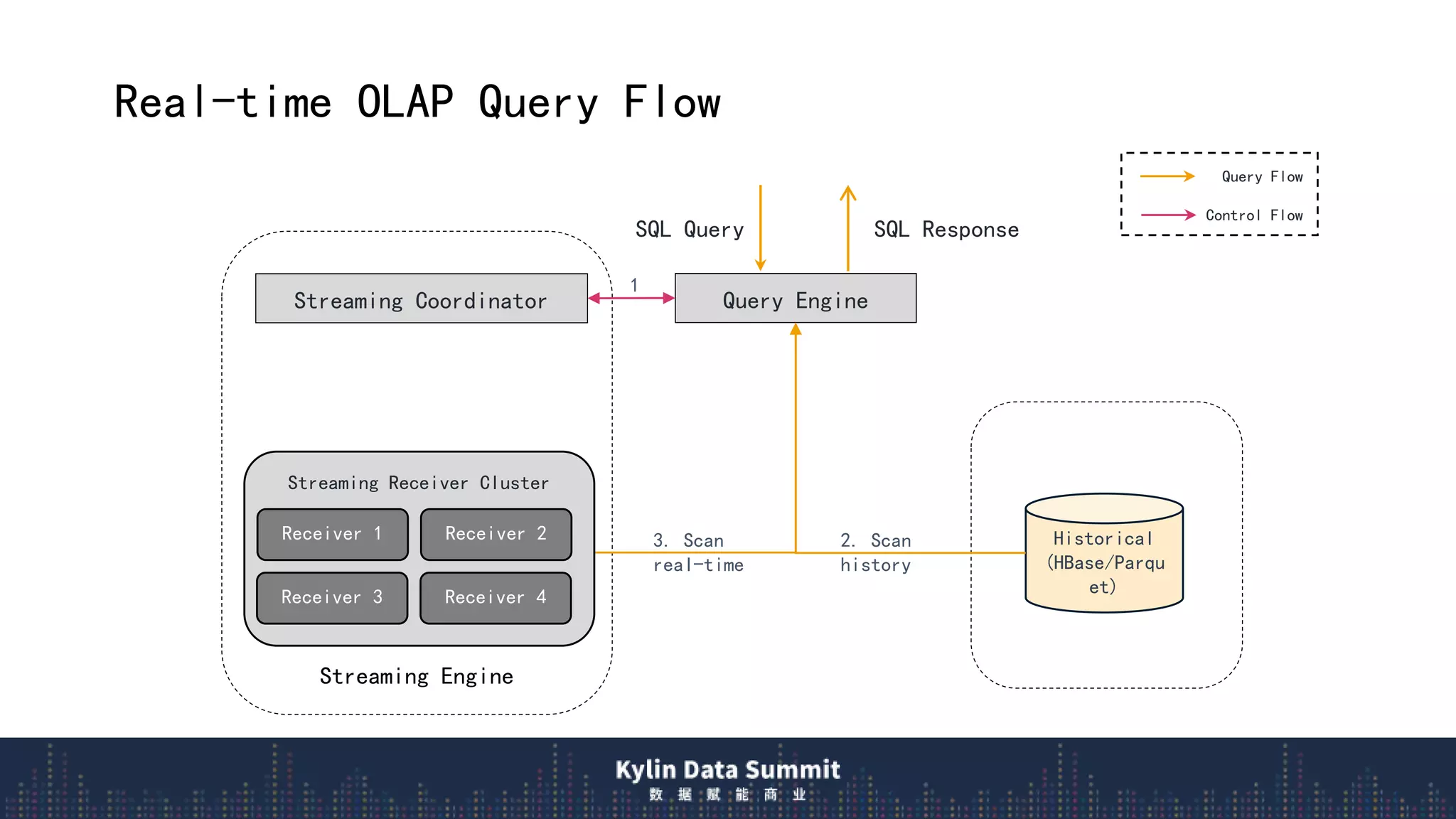
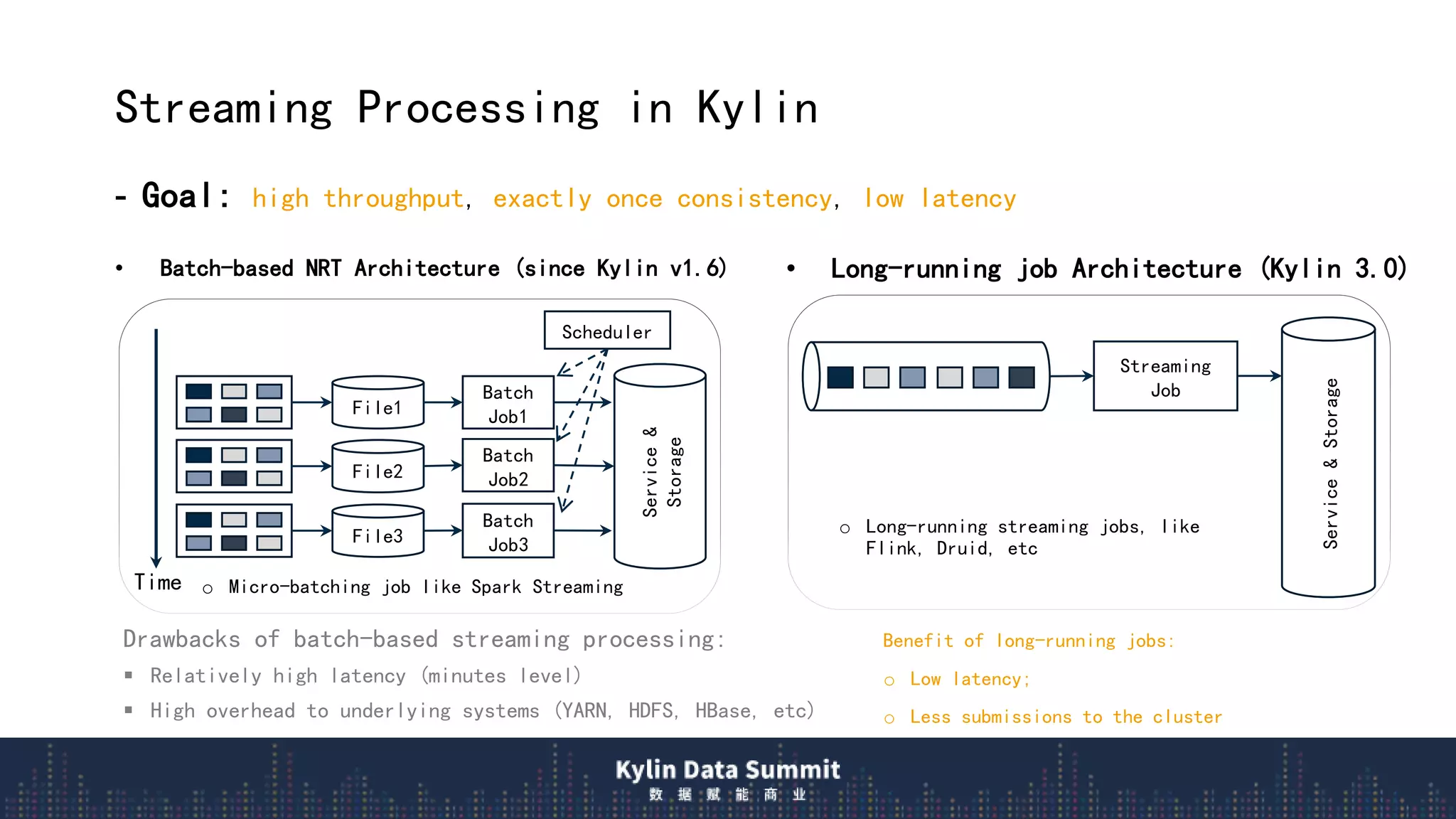
