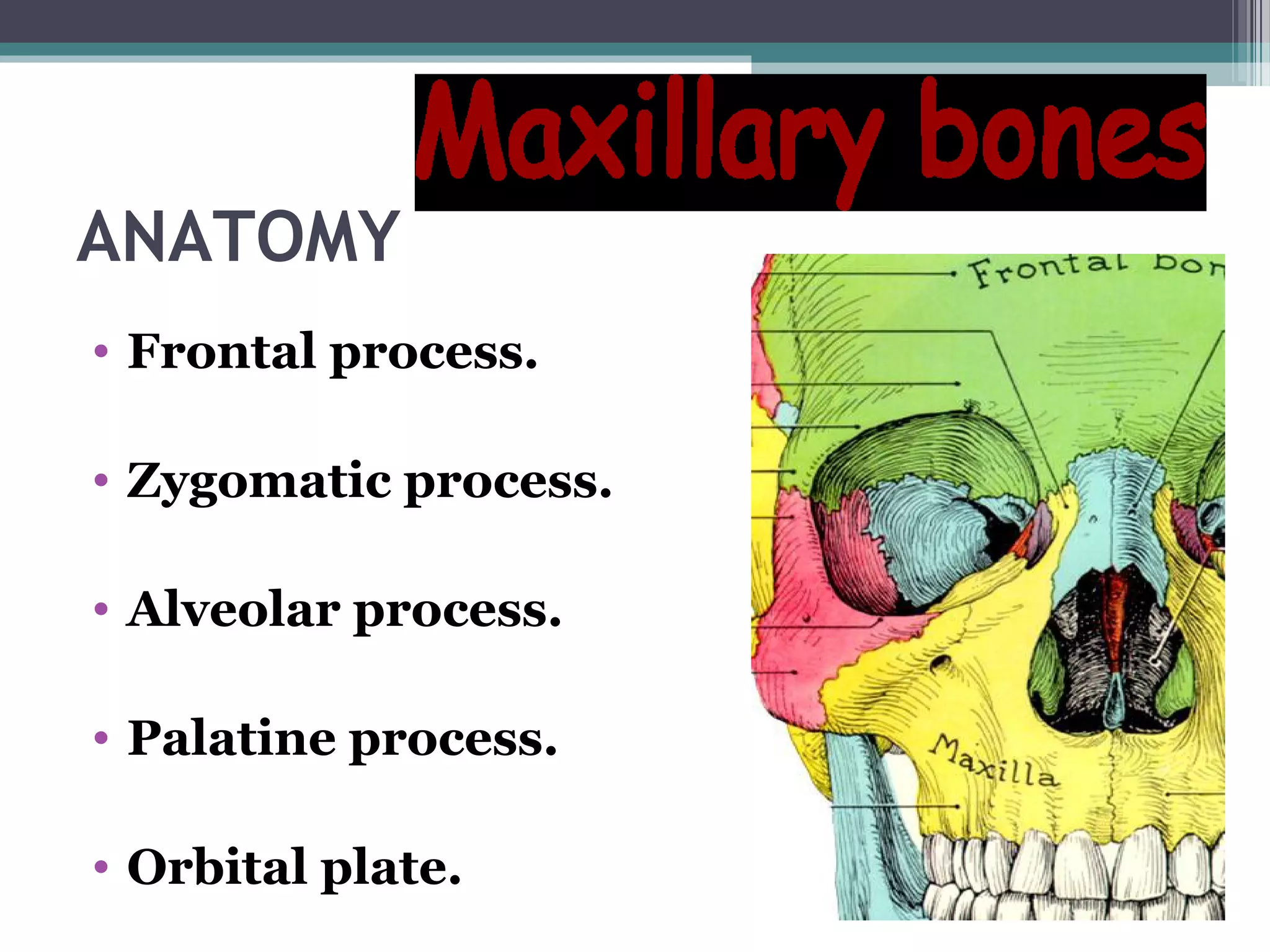
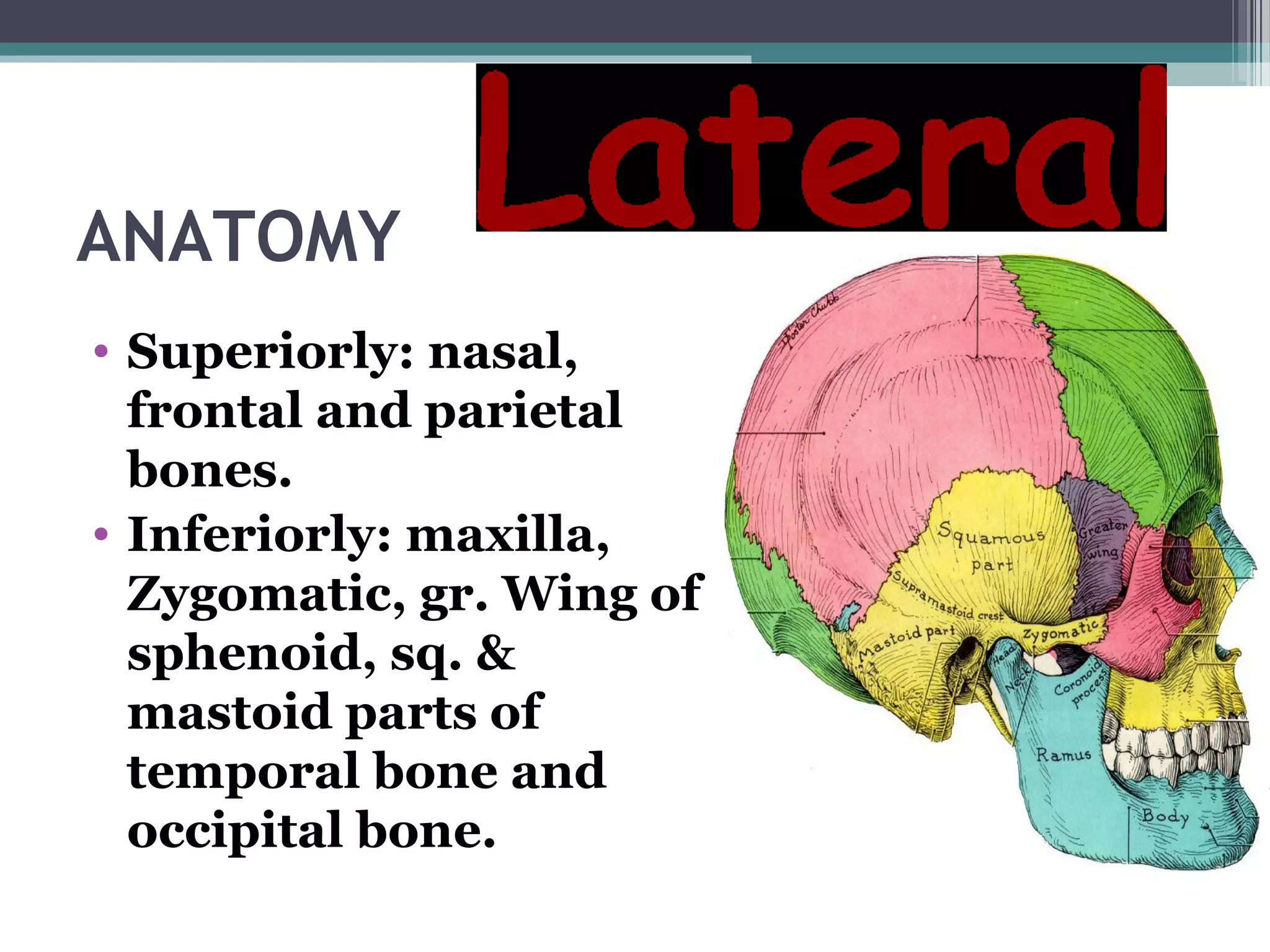
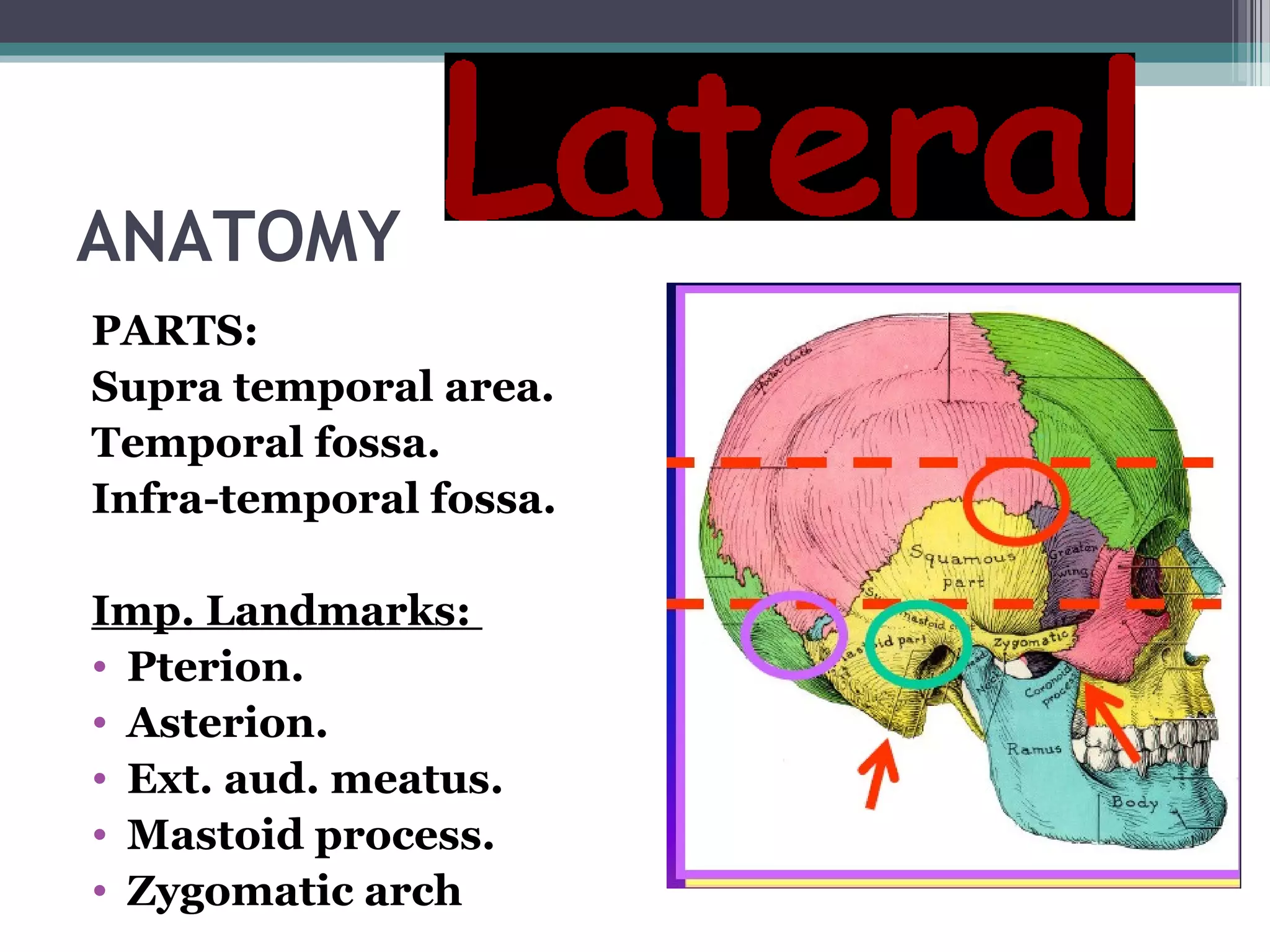
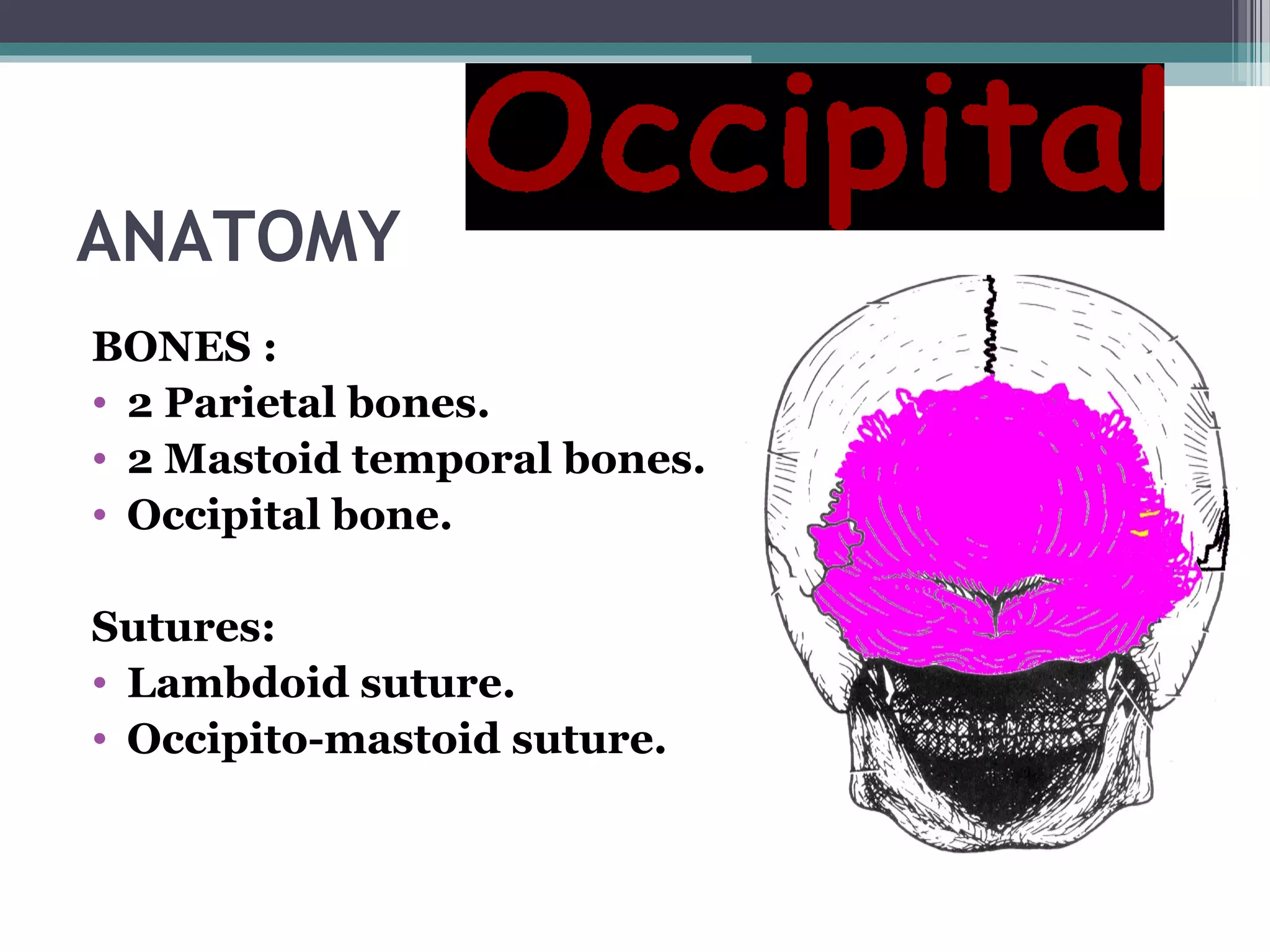
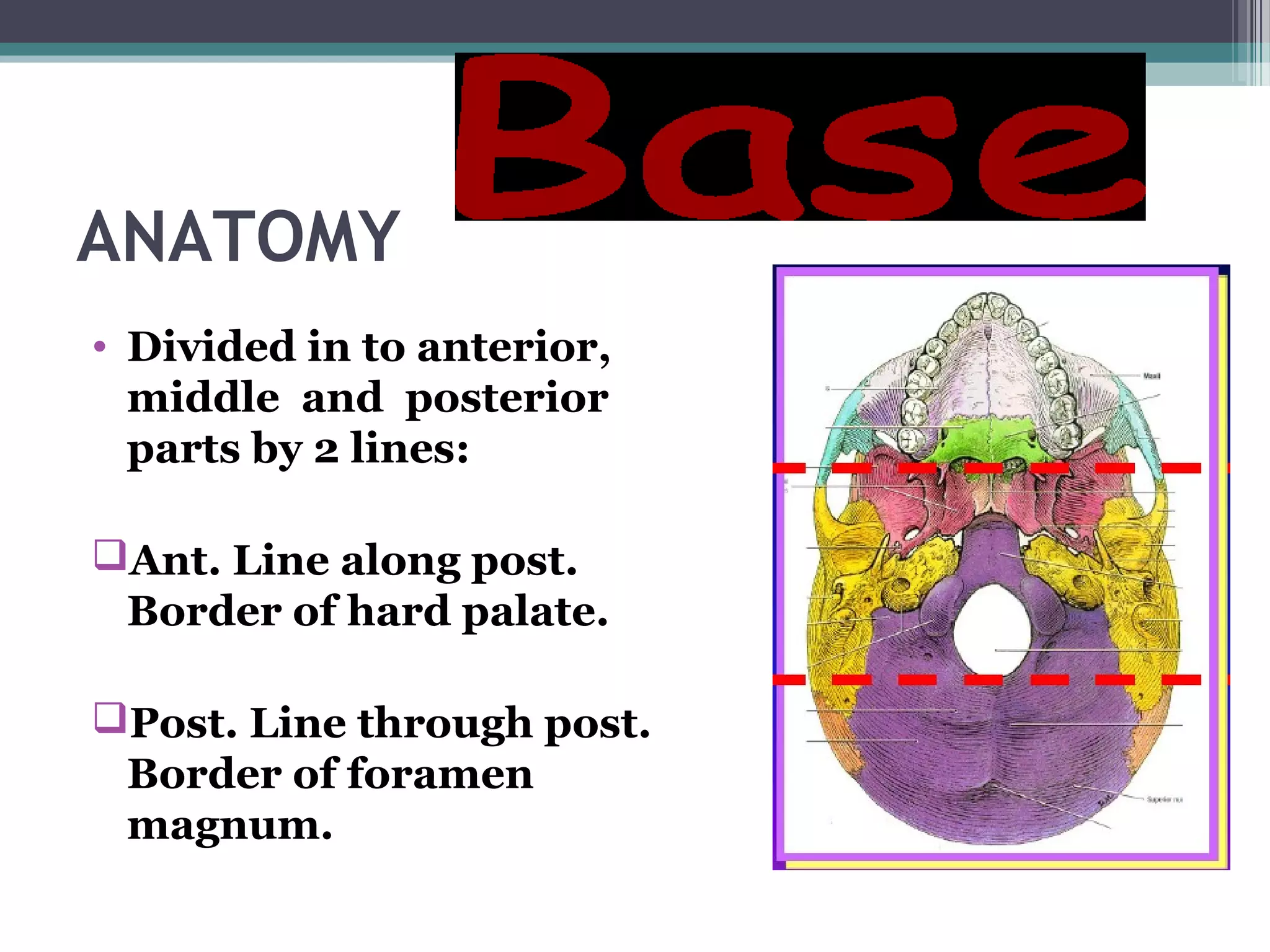
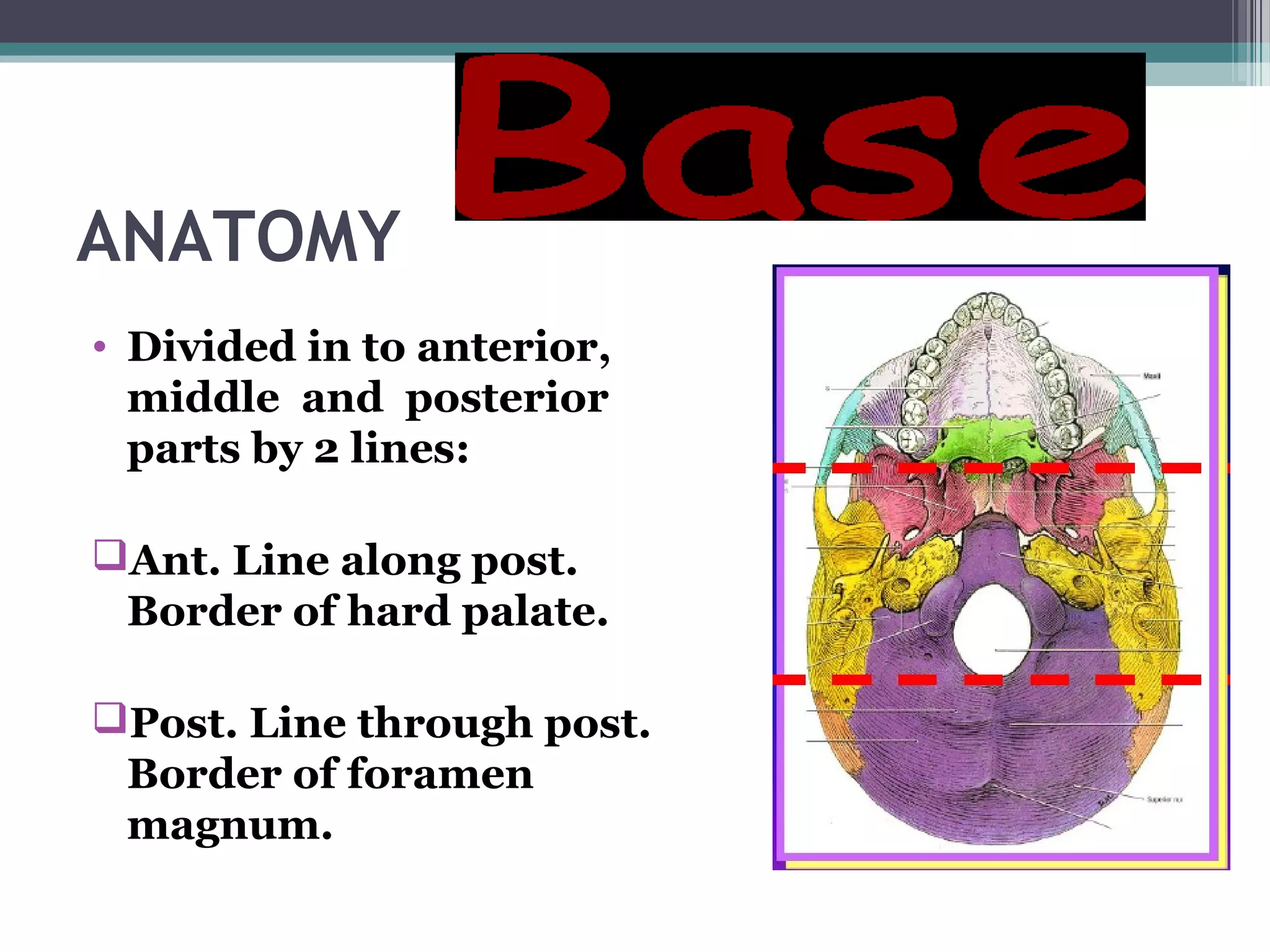
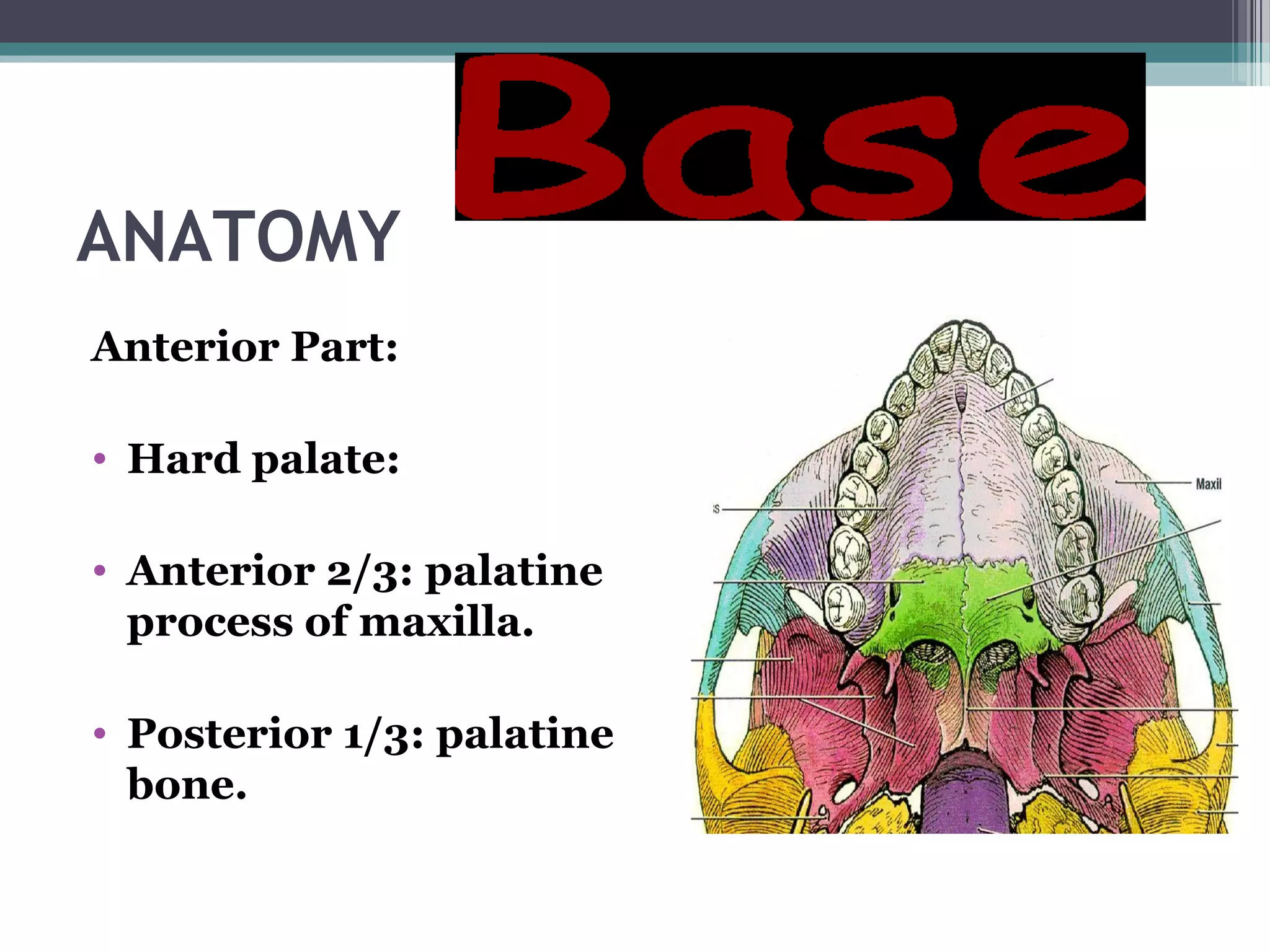
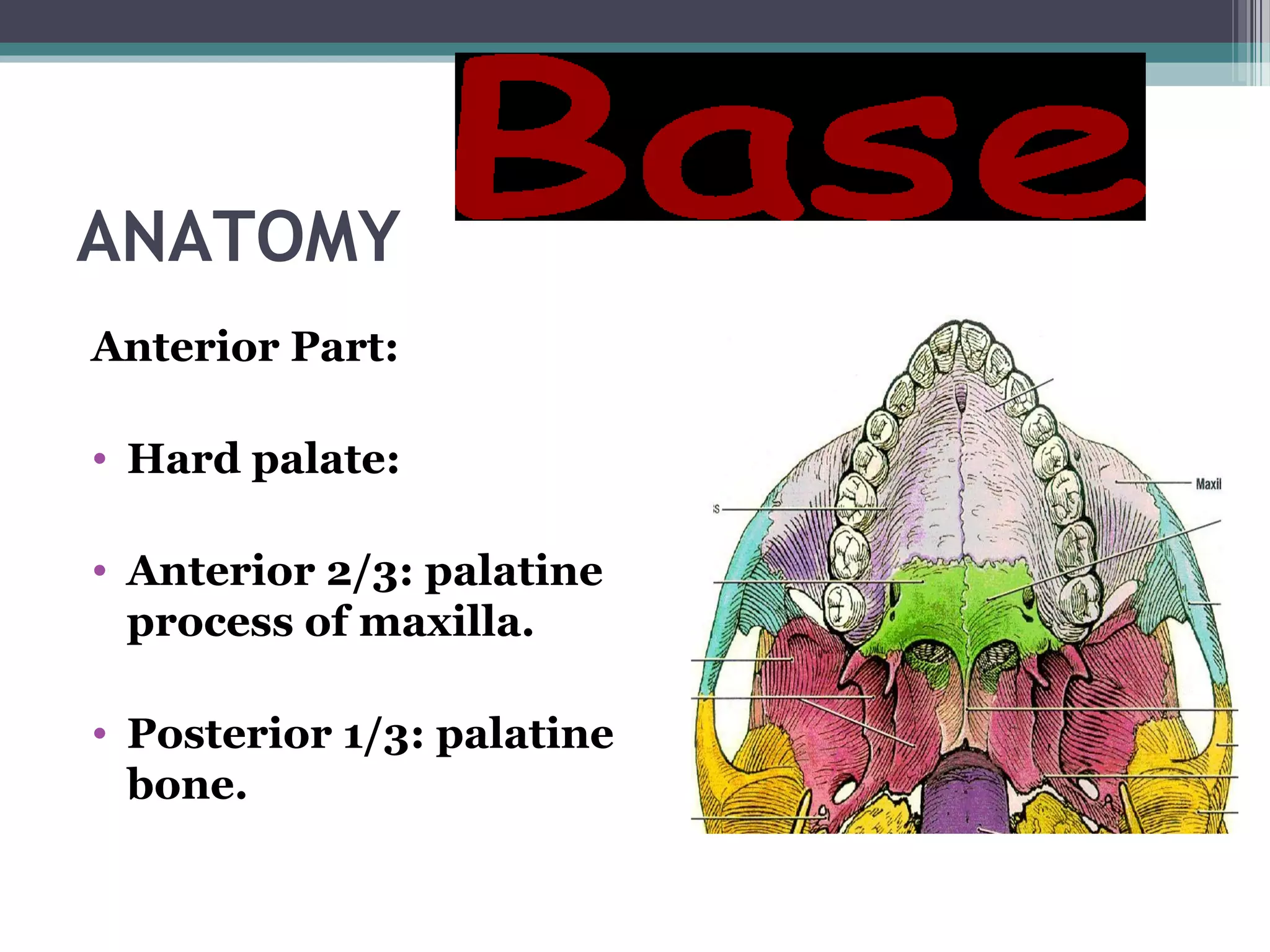
