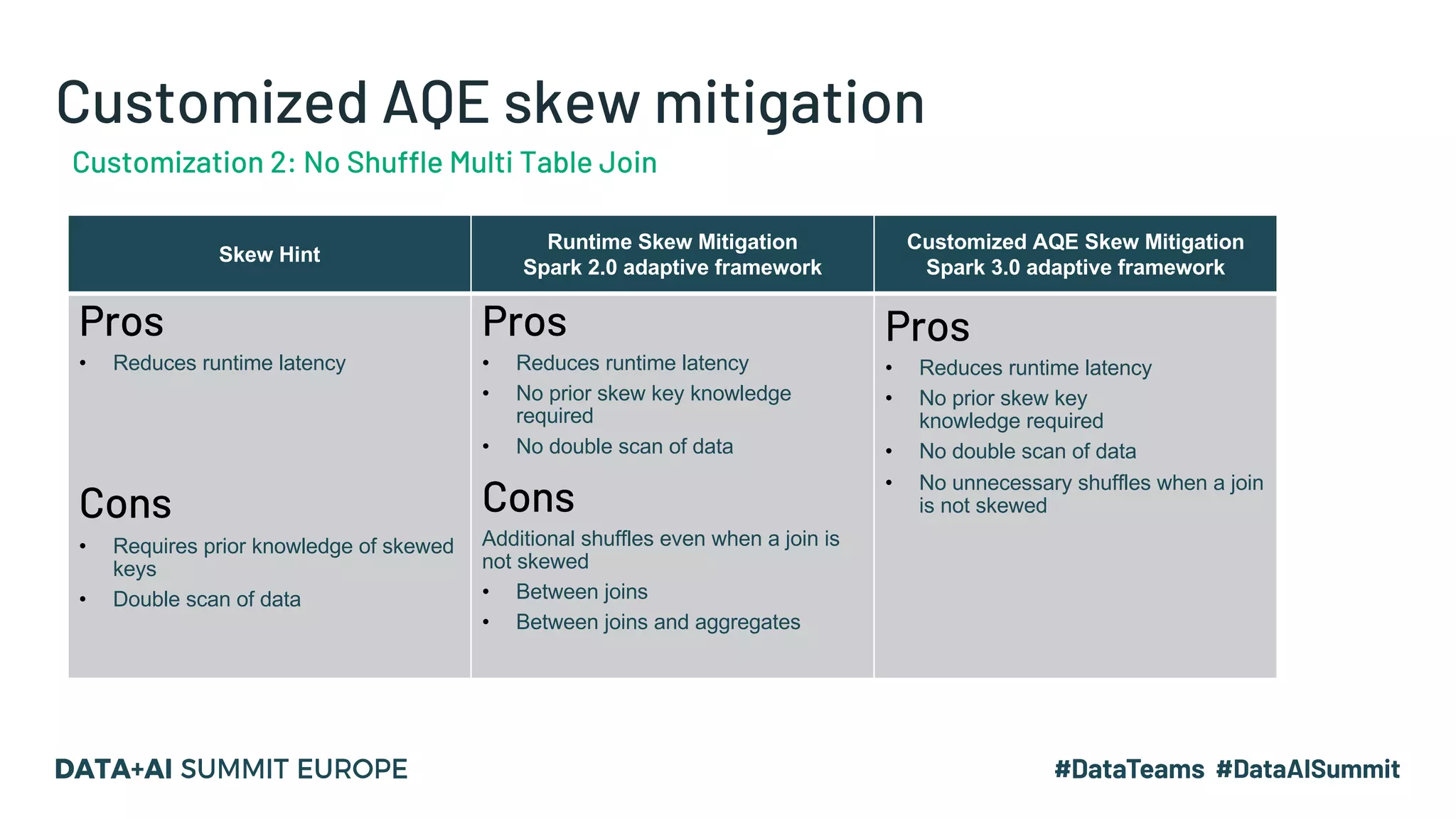
The document discusses strategies for mitigating data skew in large-scale joins within Facebook's data processing framework, focusing on techniques such as skew hints, runtime skew mitigation, and the customized Adaptive Query Execution (AQE) framework. It compares varying join strategies in Spark, explaining how skewed partitions can significantly impact task latency and system performance. Additionally, it highlights the functions of Cosco, an efficient shuffle service designed to improve I/O efficiency and reduce data redundancy during processing.