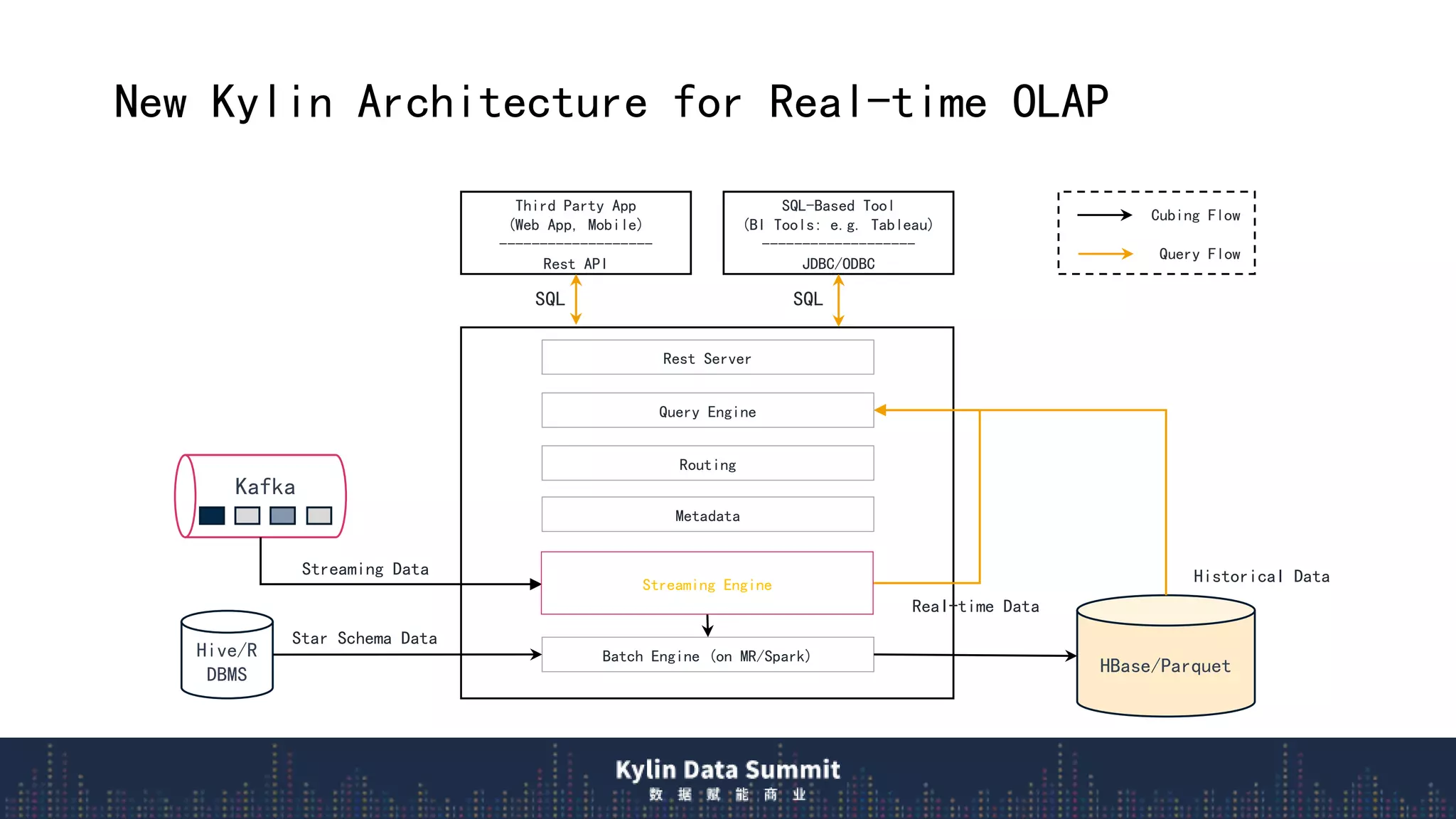
1) Apache Kylin v3.0 introduces a new real-time OLAP architecture using long-running streaming jobs to provide low latency queries over streaming data.