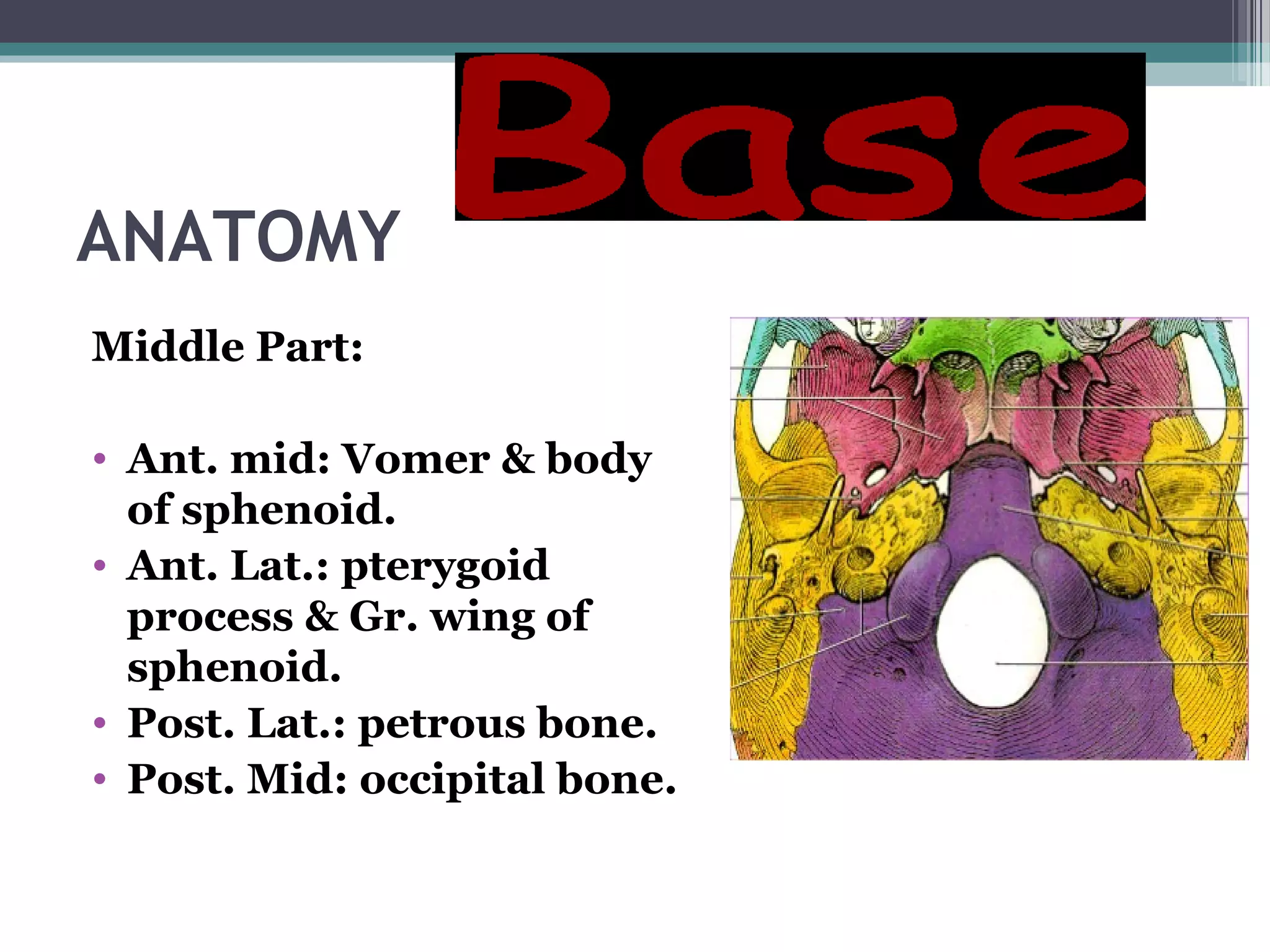
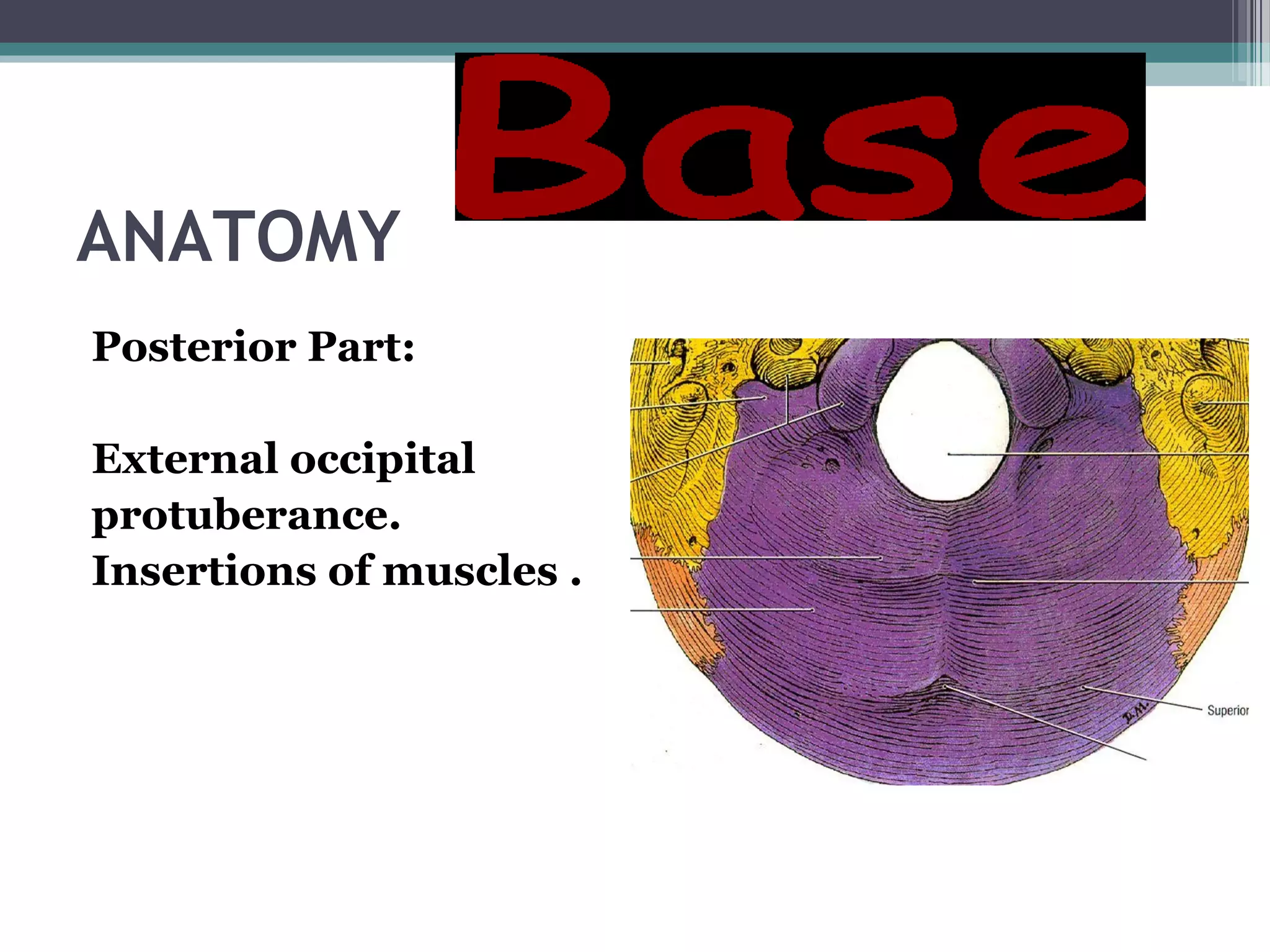
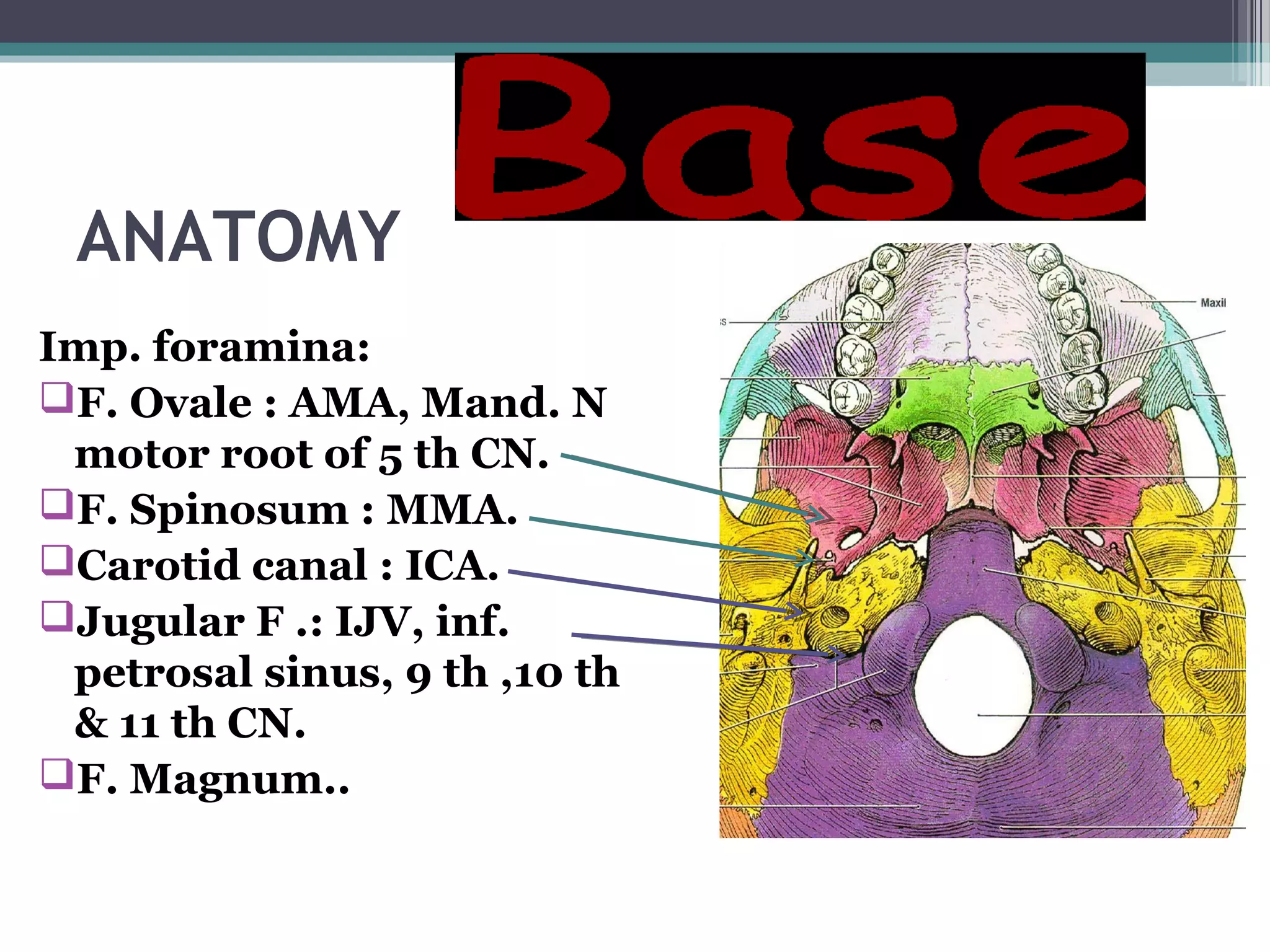
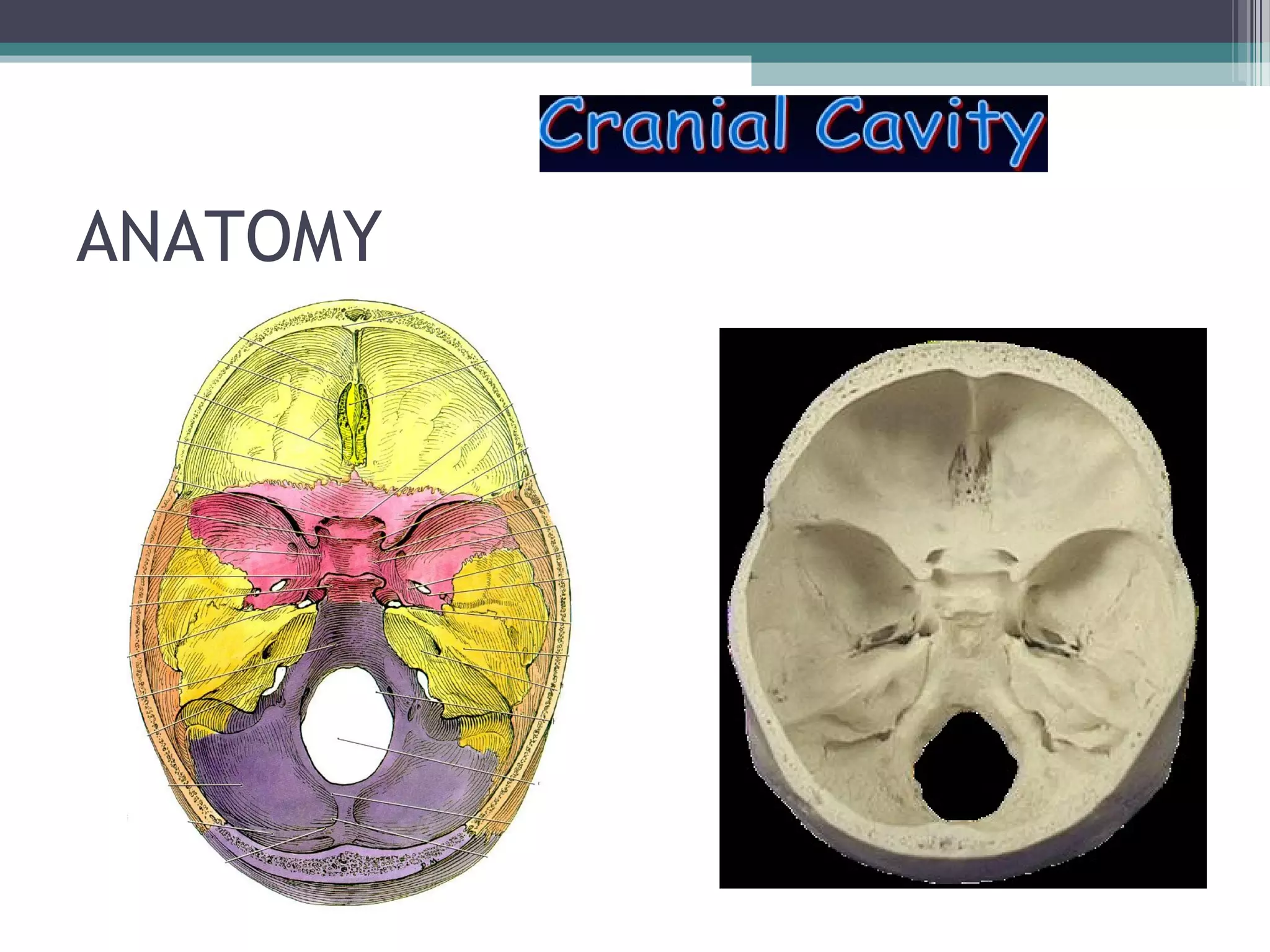
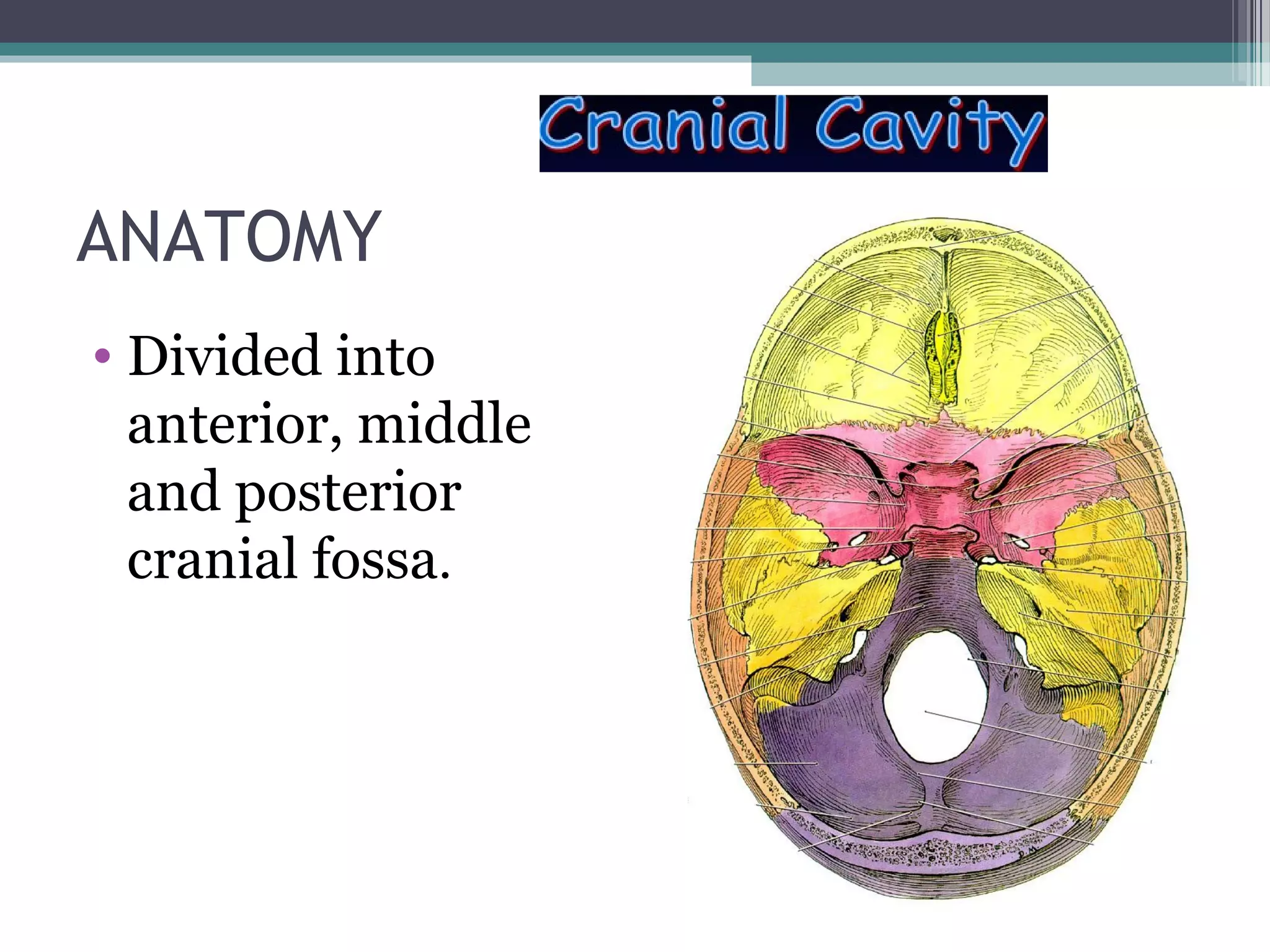
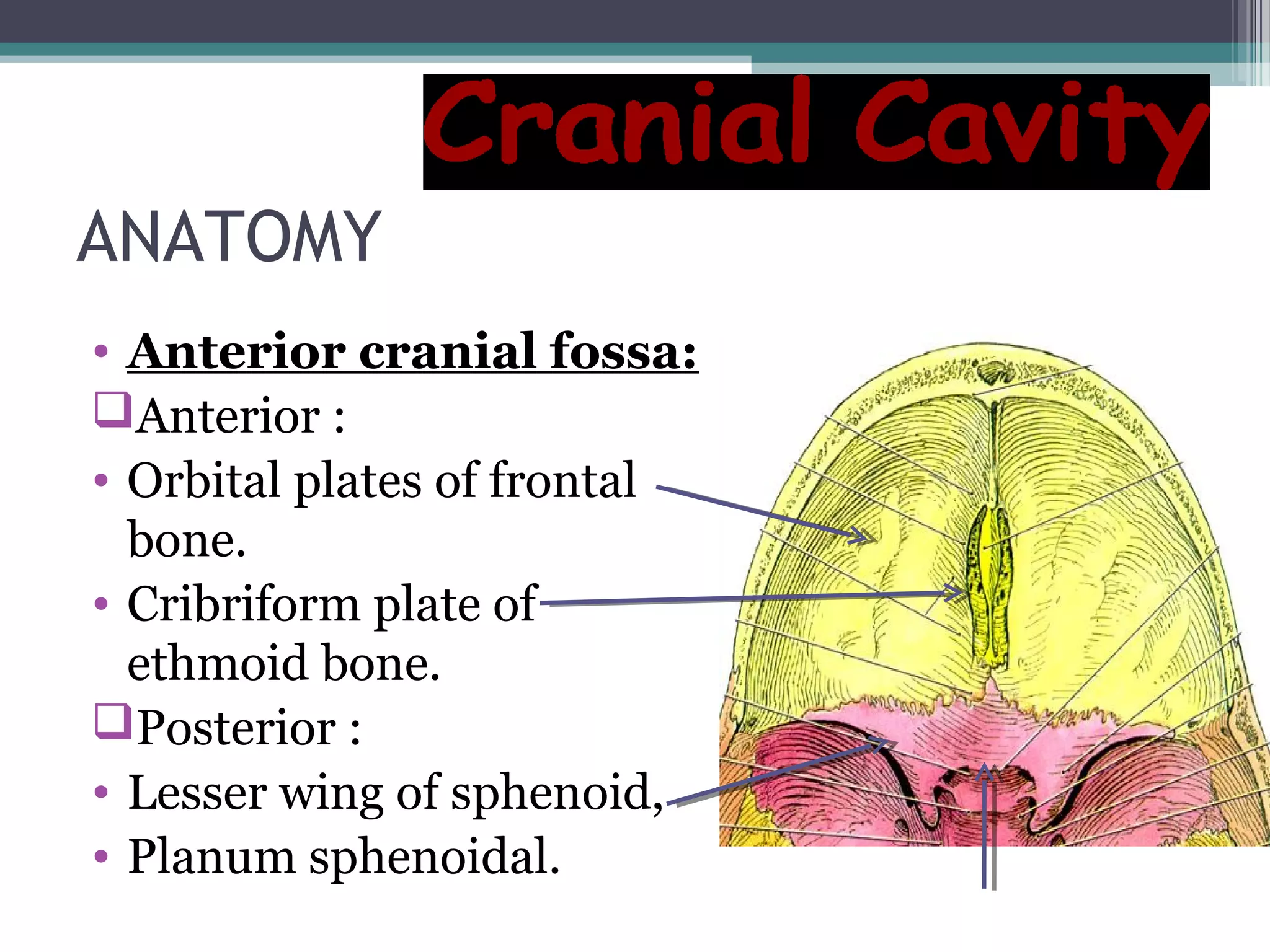
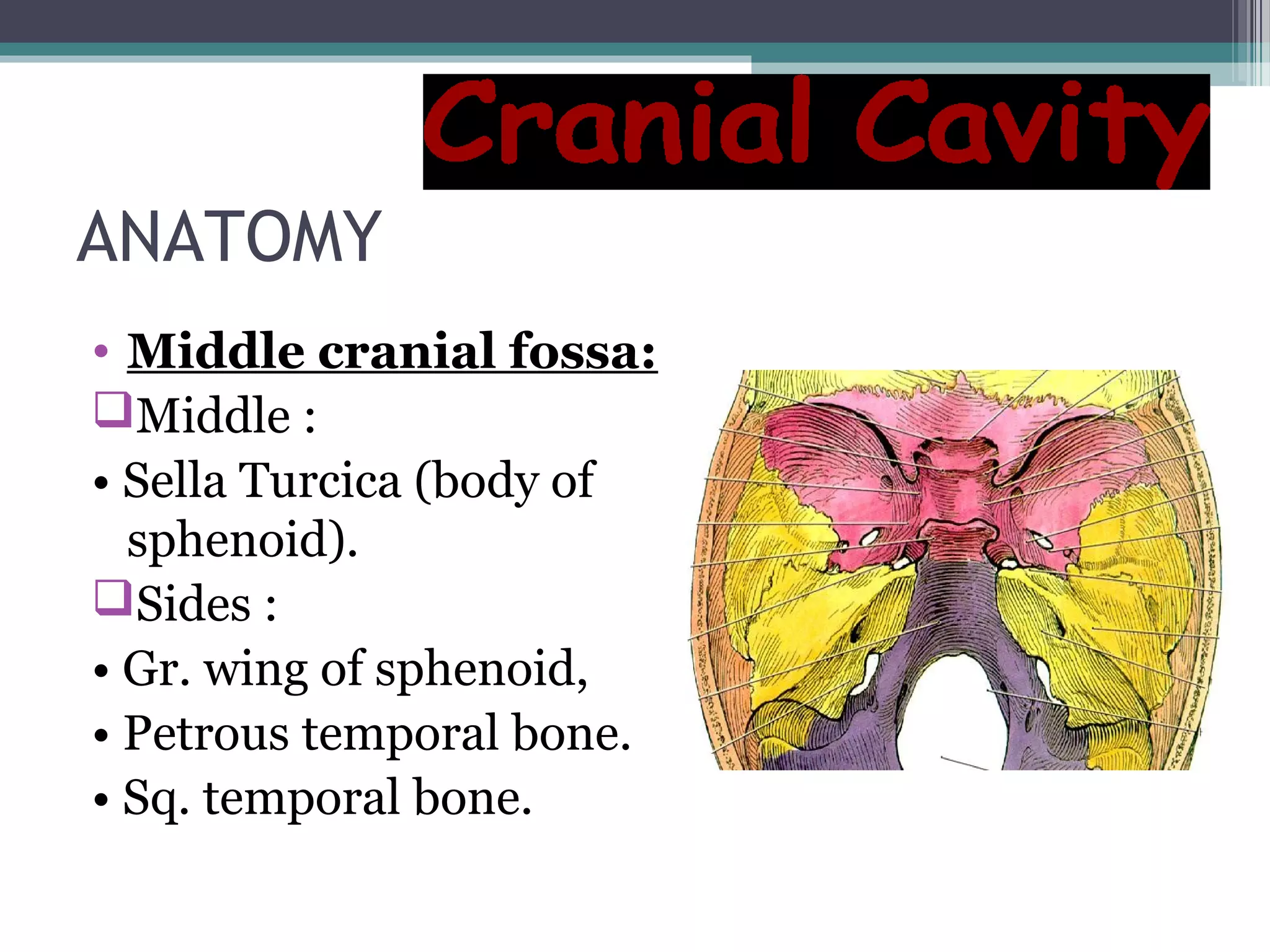