![Skew Hint
Union
Scan table_A Scan table_B
Filter
[skewed keys]
BroadcastHashJoin
Filter
[skewed keys]
Scan table_A Scan table_B
SortMergeJoin
Filter
[non-skewed keys]
Filter
[non-skewed keys]
Exchange Exchange
Skewed dataNon-skewed data](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/147dewakarxu-201129185214/75/Skew-Mitigation-For-Facebook-PetabyteScale-Joins-9-2048.jpg)








![table_A (petabye) table_B
Left Outer Join
table_C
Left Outer Join
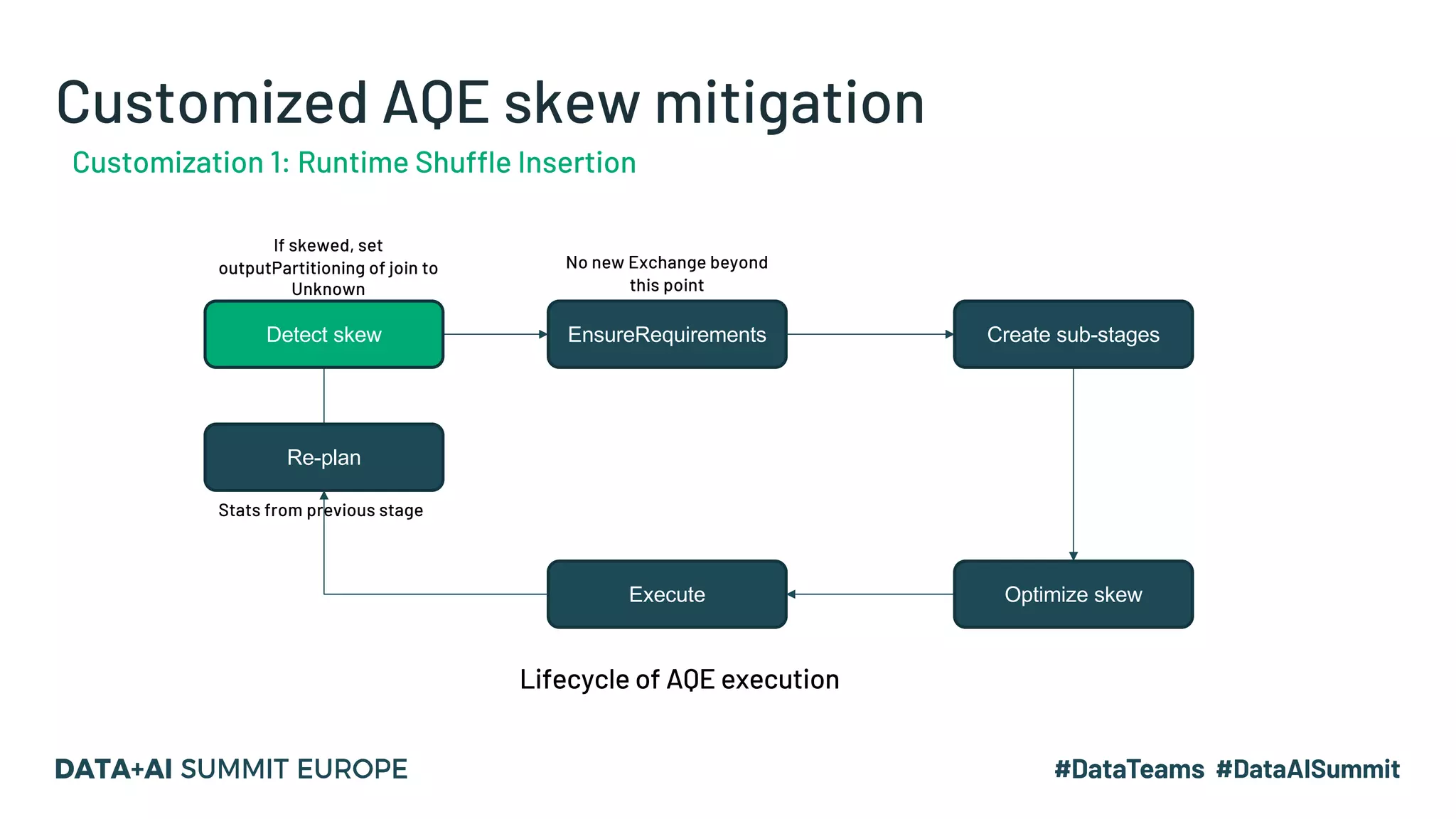
Customized AQE skew mitigation
[Limitation] Customization 1: Runtime Shuffle Insertion
table_D
Left Outer Join](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/147dewakarxu-201129185214/75/Skew-Mitigation-For-Facebook-PetabyteScale-Joins-20-2048.jpg)
![table_A (petabye) table_B
Left Outer Join
table_C
Left Outer Join
Customized AQE skew mitigation
[Limitation] Customization 1: Runtime Shuffle Insertion
table_D
Left Outer Join
Exchange
Exchange
Shuffles PB sized
data
Shuffles PB sized
data](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/147dewakarxu-201129185214/75/Skew-Mitigation-For-Facebook-PetabyteScale-Joins-21-2048.jpg)