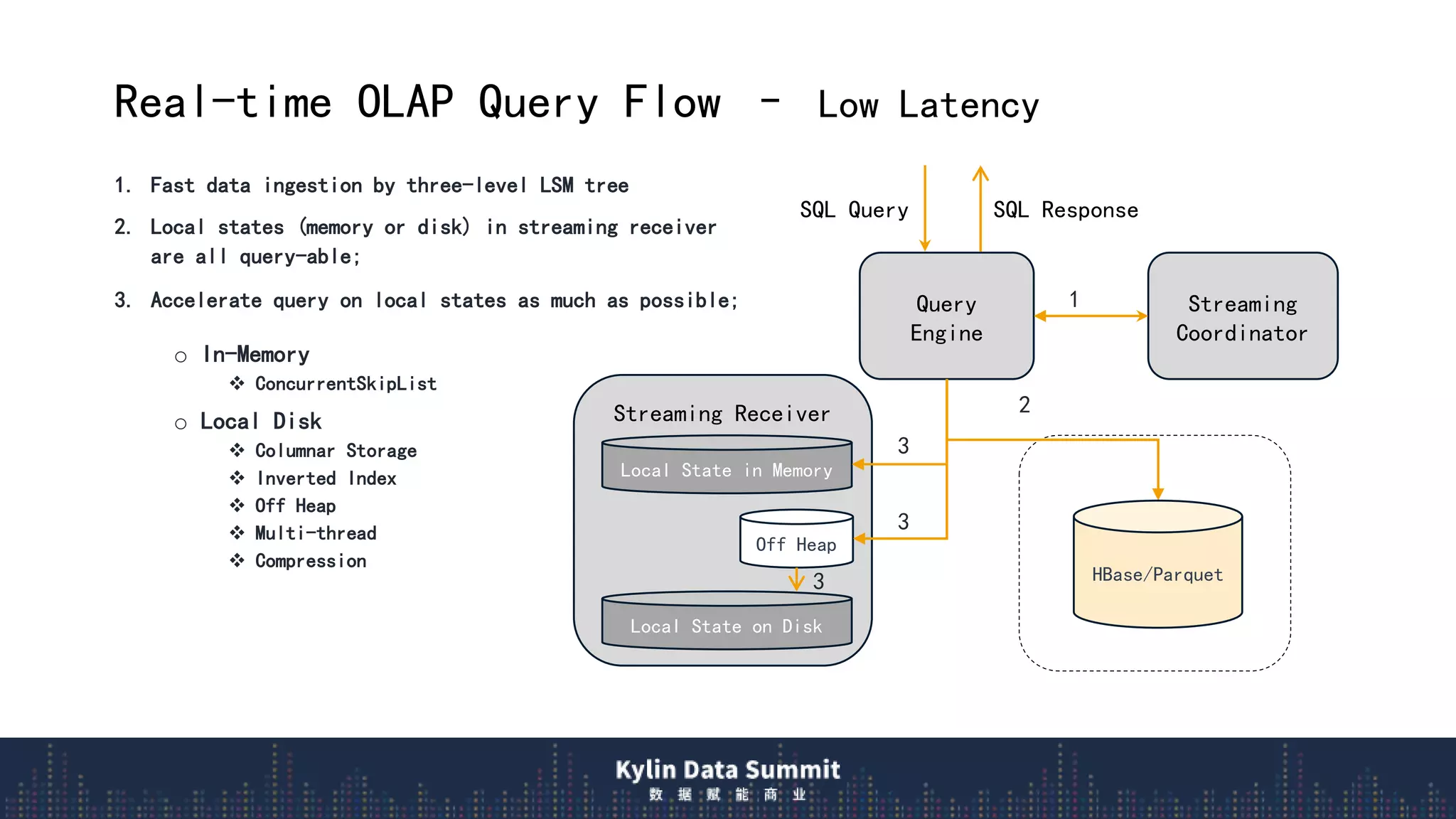
