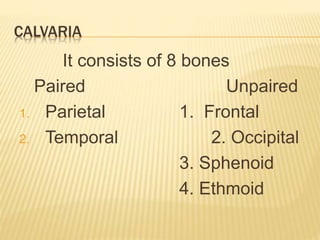
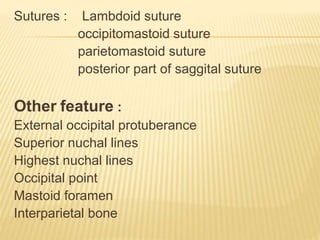
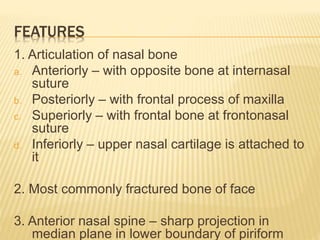
The skull consists of 22 bones that protect and house the brain. It can be divided into the calvaria and facial skeleton. The calvaria includes the frontal, parietal, occipital, sphenoid, and ethmoid bones. The facial skeleton includes the maxilla, zygomatic, nasal, lacrimal, palatine, vomer, and mandible bones. Sutures connect the bones of the skull. The skull changes in shape and size from infancy through adulthood due to growth and development. Measurements of the skull can provide information about sex and ancestral origin.