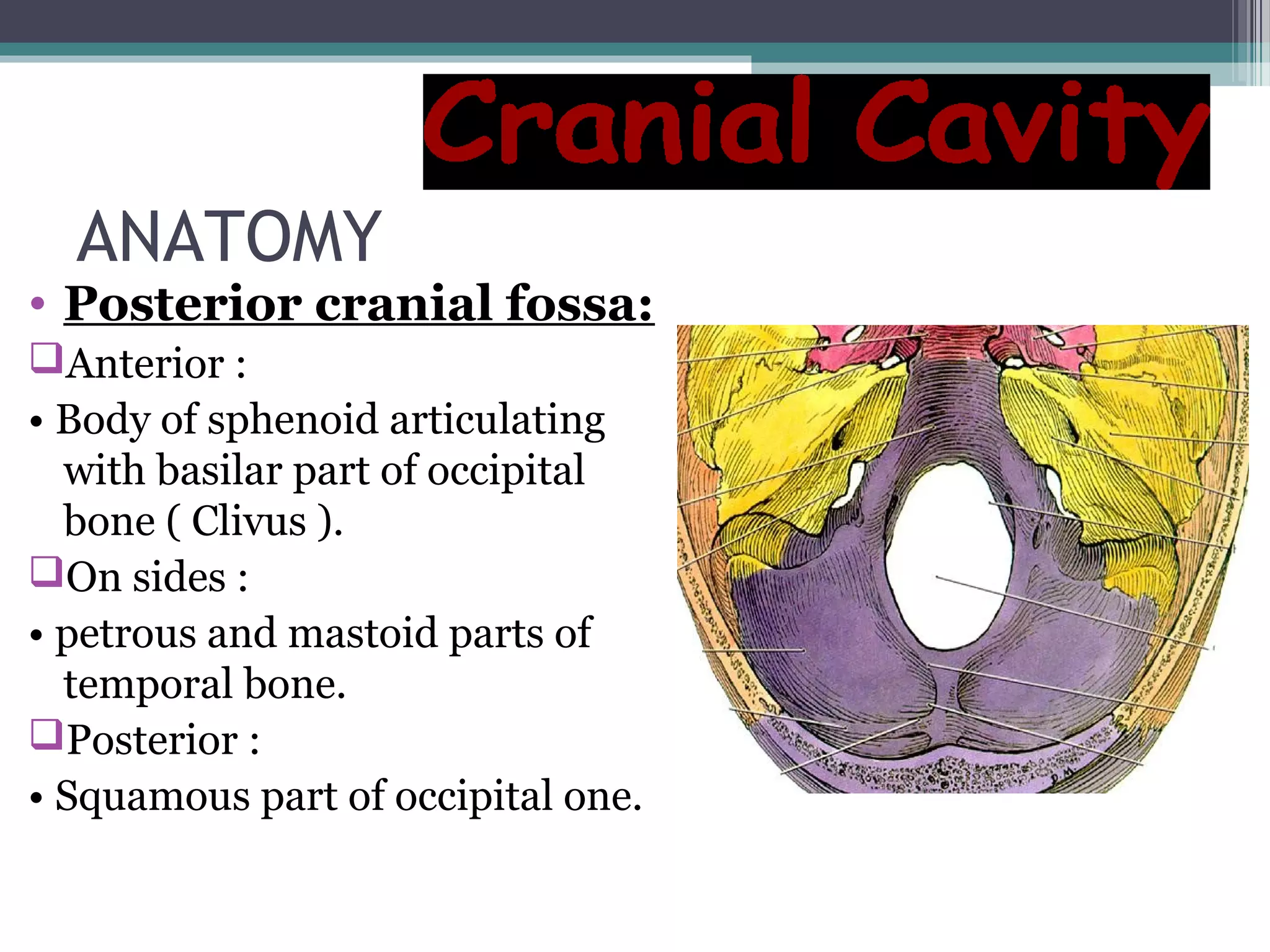
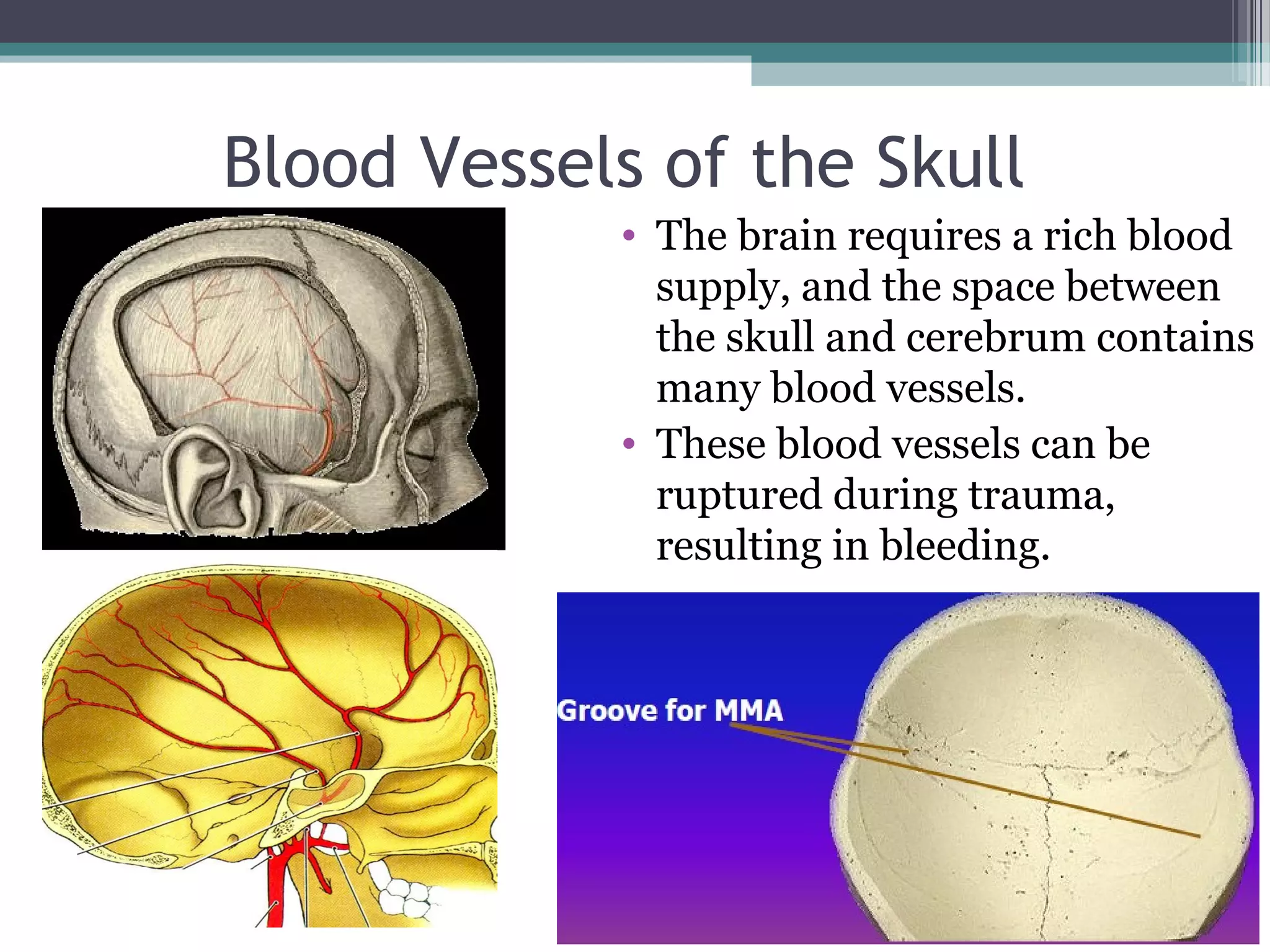
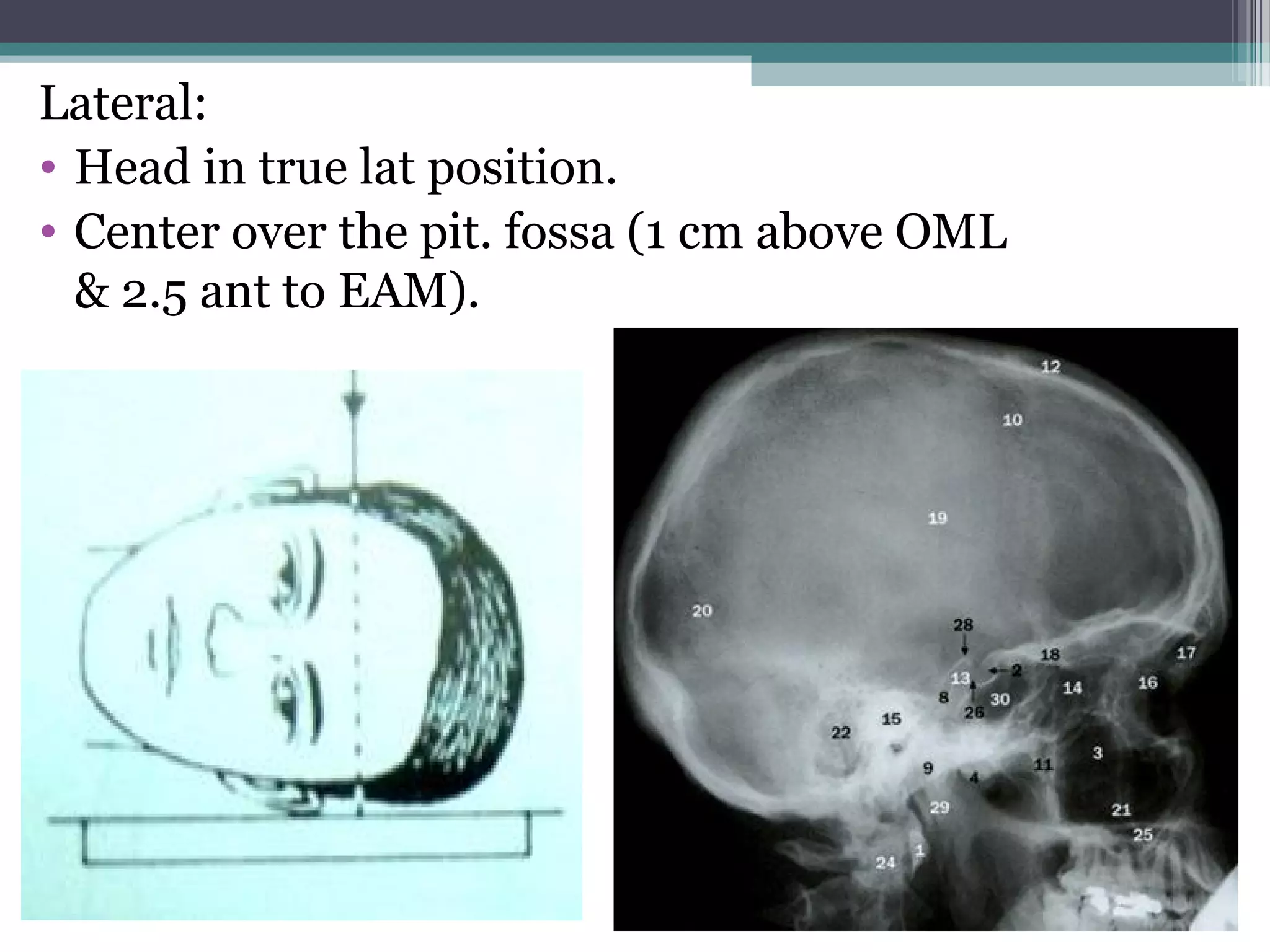
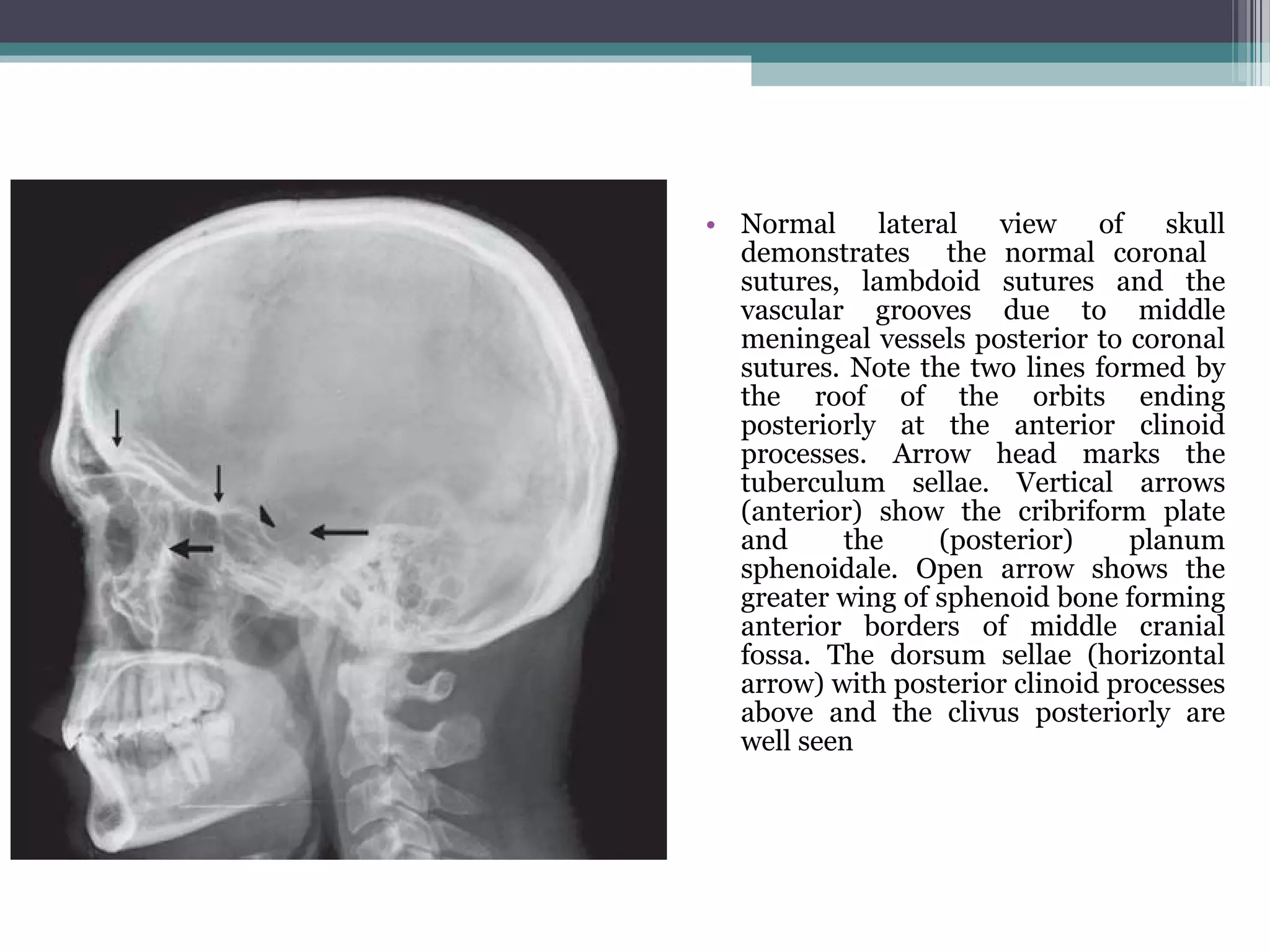
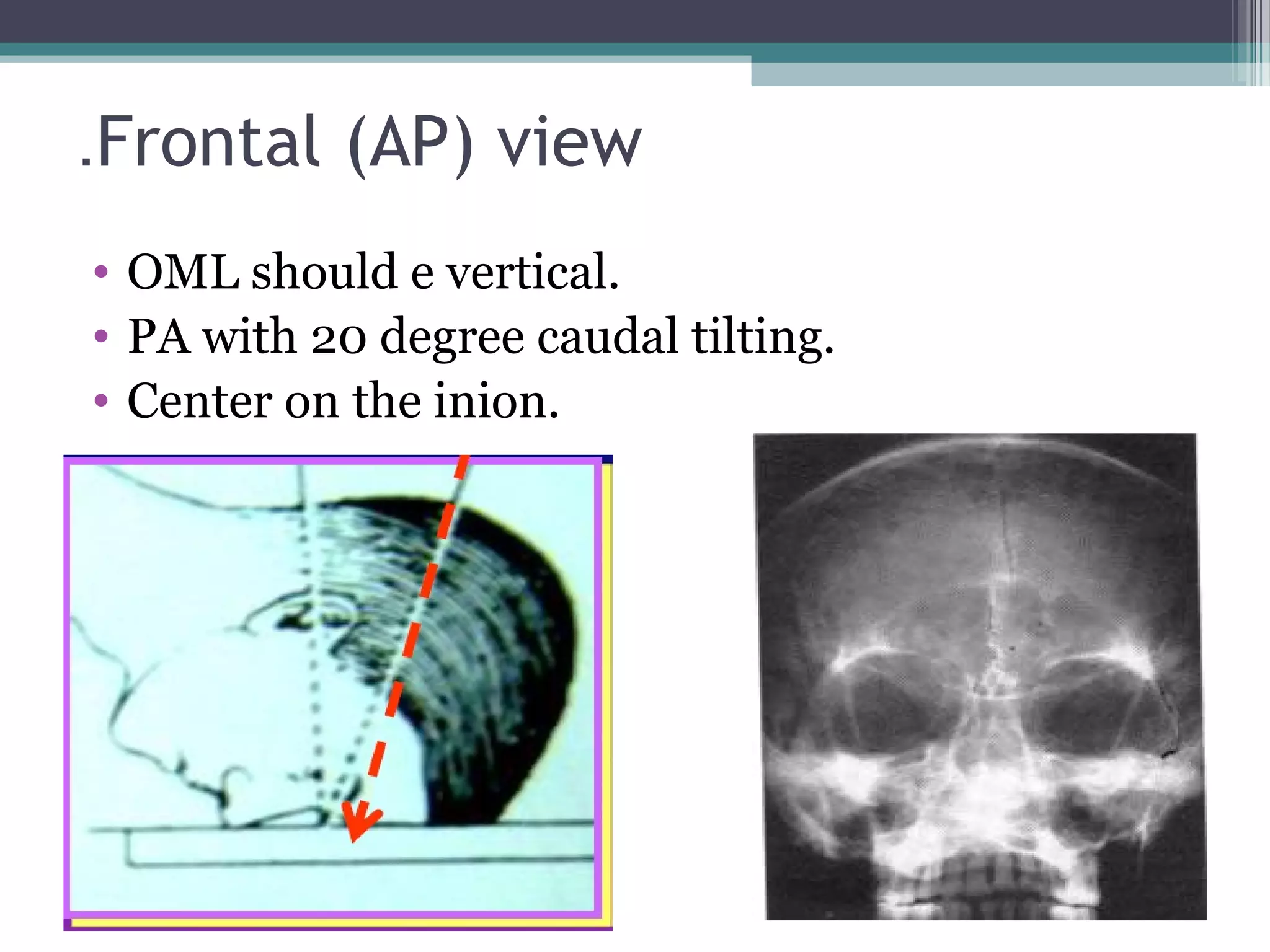
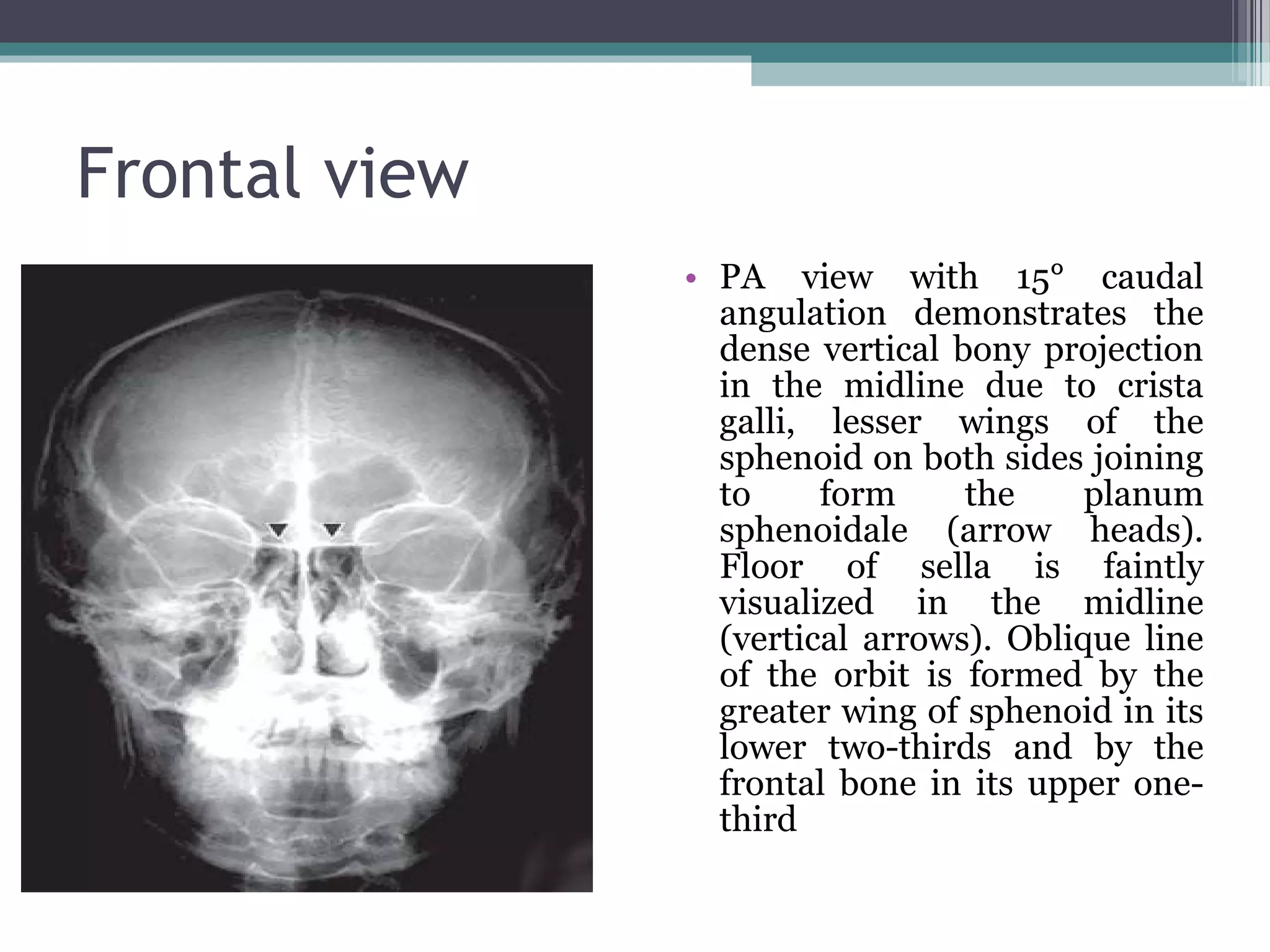
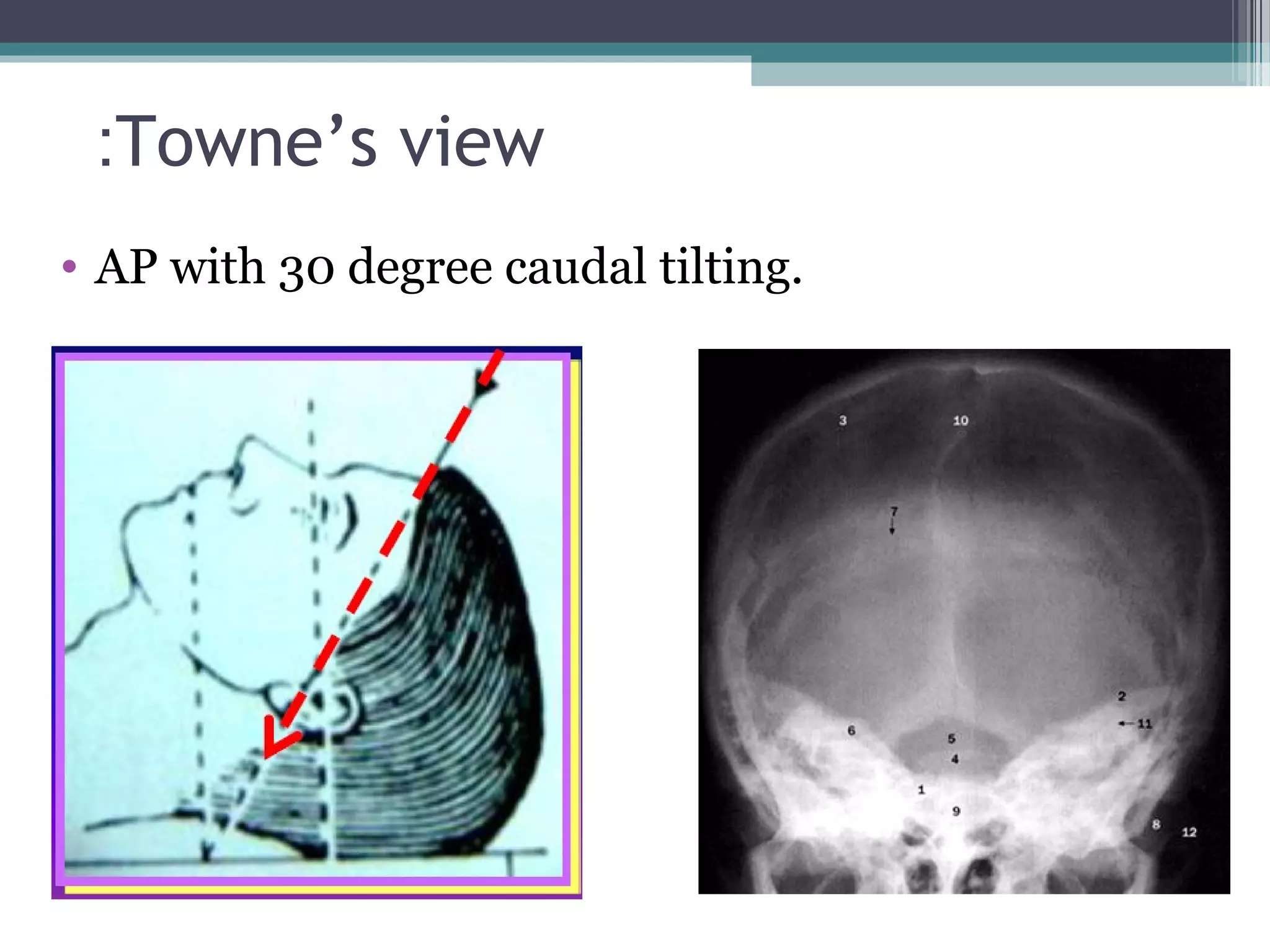
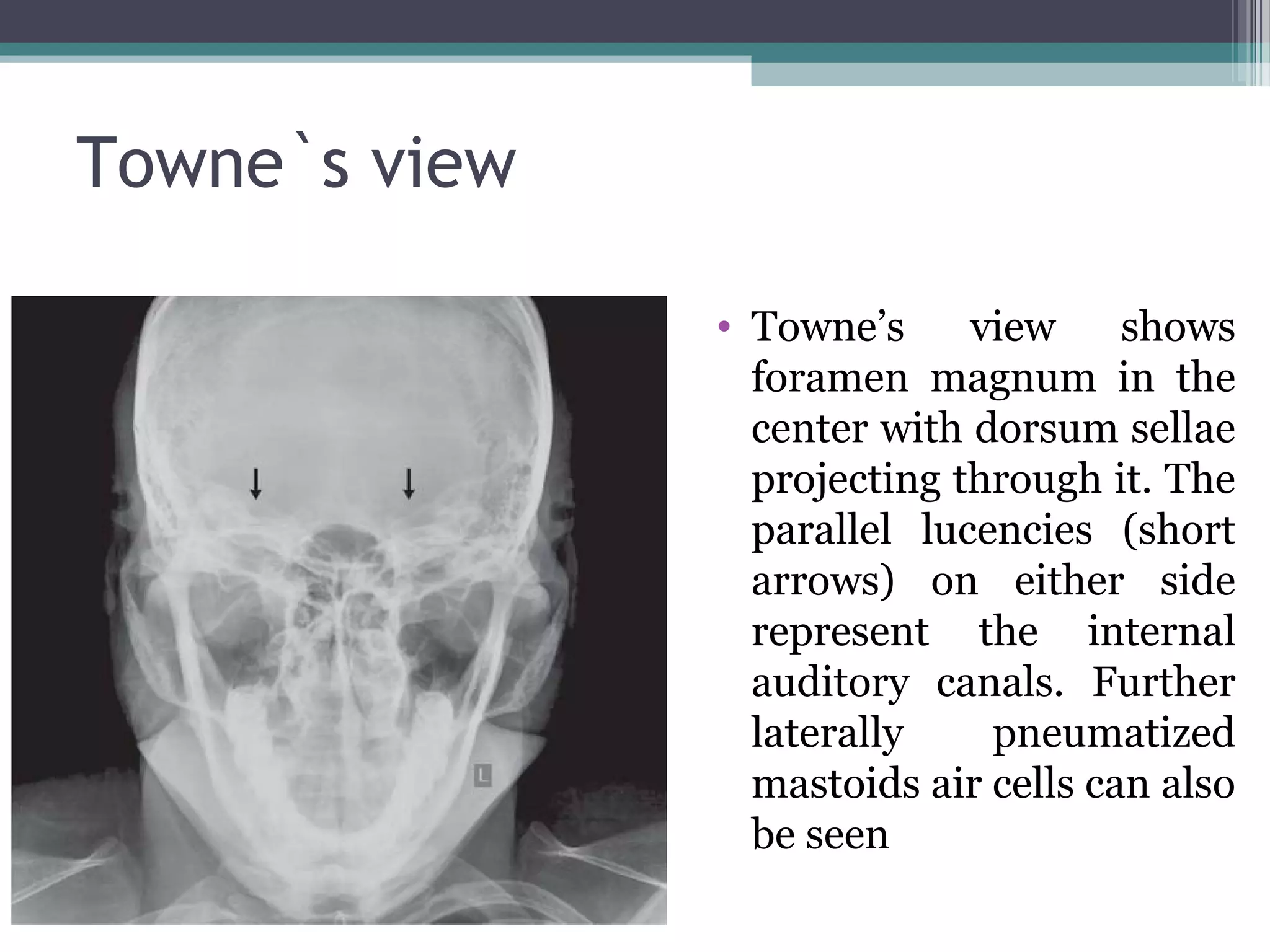