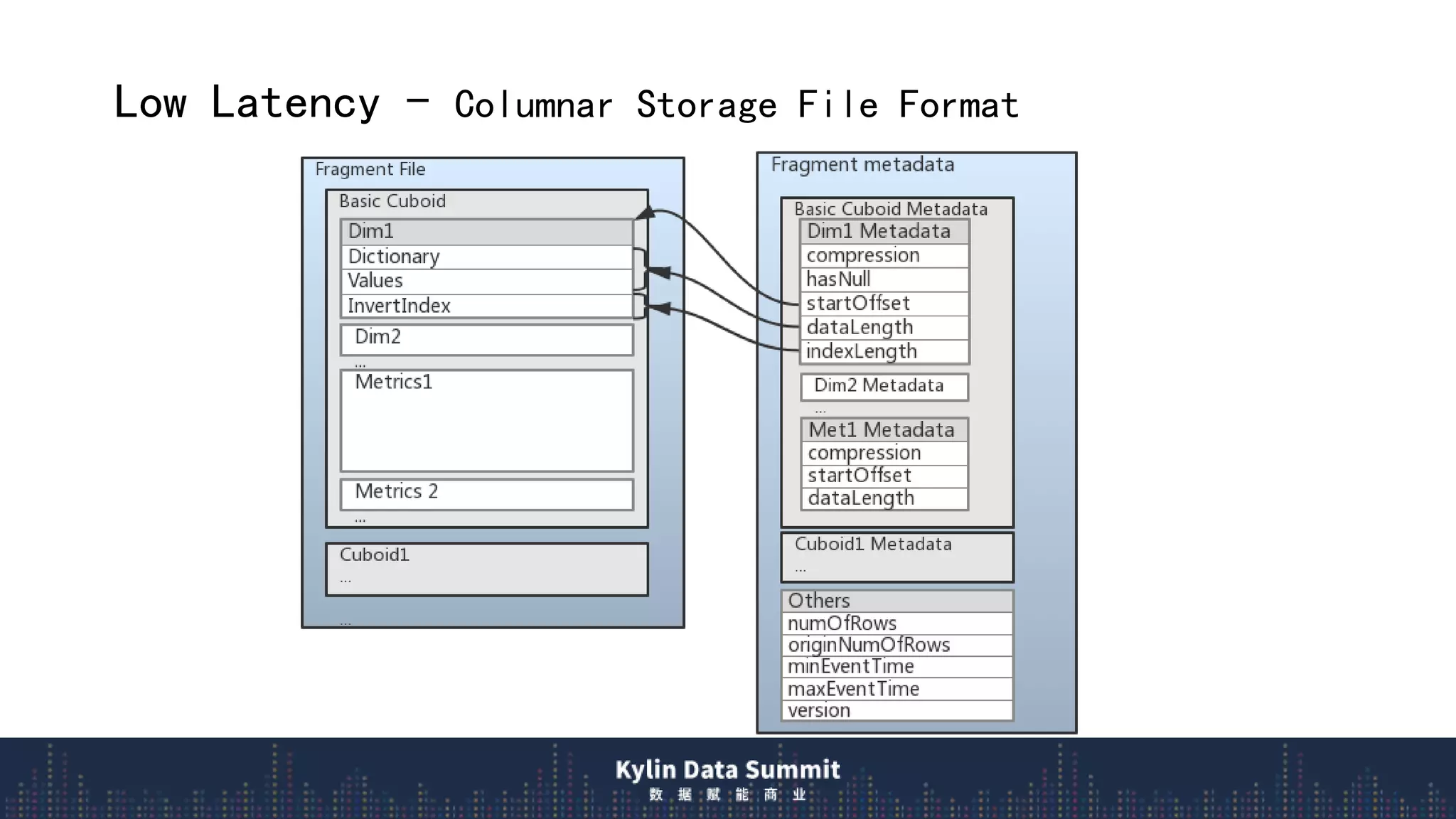
