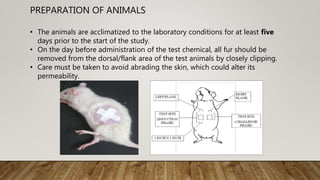
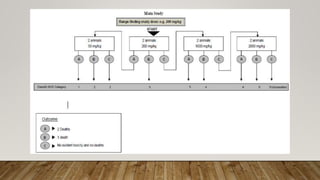
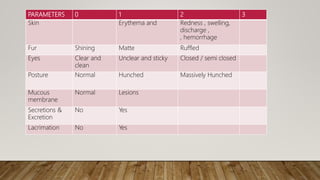
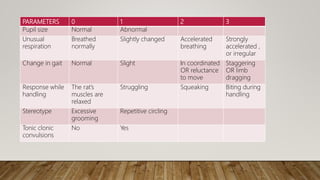
This document summarizes guidelines for conducting acute dermal toxicity studies as per OECD, EPA, and Schedule Y. It describes the key steps in the studies including animal selection, dosing procedures, observations, and criteria for categorizing toxicity. The revised OECD guideline uses fewer animals in a stepwise procedure to identify the dose causing toxicity or mortality. It is reproducible and able to rank chemicals similarly to other acute toxicity methods.