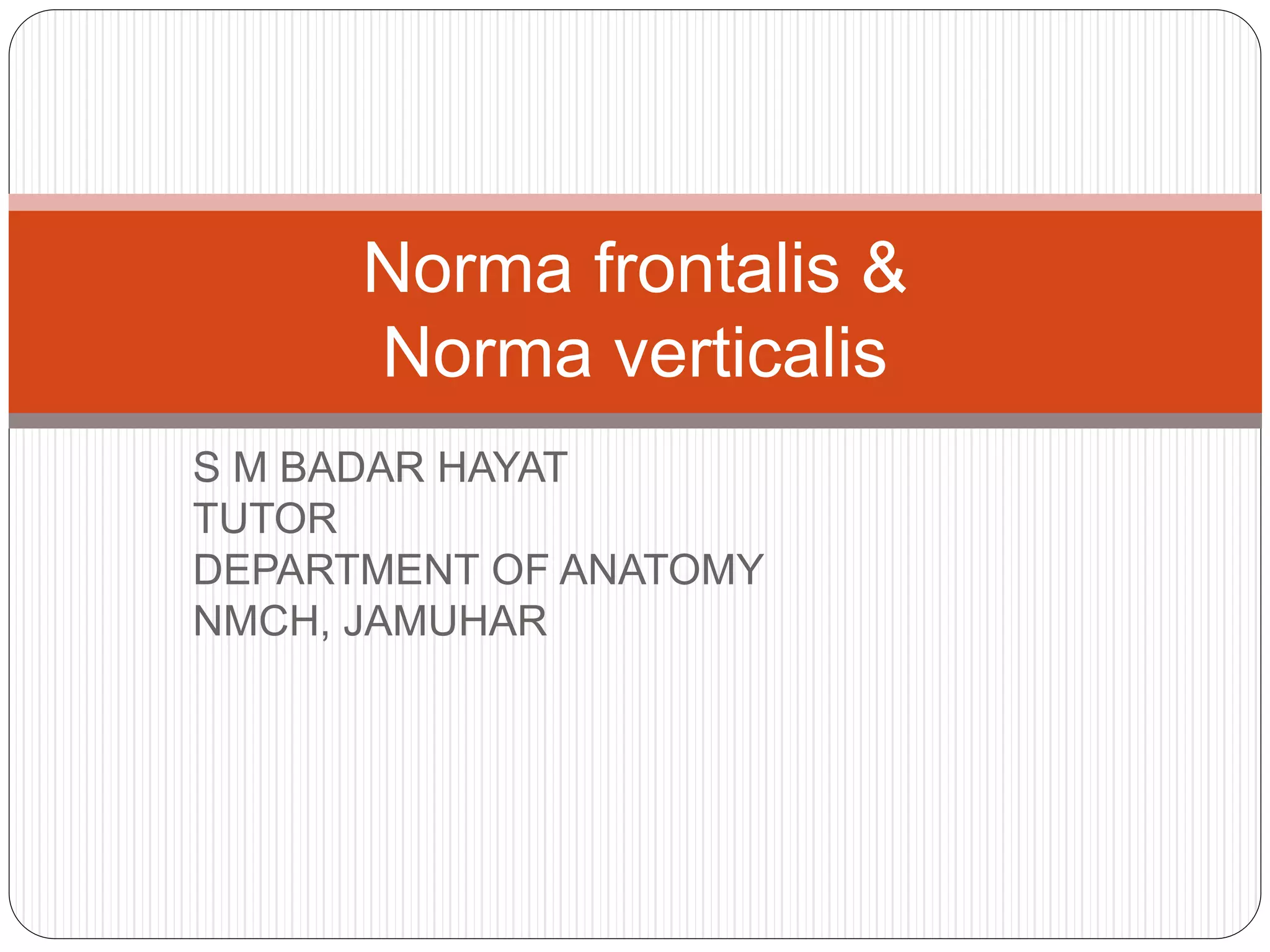
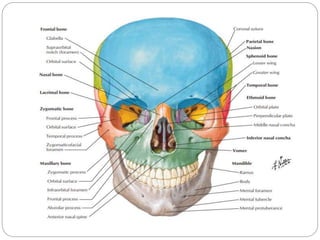
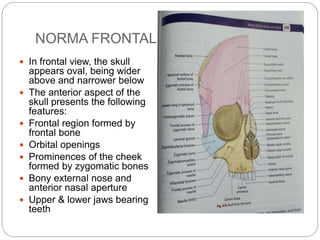
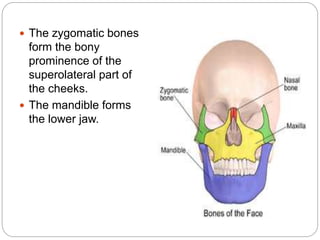
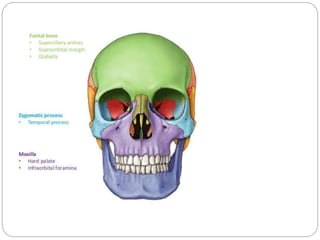
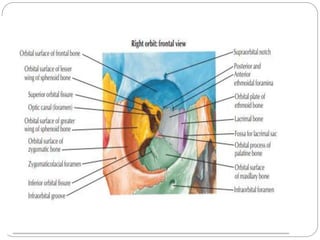
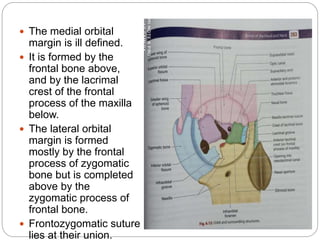
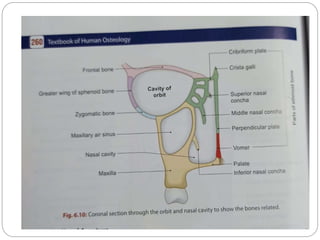
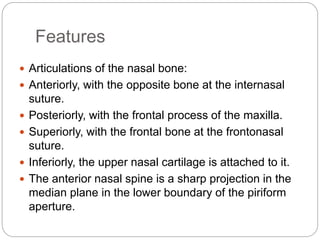
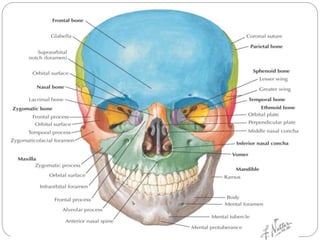
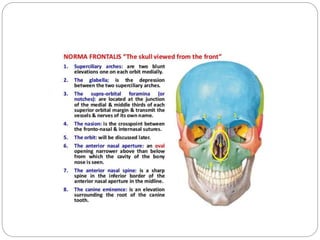
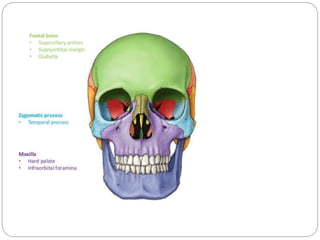
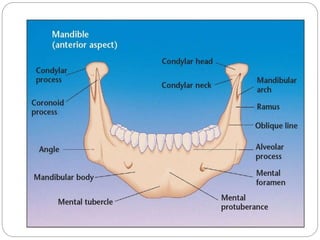
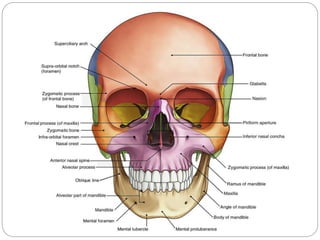
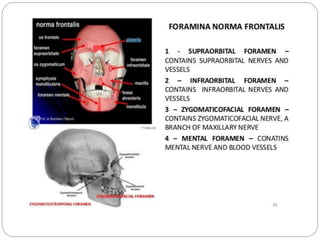
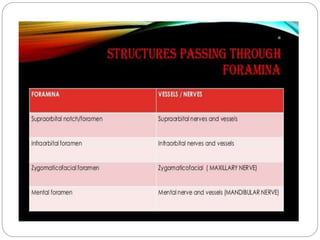
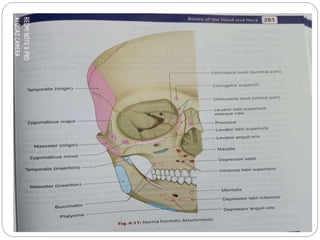