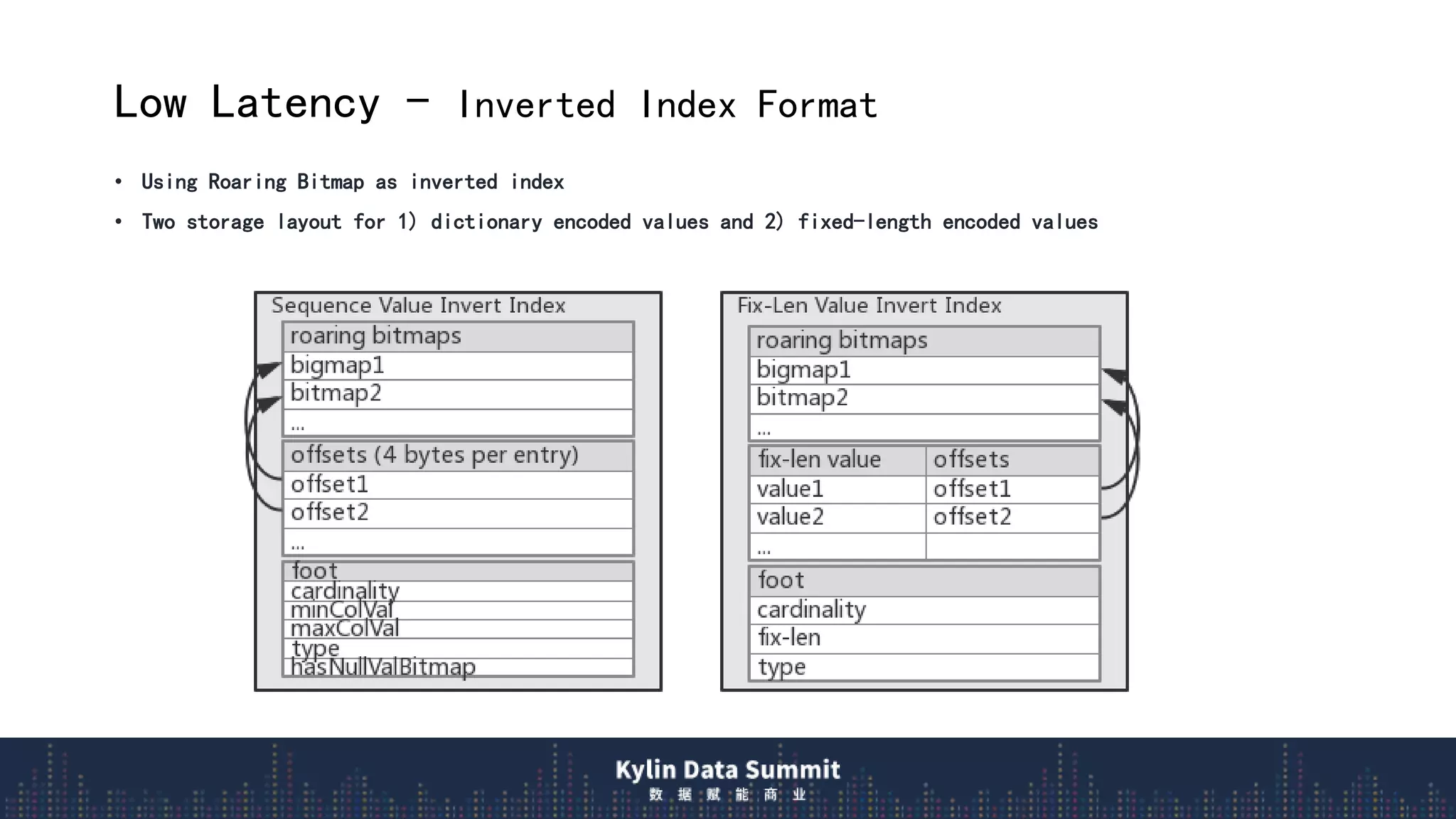