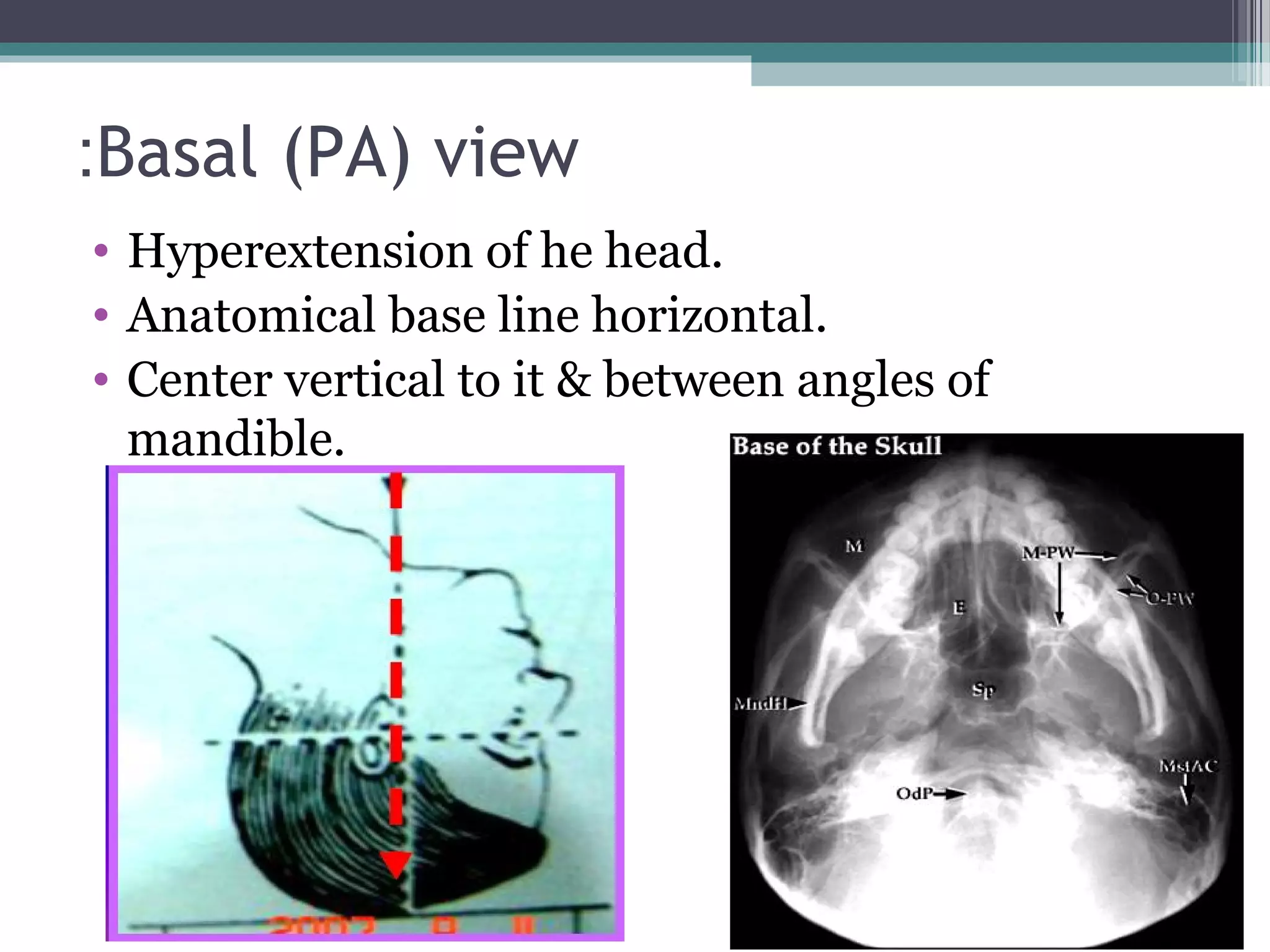
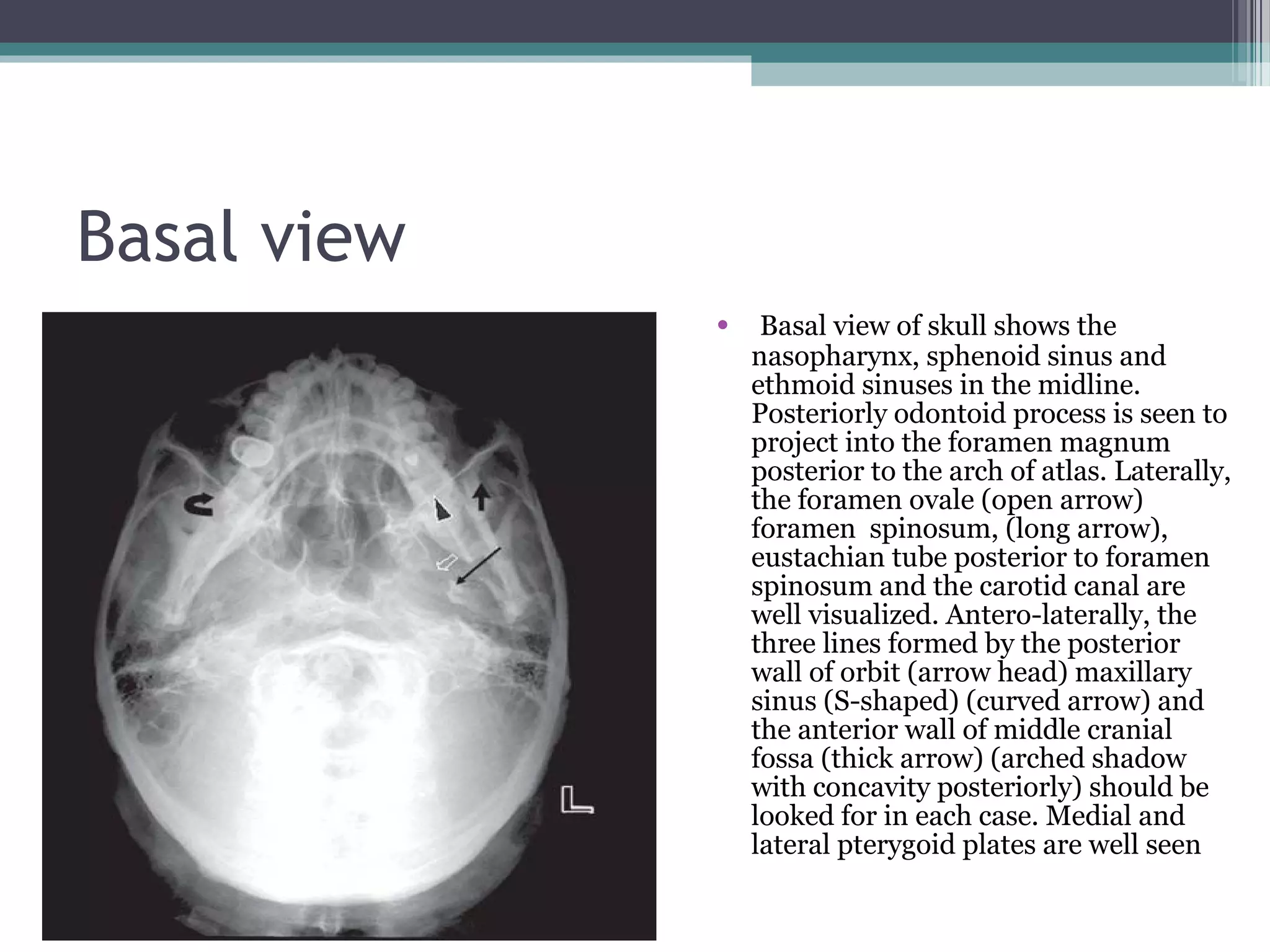
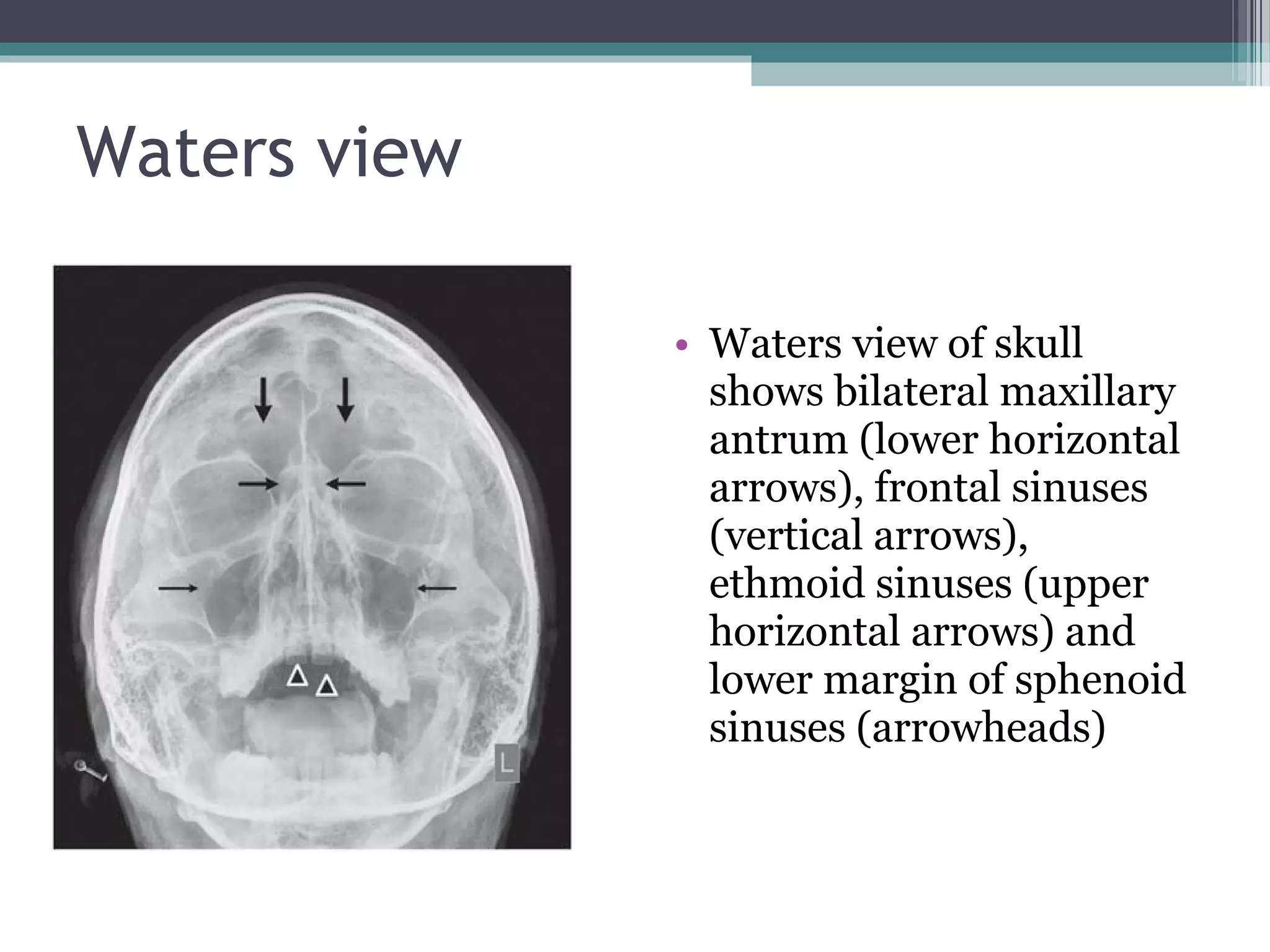
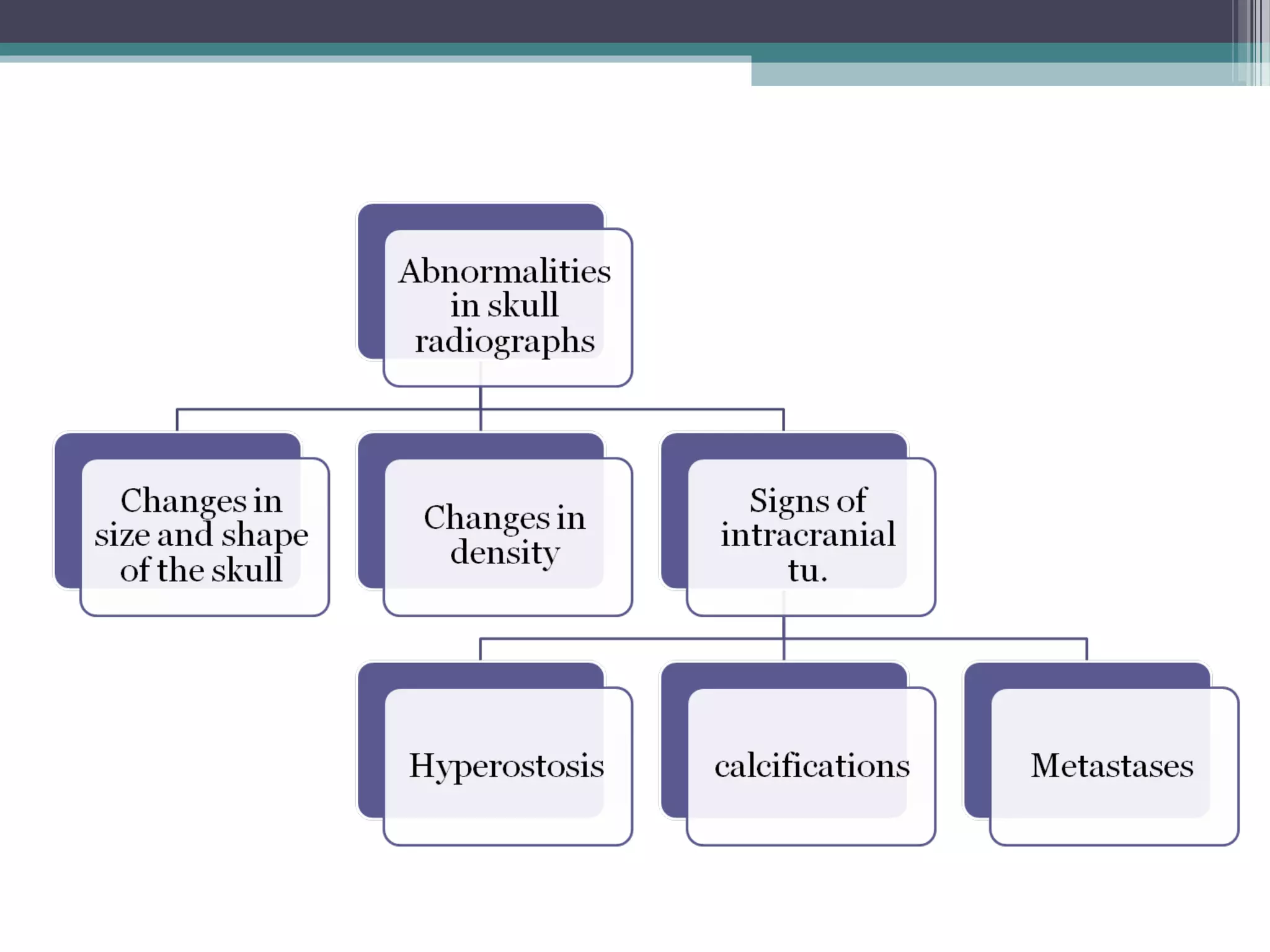
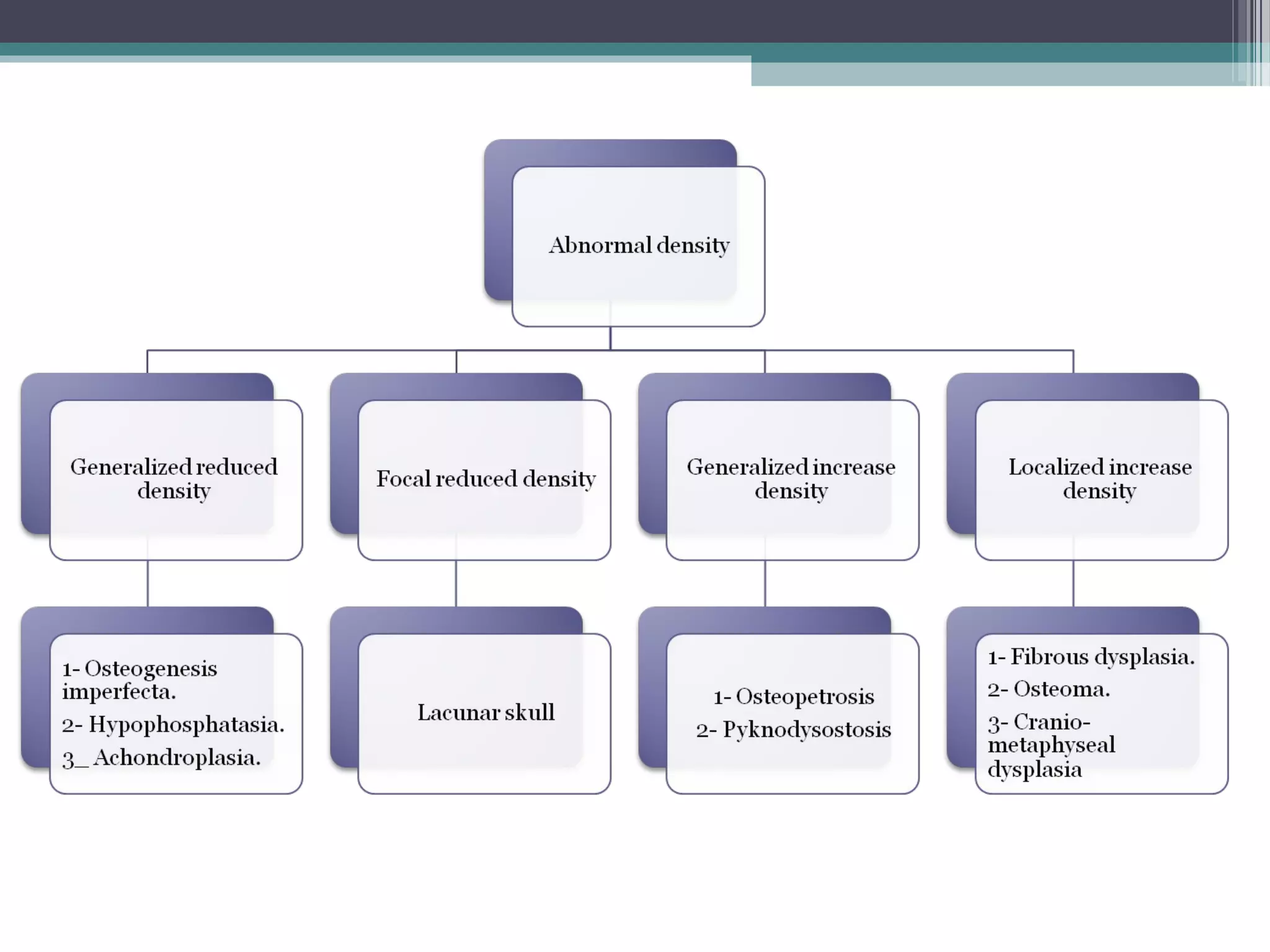
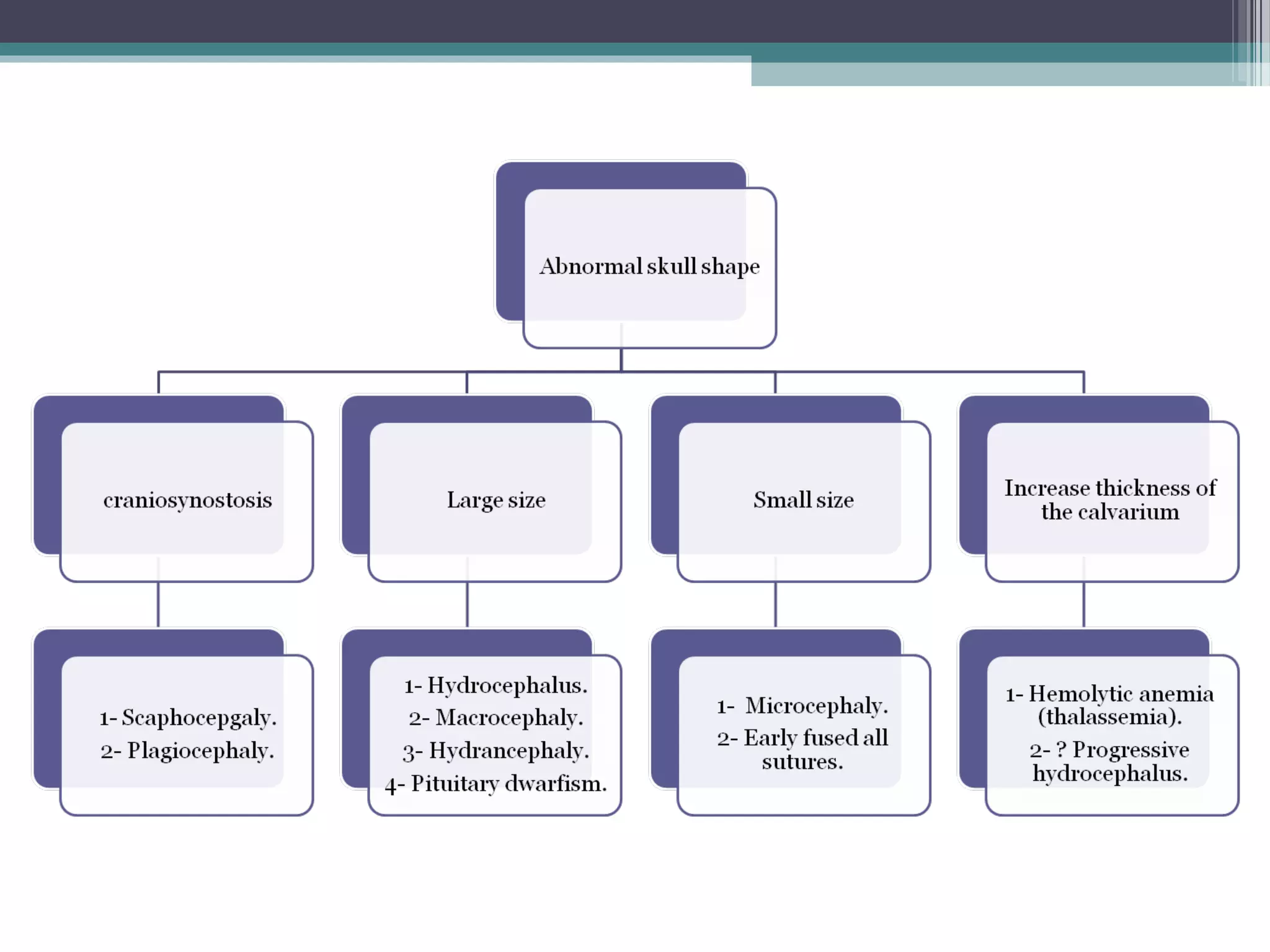
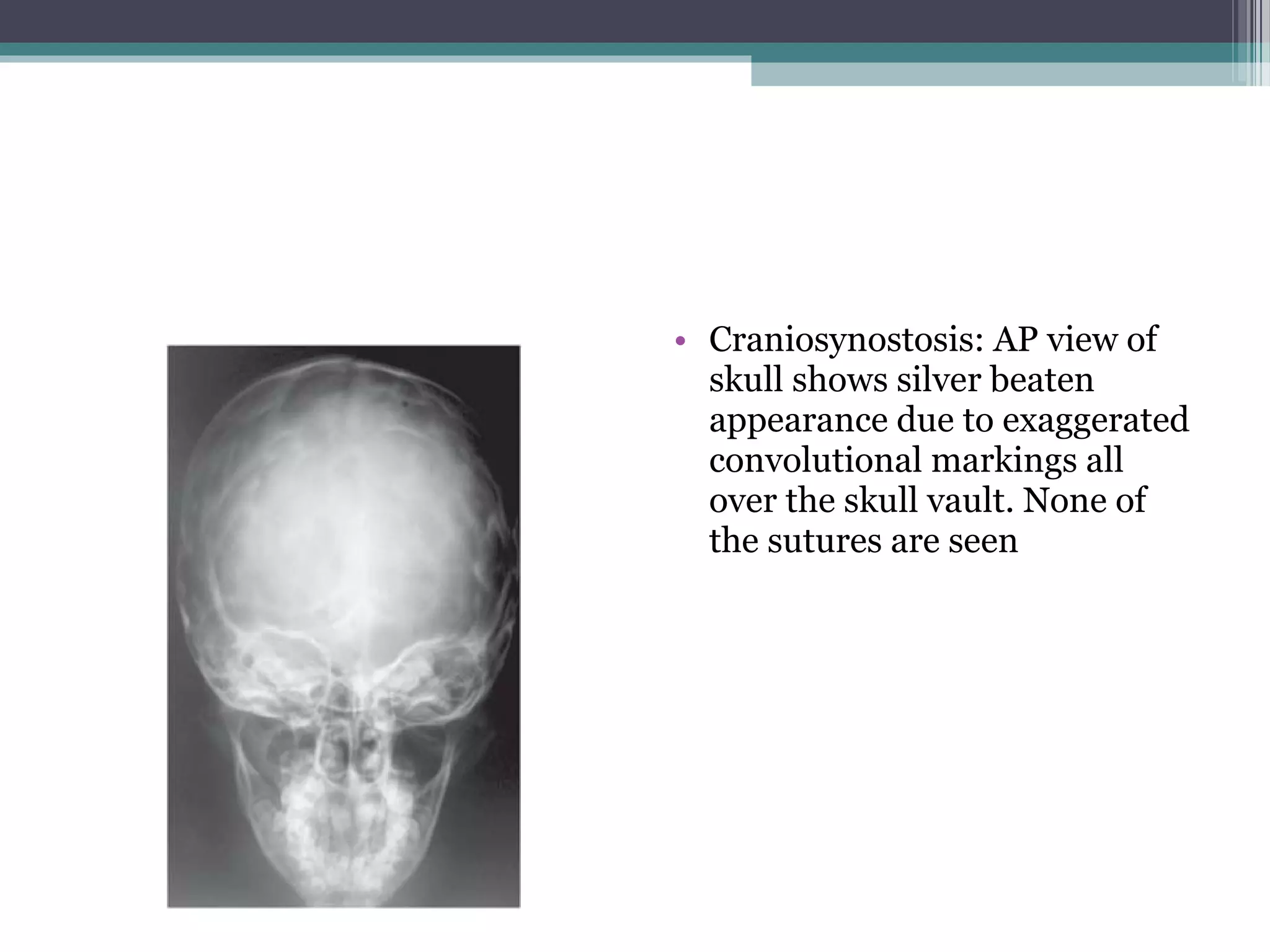
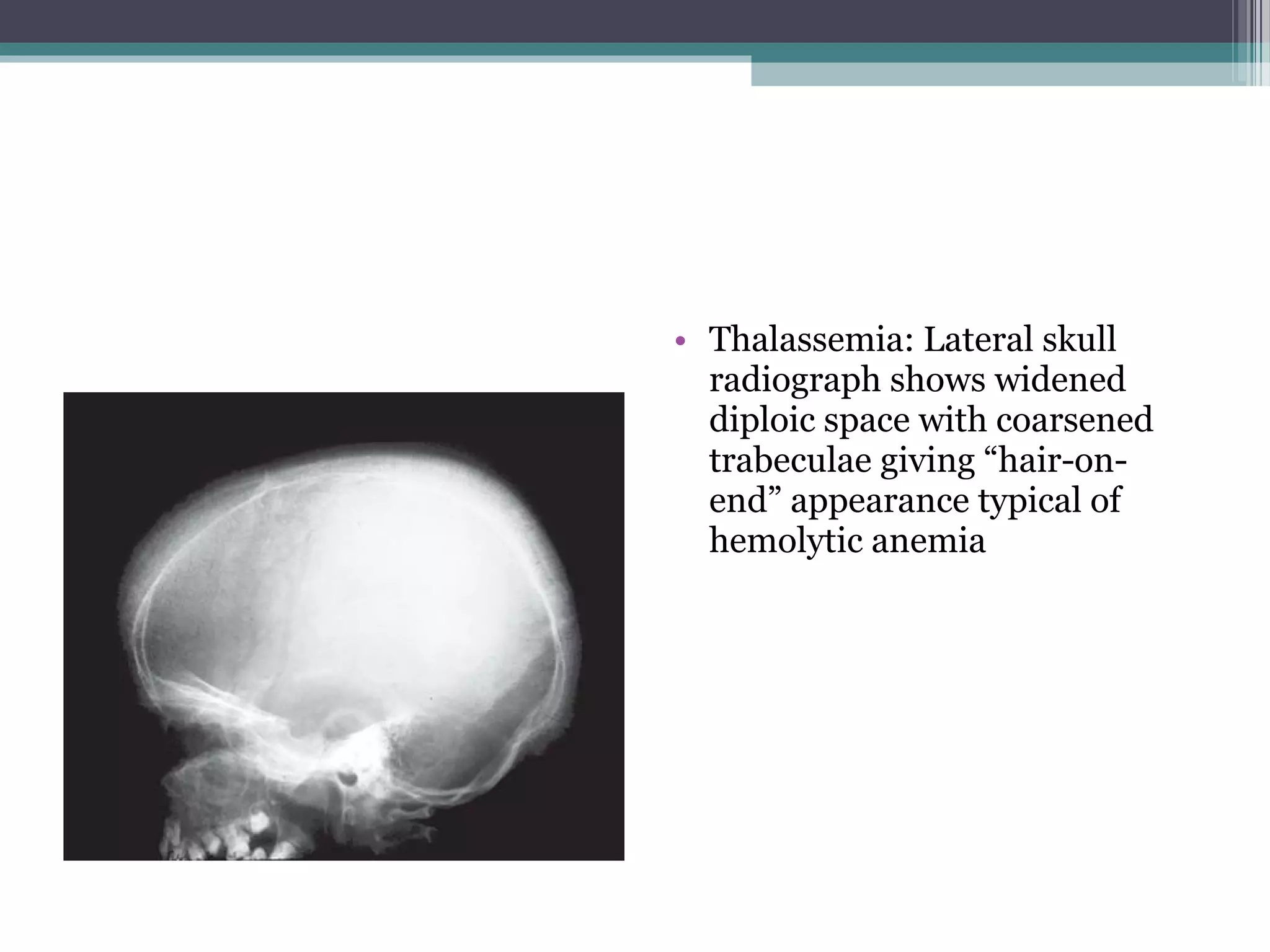
