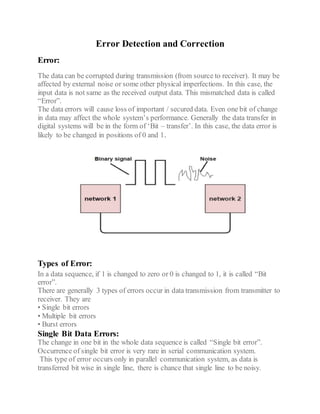
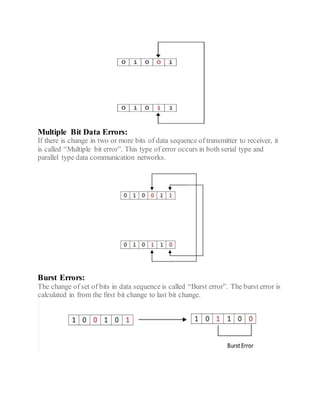
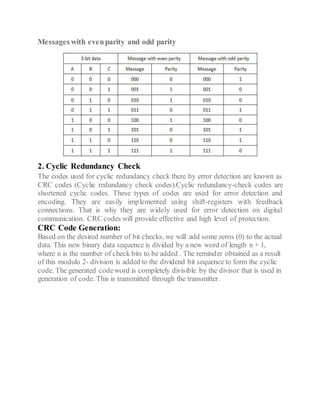
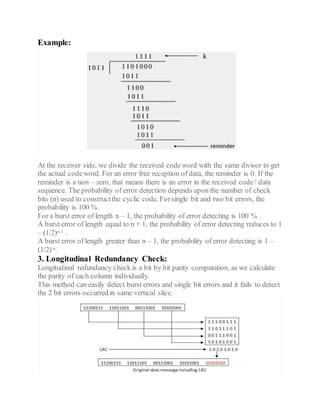
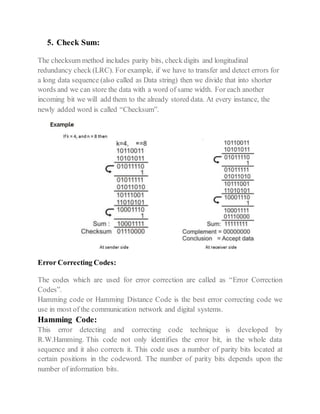
This document discusses error detection and correction techniques used in digital communication systems. It describes three types of errors that can occur during data transmission - single bit errors, multiple bit errors, and burst errors. It then explains various error detection codes like parity checking, cyclic redundancy check (CRC), longitudinal redundancy check (LRC), and checksum that are used to detect errors by adding redundancy to transmitted data. Finally, it discusses error correcting codes like Hamming codes that can detect and correct errors in the received data.