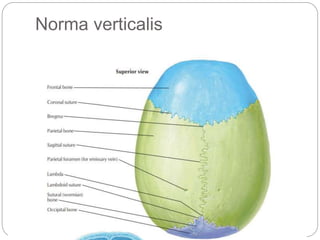
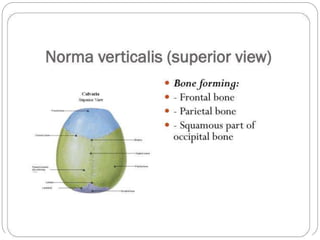
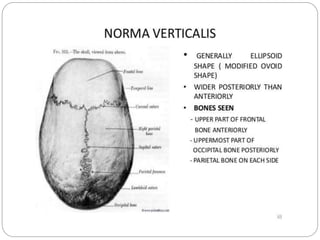
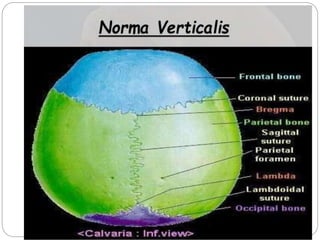
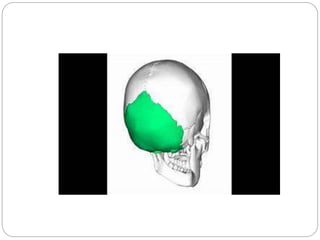
The document describes the key features of the front and top views of the human skull. In the front view (norma frontalis), it outlines the bones that form the forehead, eye sockets, nose, cheeks, and jaws. It also details features like the supraorbital arch. The top view (norma verticalis) presents the oval shape of the skull and bones like the frontal and parietal that form its framework. It lists important sutures like the coronal, sagittal, and lambdoid sutures and named landmarks like bregma and lambda.