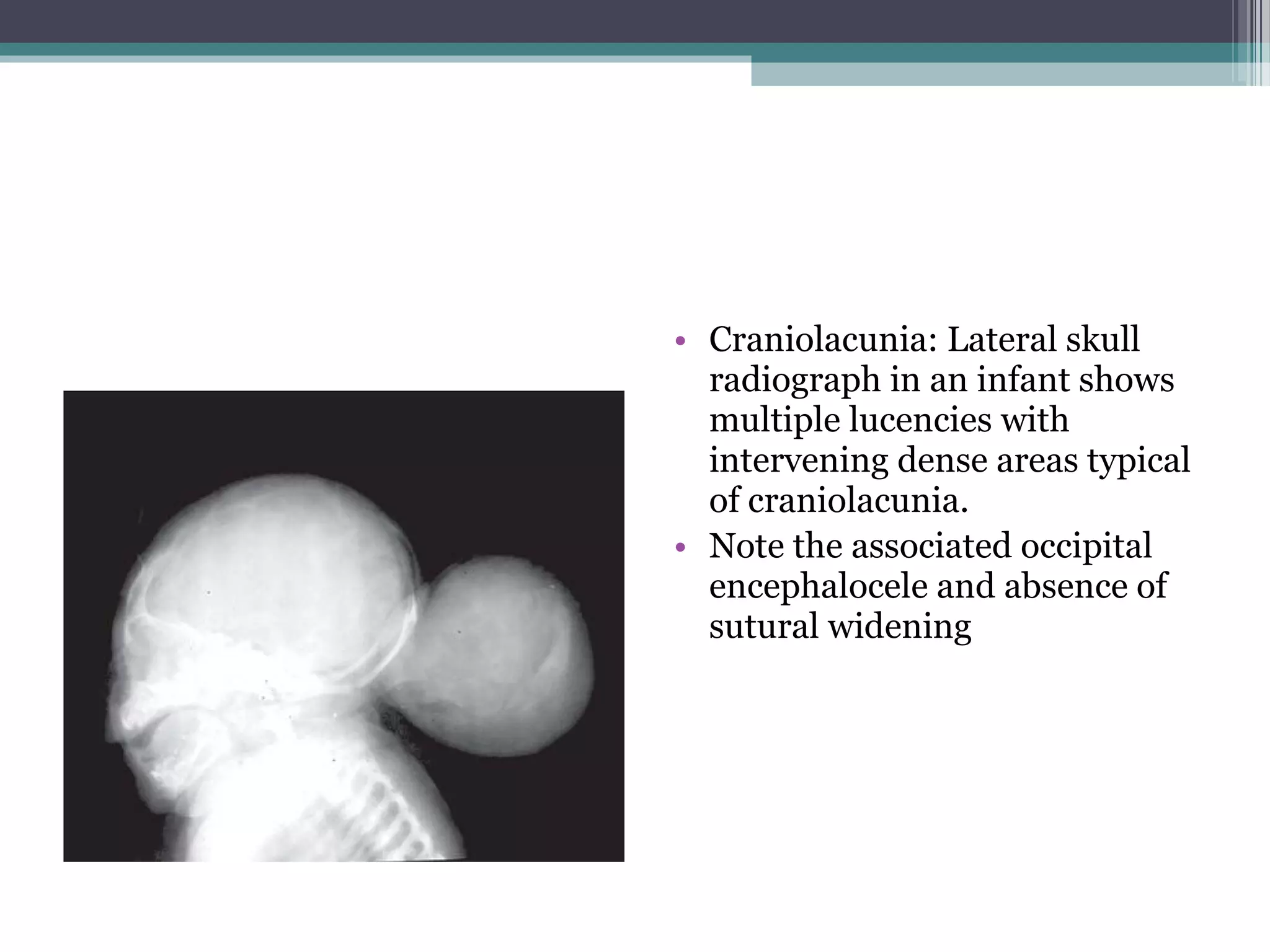
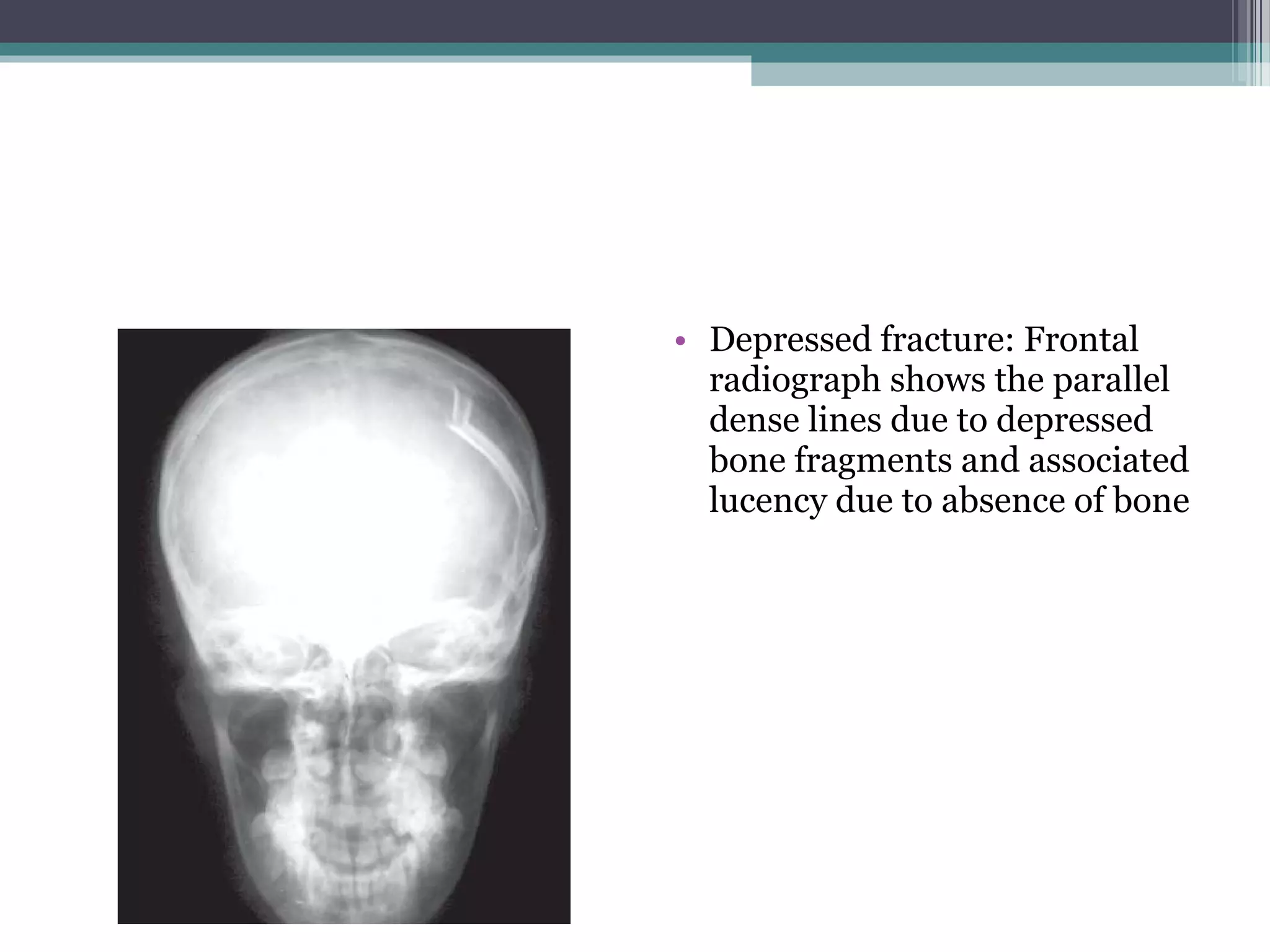
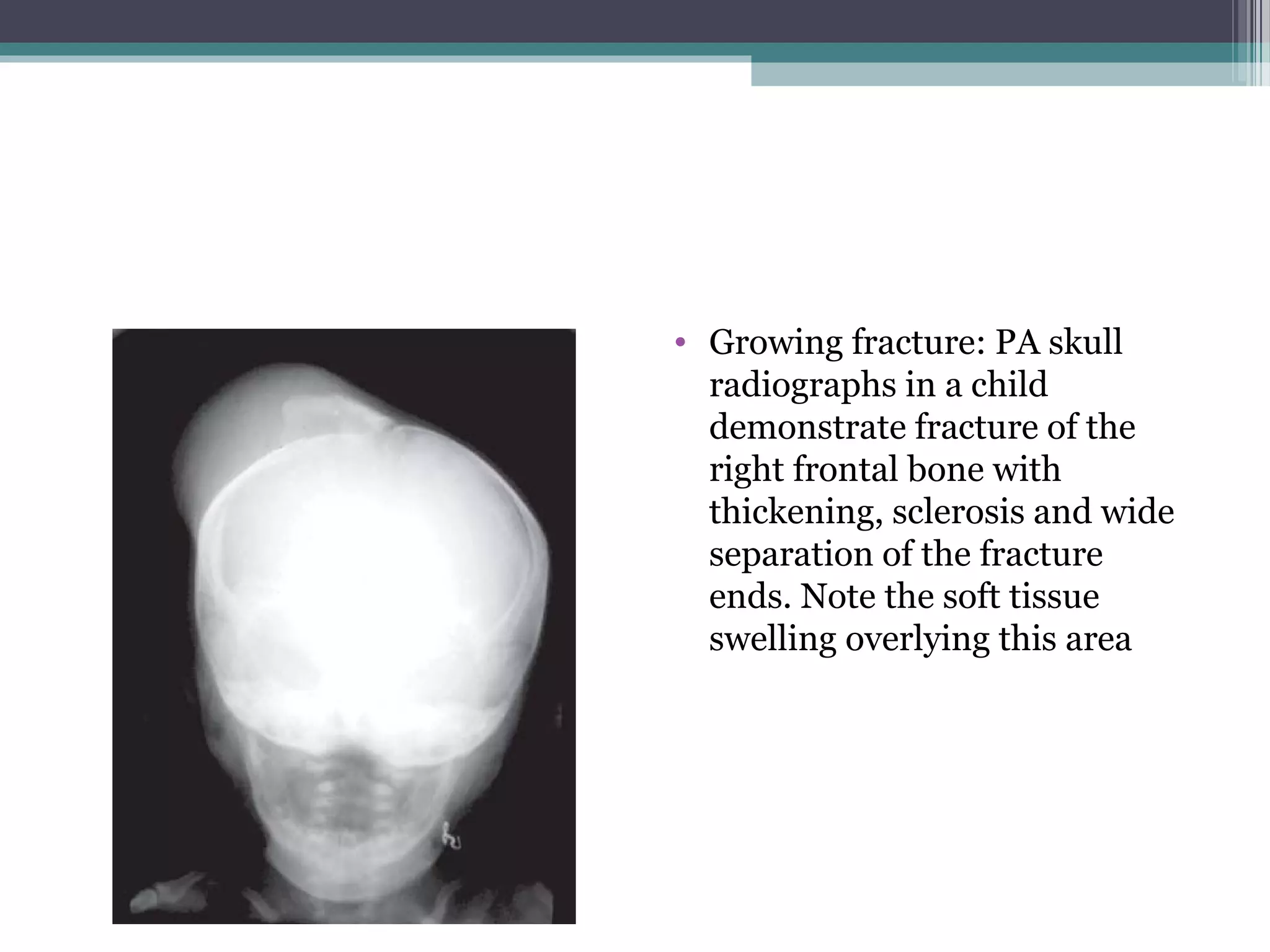
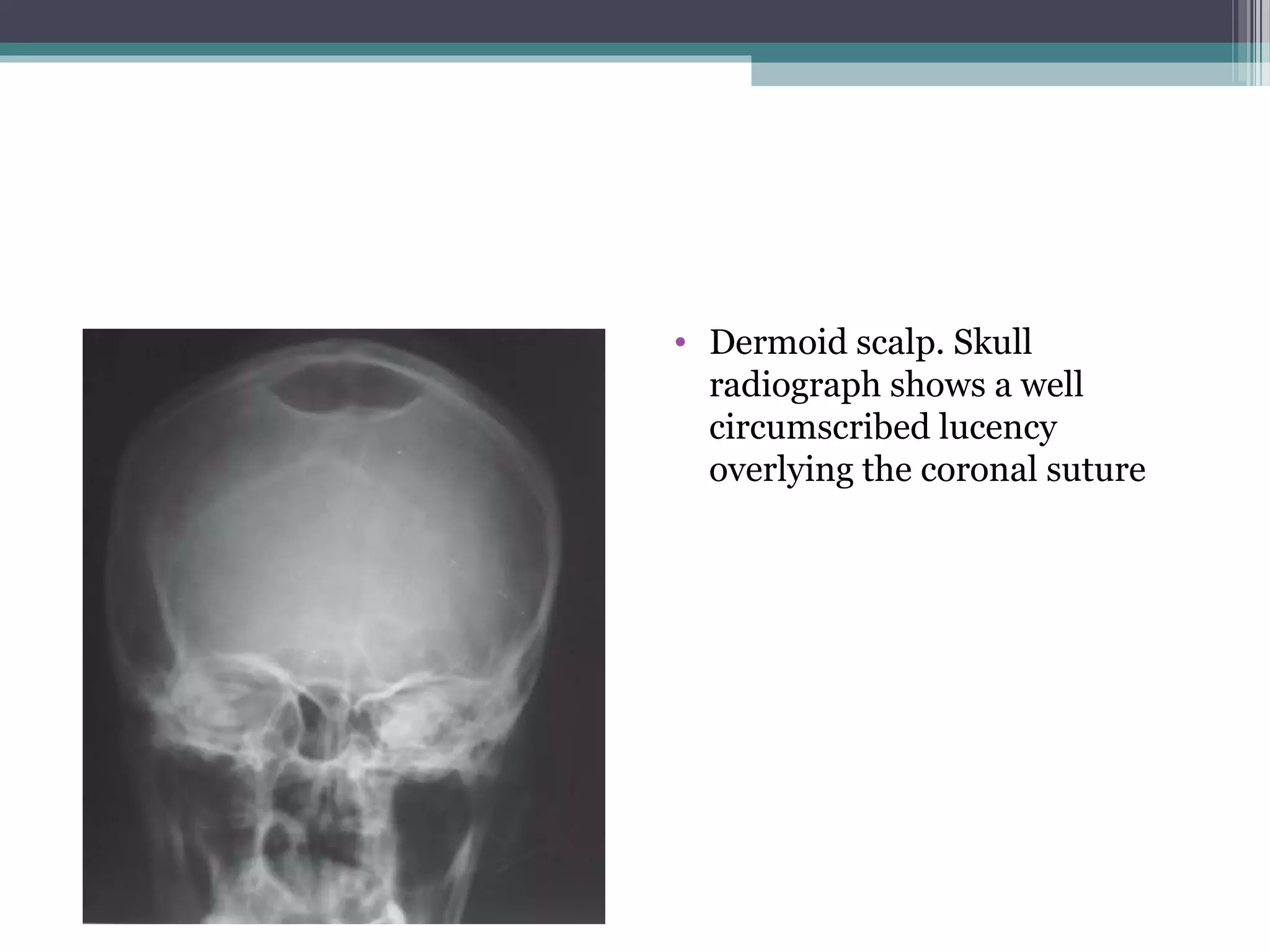
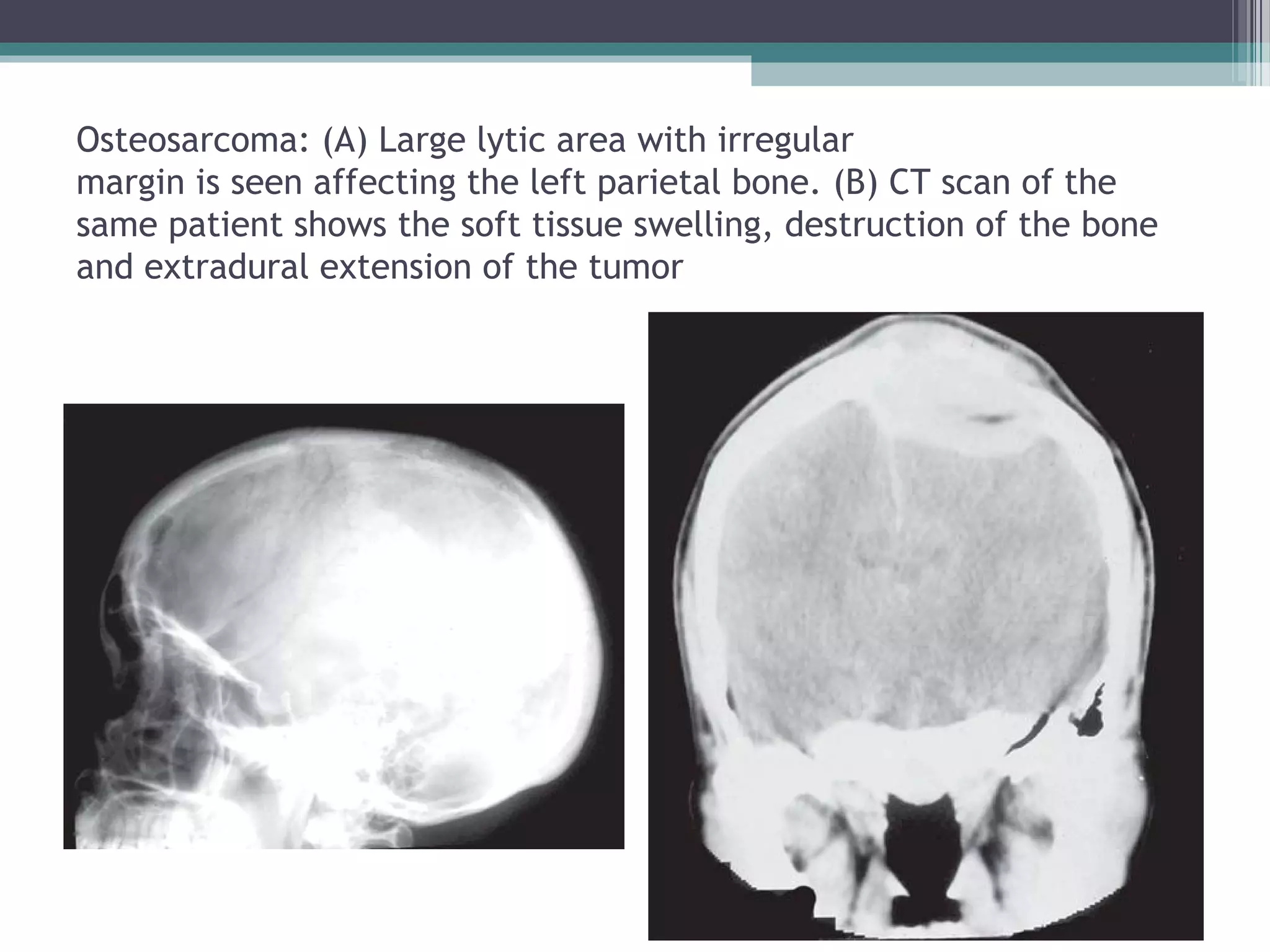
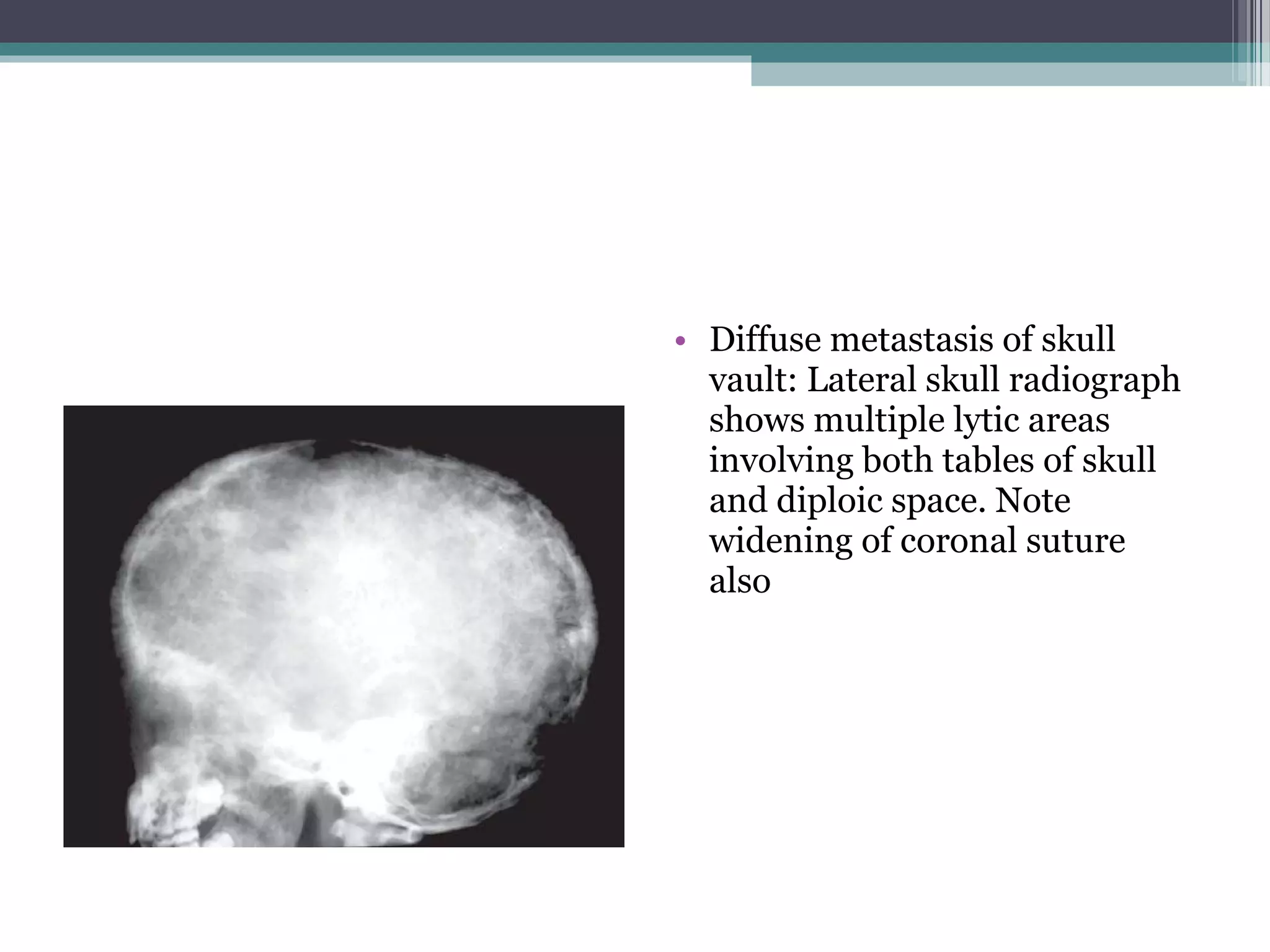
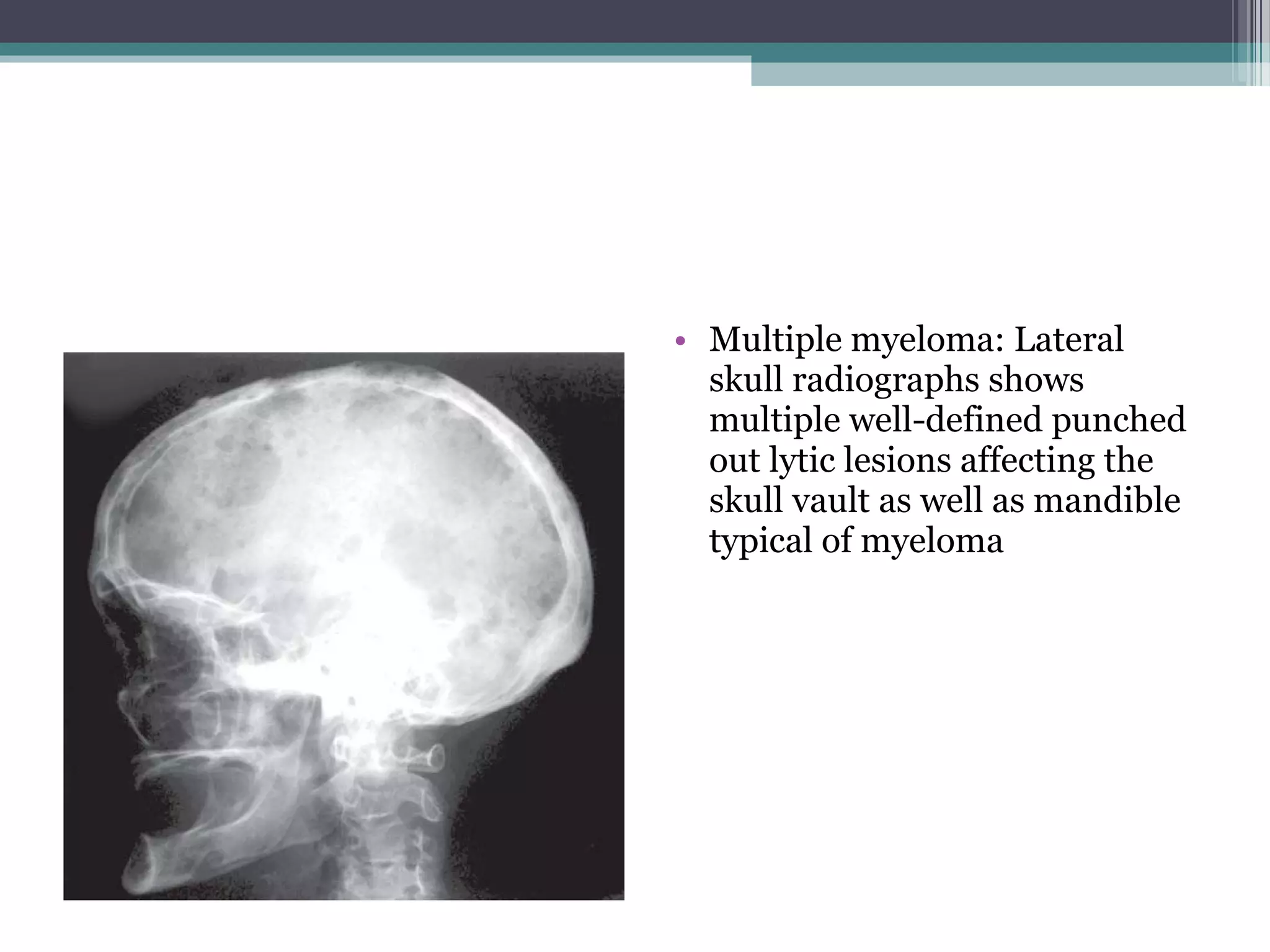