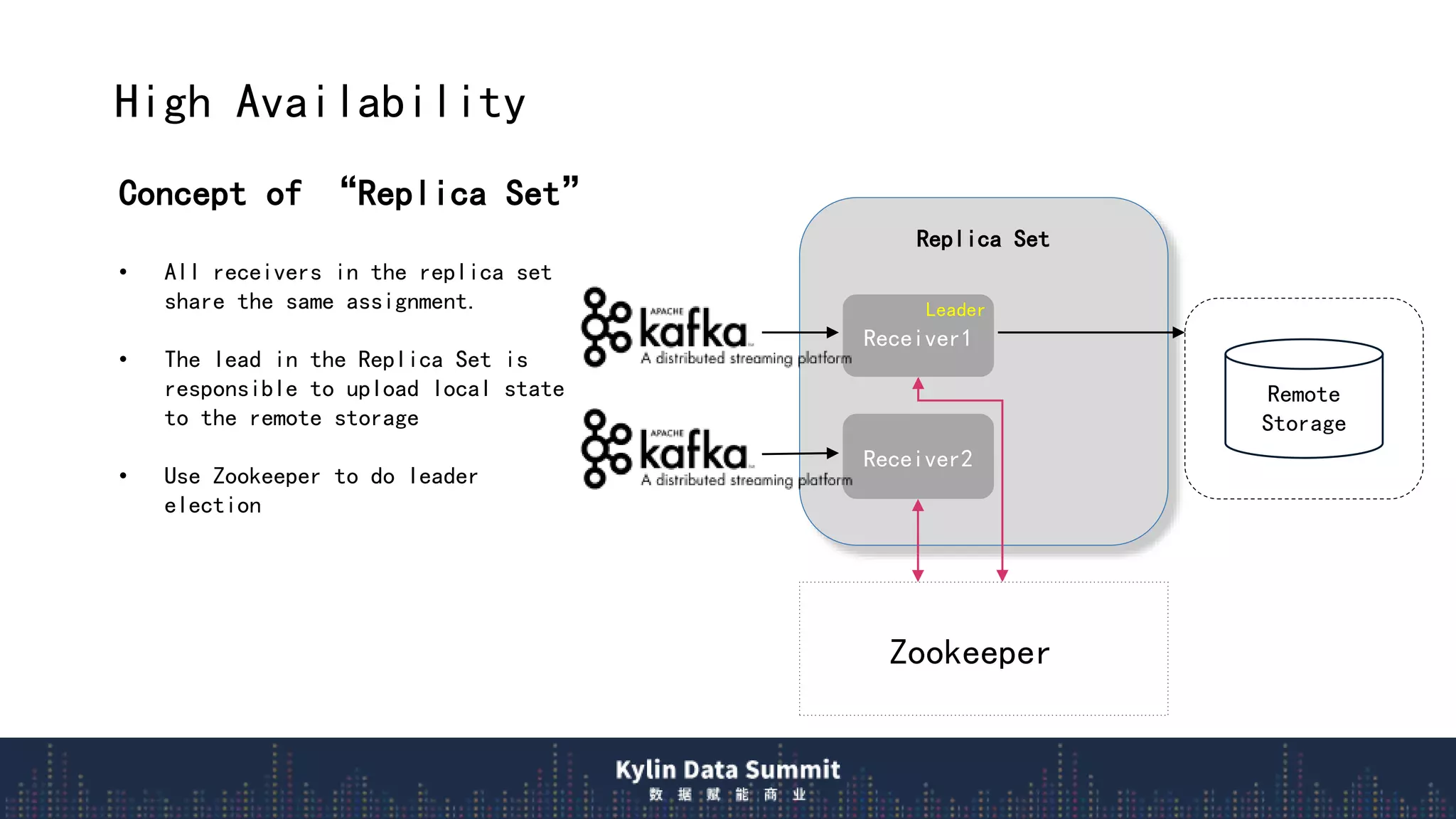
