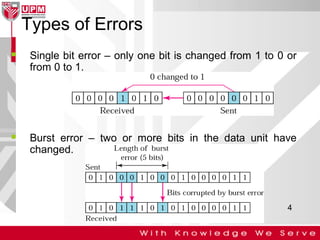
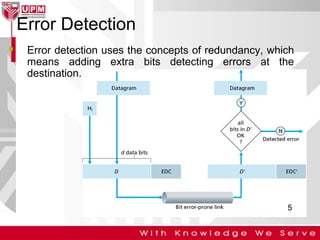
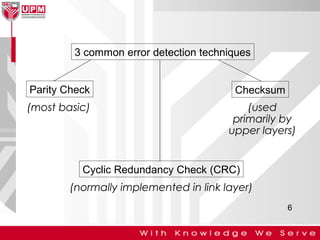
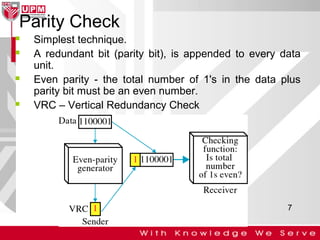
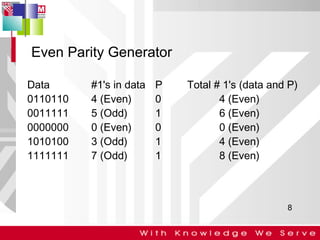
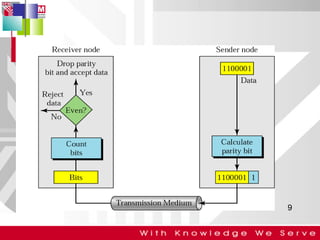
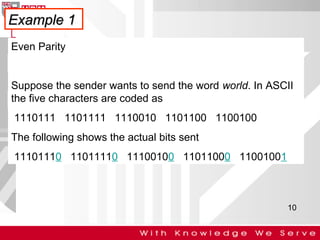
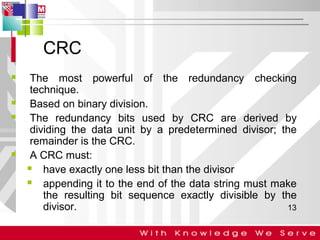
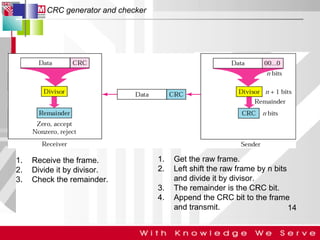
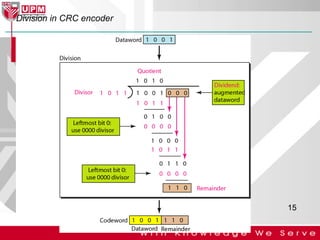
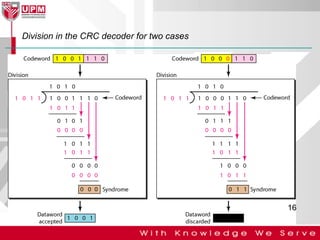
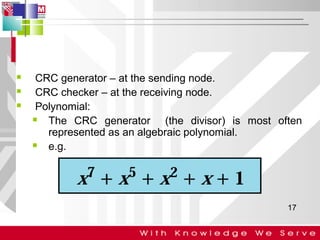
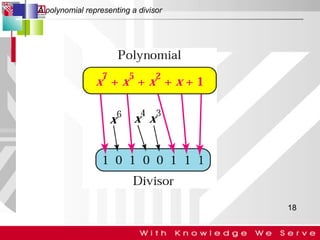
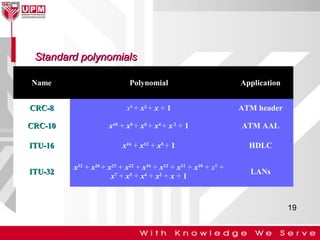
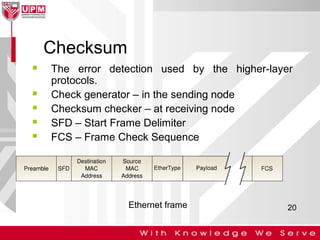
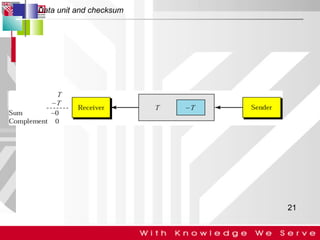
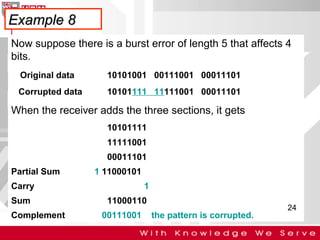
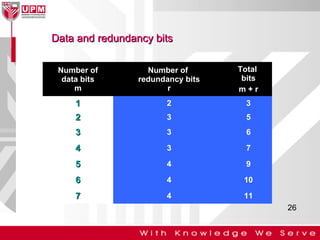
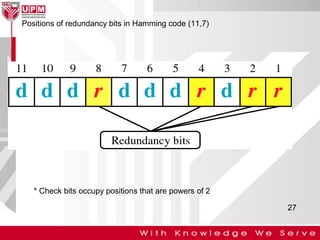
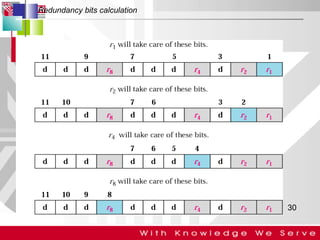
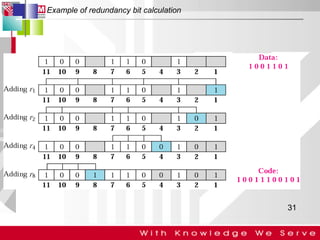
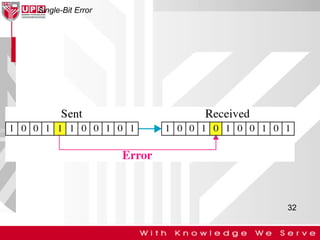
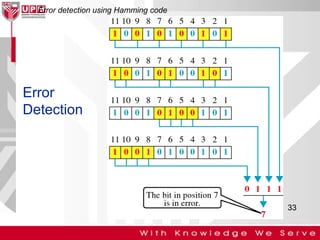
This document discusses computer network error detection and correction. It begins by defining single-bit errors and burst errors. It then explains three common error detection techniques: parity check, cyclic redundancy check (CRC), and checksum. Parity check uses a redundant bit to make the total number of 1s even or odd. CRC performs binary division to generate redundant bits. Checksum adds data bits and compares the sum. For error correction, it describes Hamming codes, which add redundant bits in specific positions to detect and correct single-bit errors.