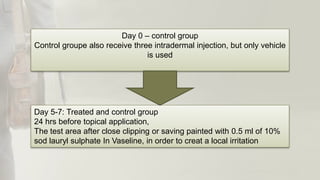
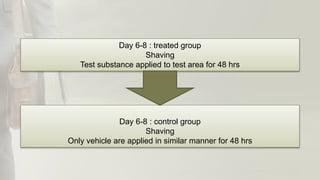
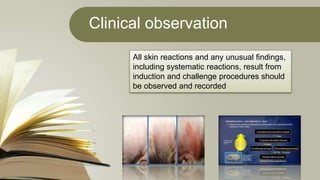
The document summarizes skin sensitization testing methods according to OECD Guideline 406. It describes two common animal models - the guinea pig and mouse - and tests used, including the Guinea Pig Maximization Test and Buehler Test. It provides details on study design, including number of animals, induction and challenge procedures, observations, and scoring of skin reactions. The goal is to screen substances for their potential to cause skin sensitization or allergic contact dermatitis in humans.