This presentation discusses checksums, which are an error-detecting technique used at the network and transport layers. The document provides the following information:
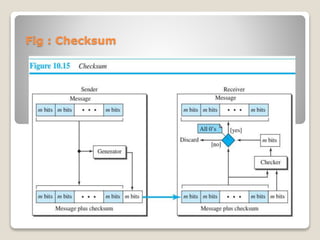
- Checksums work by dividing a message into bits, generating an extra "checksum" bits unit, and comparing the checksum at the destination to detect errors.
- An example is provided where numbers are summed and the checksum is the sum, which is compared at the destination to validate the message.
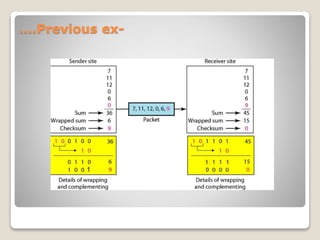
- A second example uses ones' complement, where numbers are represented with a set number of bits and extra bits are added for numbers larger than that size.
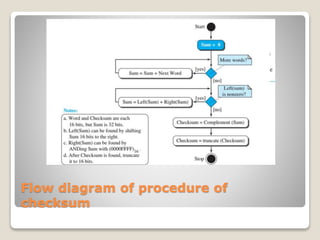
- Diagrams show the procedure and flow of checksum calculation and comparison to detect errors in transmitted data.



![Method 1.
Example-
4-bit numbers are: 7, 11, 12, 0, 6
Message to be sent:7,11,12,0,6,36
[7+11+12+0+6=36]
Receiver adds actual nos. and compares with
the sum(36)
If the two are the same
receiver assumes no error, nos. accepted
and sum discarded.
Else
an error somewhere and data are not
accepted.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/checksum-copy-161130143912/85/Check-sum-5-320.jpg)