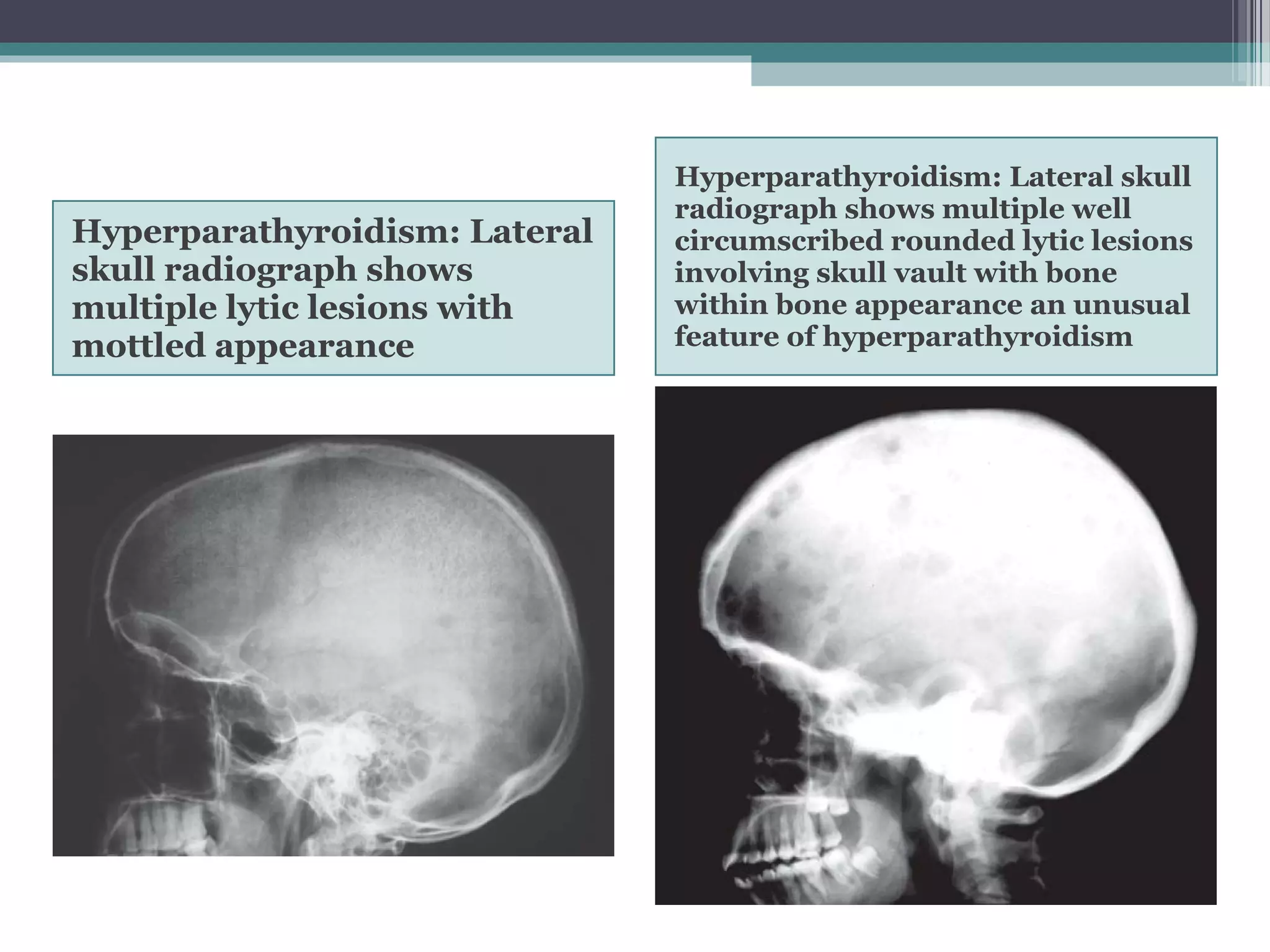
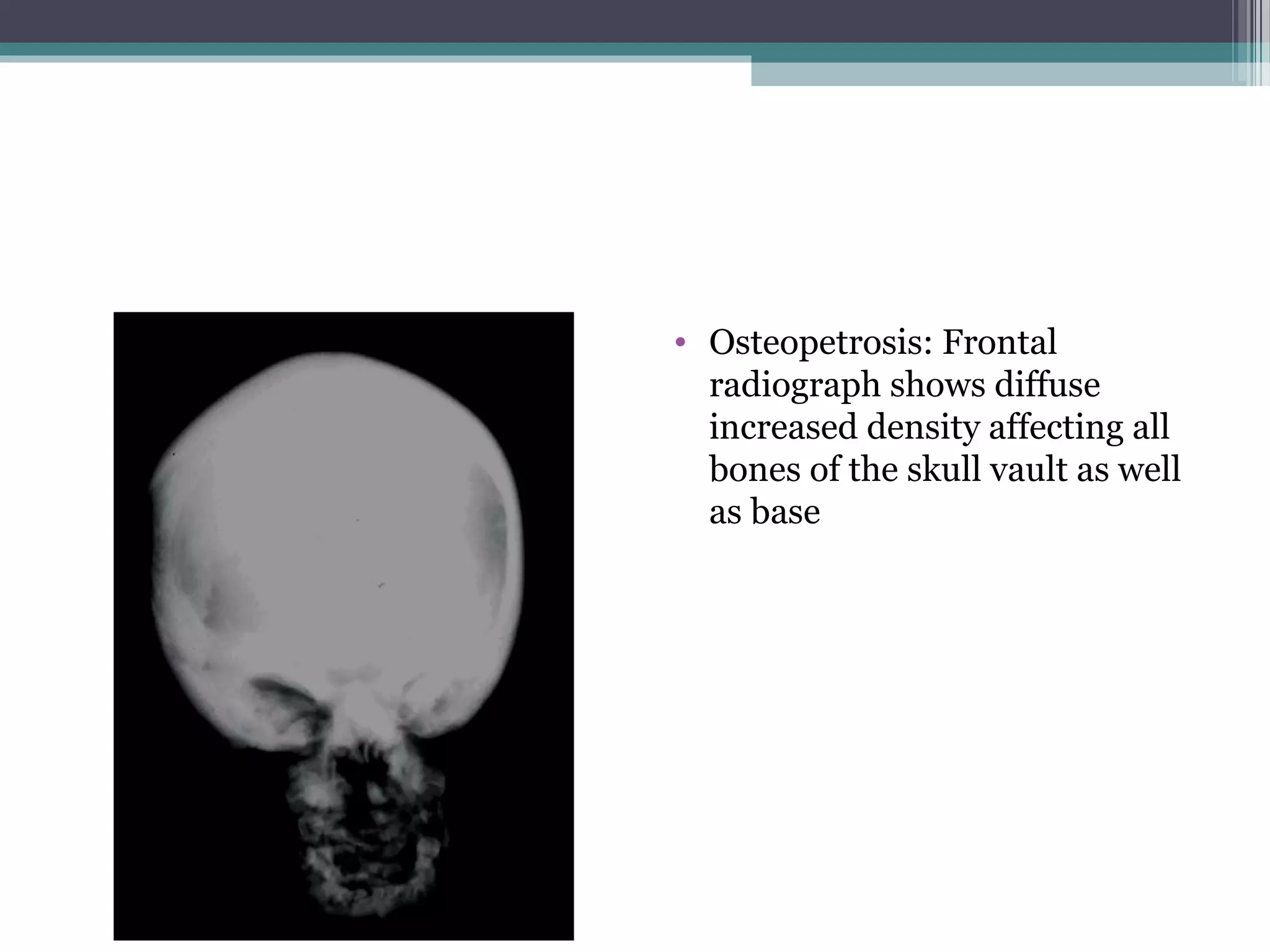
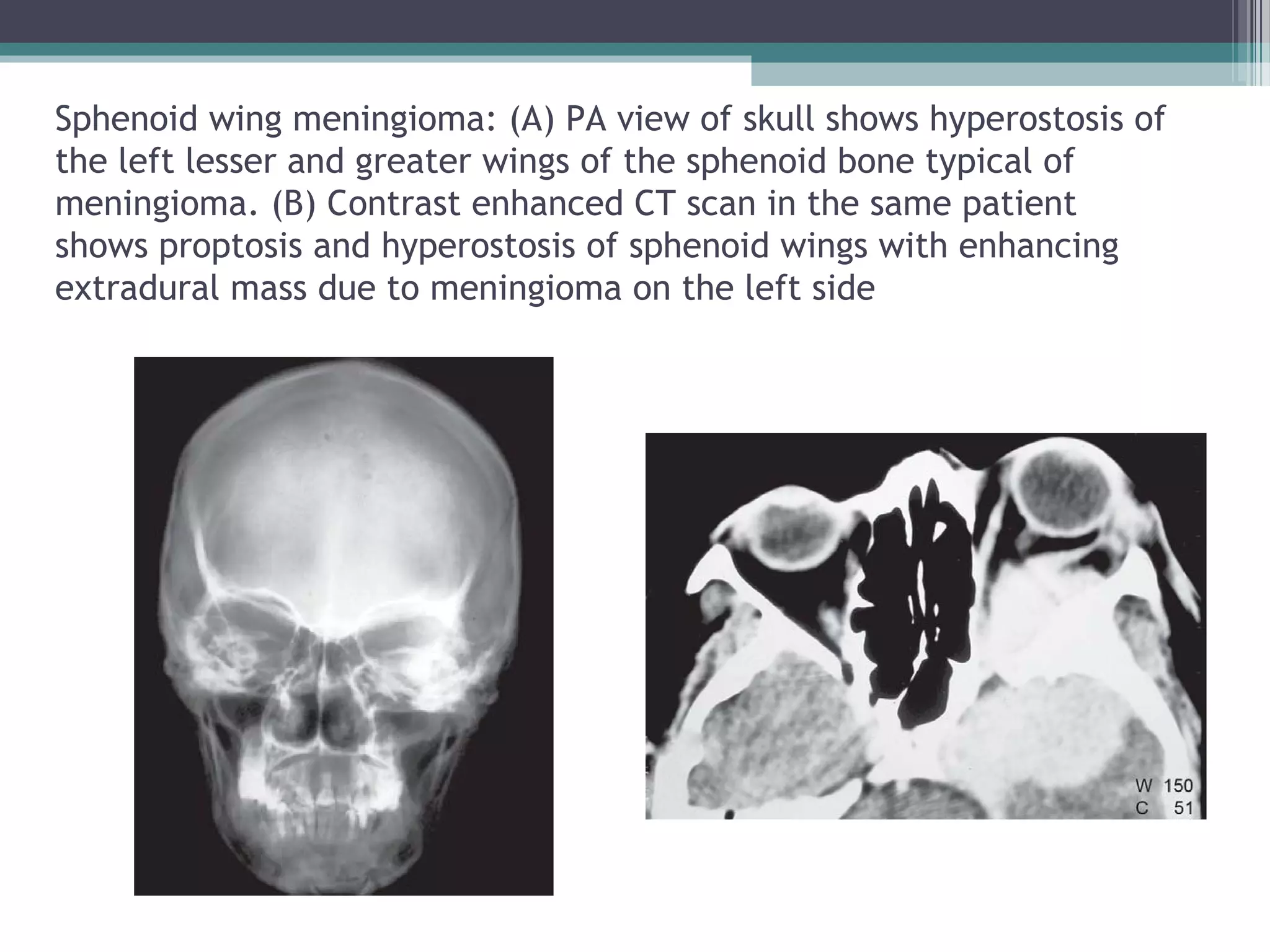
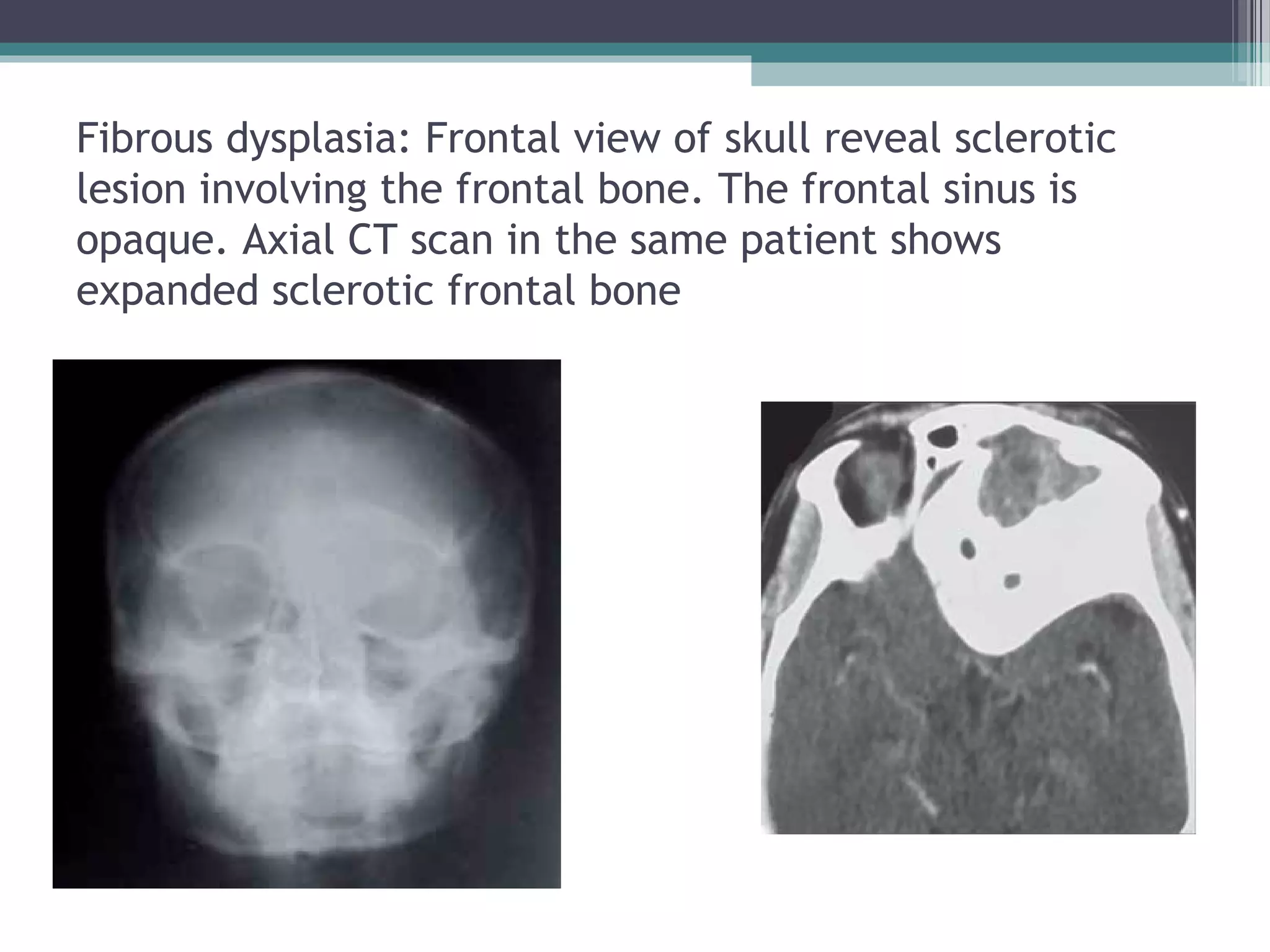
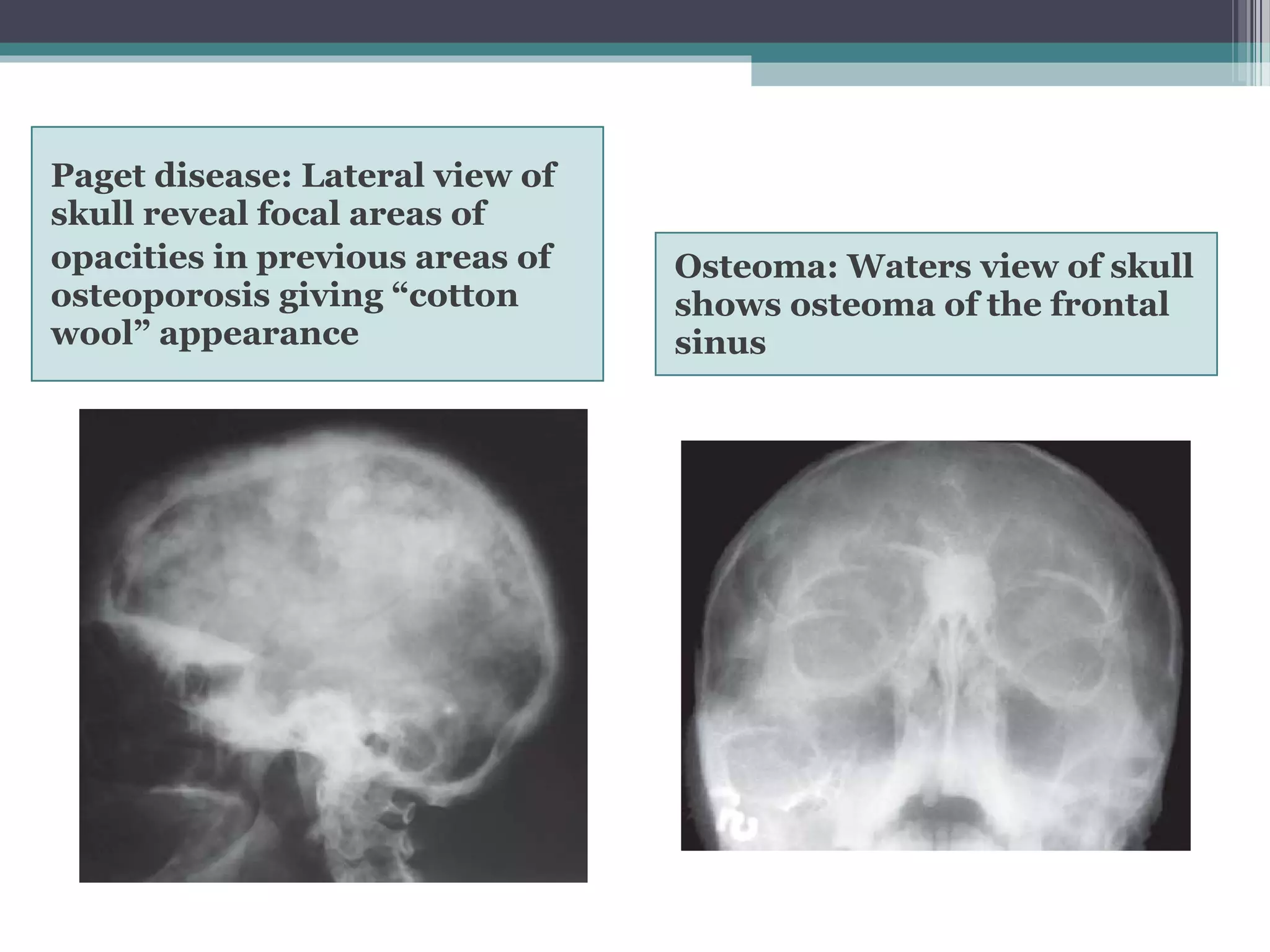
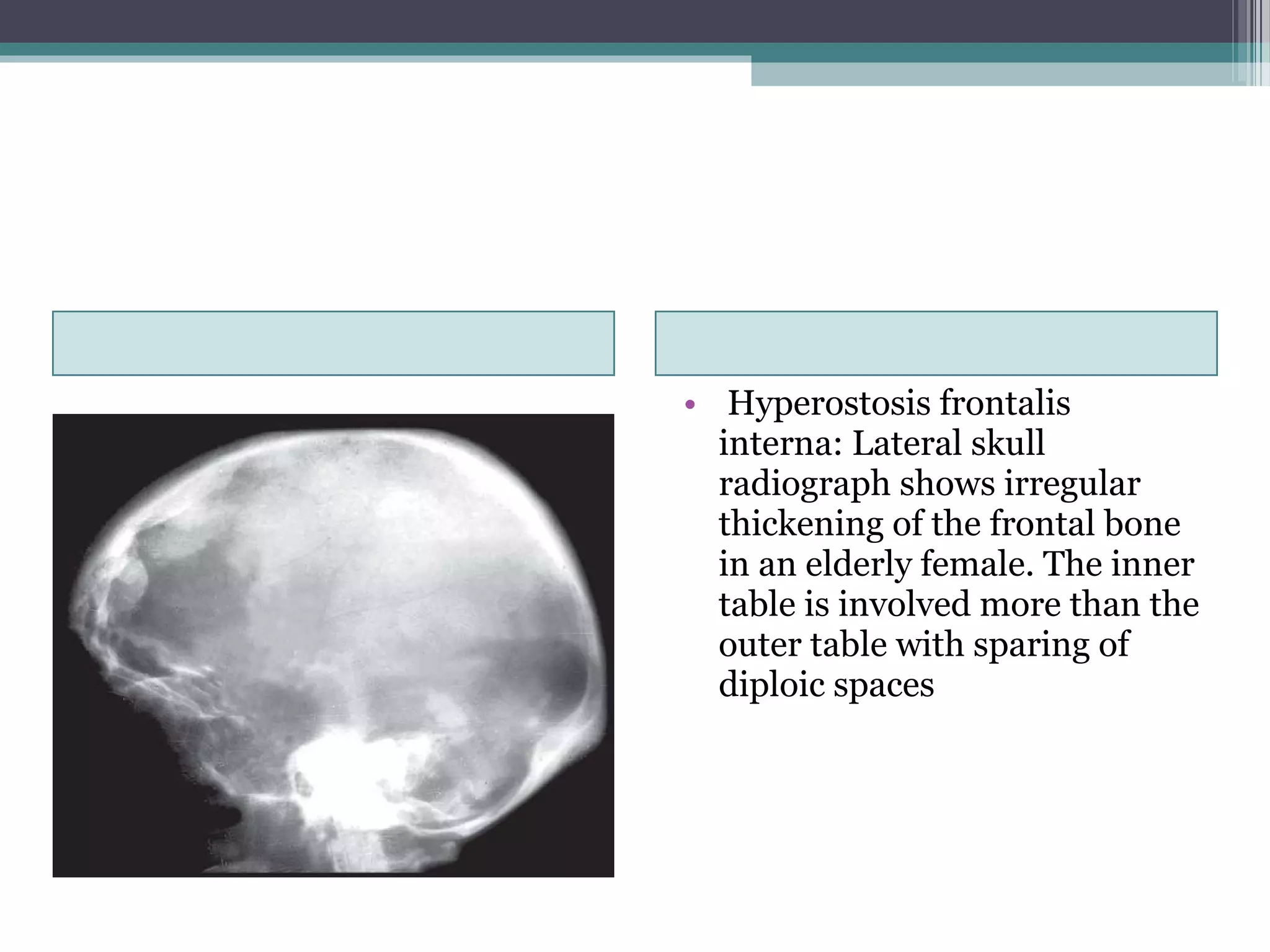
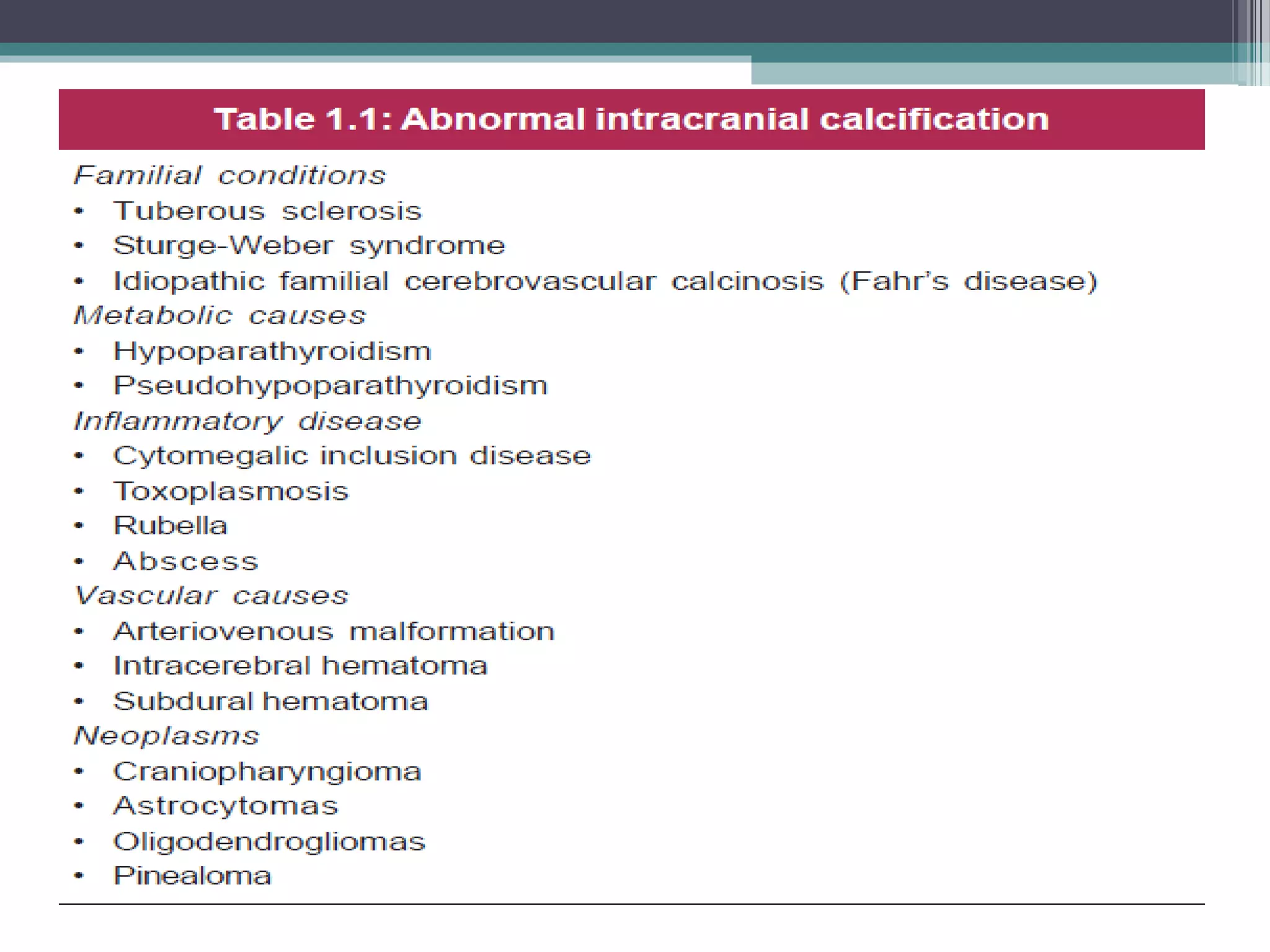
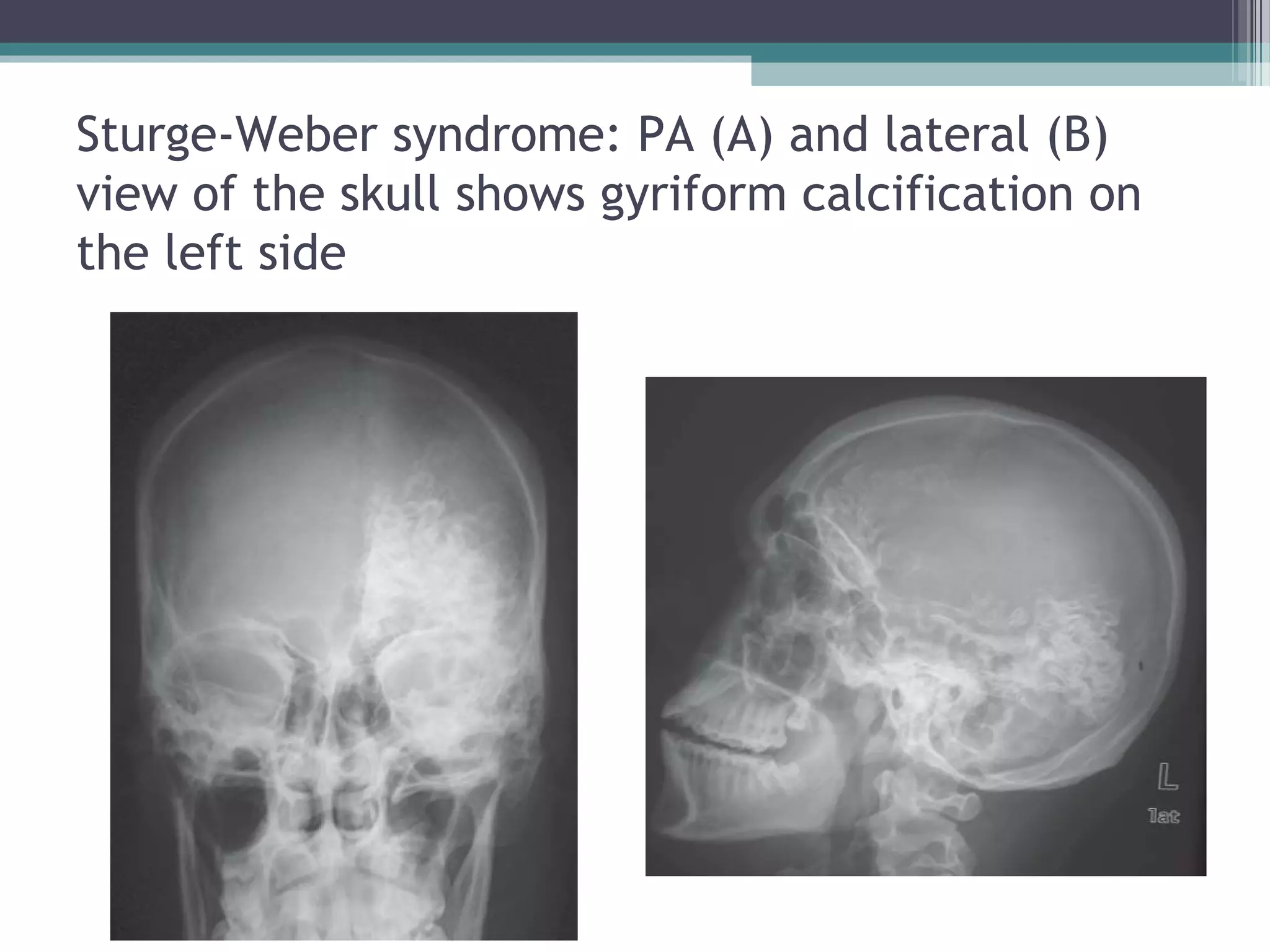
This document provides an overview of skull anatomy and evaluation of plain x-rays of the skull. It describes the bones that make up the skull and their sutures and fontanelles. It outlines the indications for skull x-rays including evaluation of skeletal dysplasias, infections, tumors and metabolic bone diseases. Common x-ray views of the skull are described including lateral, frontal, Towne's and basal views. Abnormal findings on skull x-rays can include changes in density, contour, intracranial volume, calcifications and lucent defects. Specific conditions like craniosynostosis, anemia and fractures are discussed.