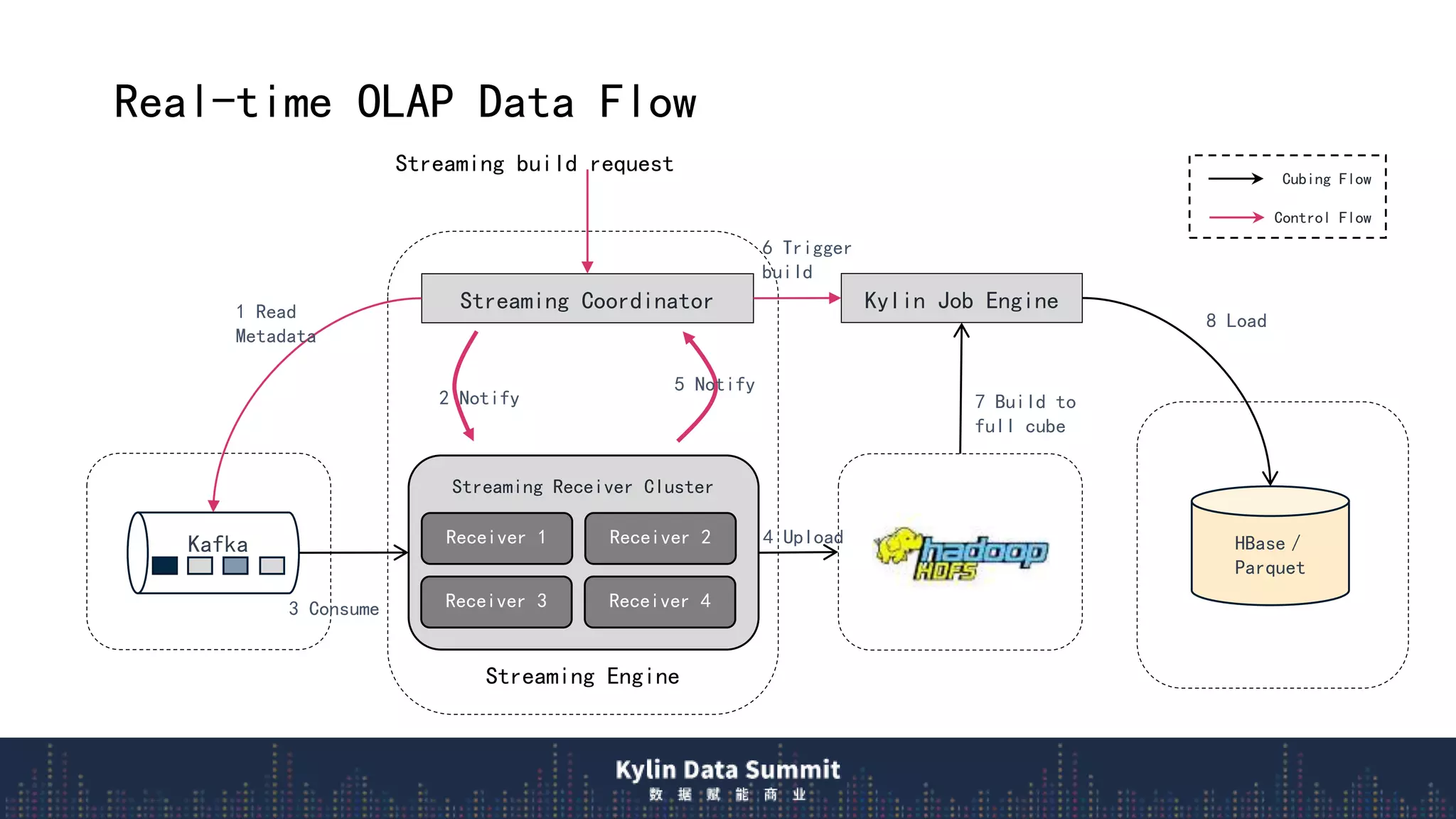
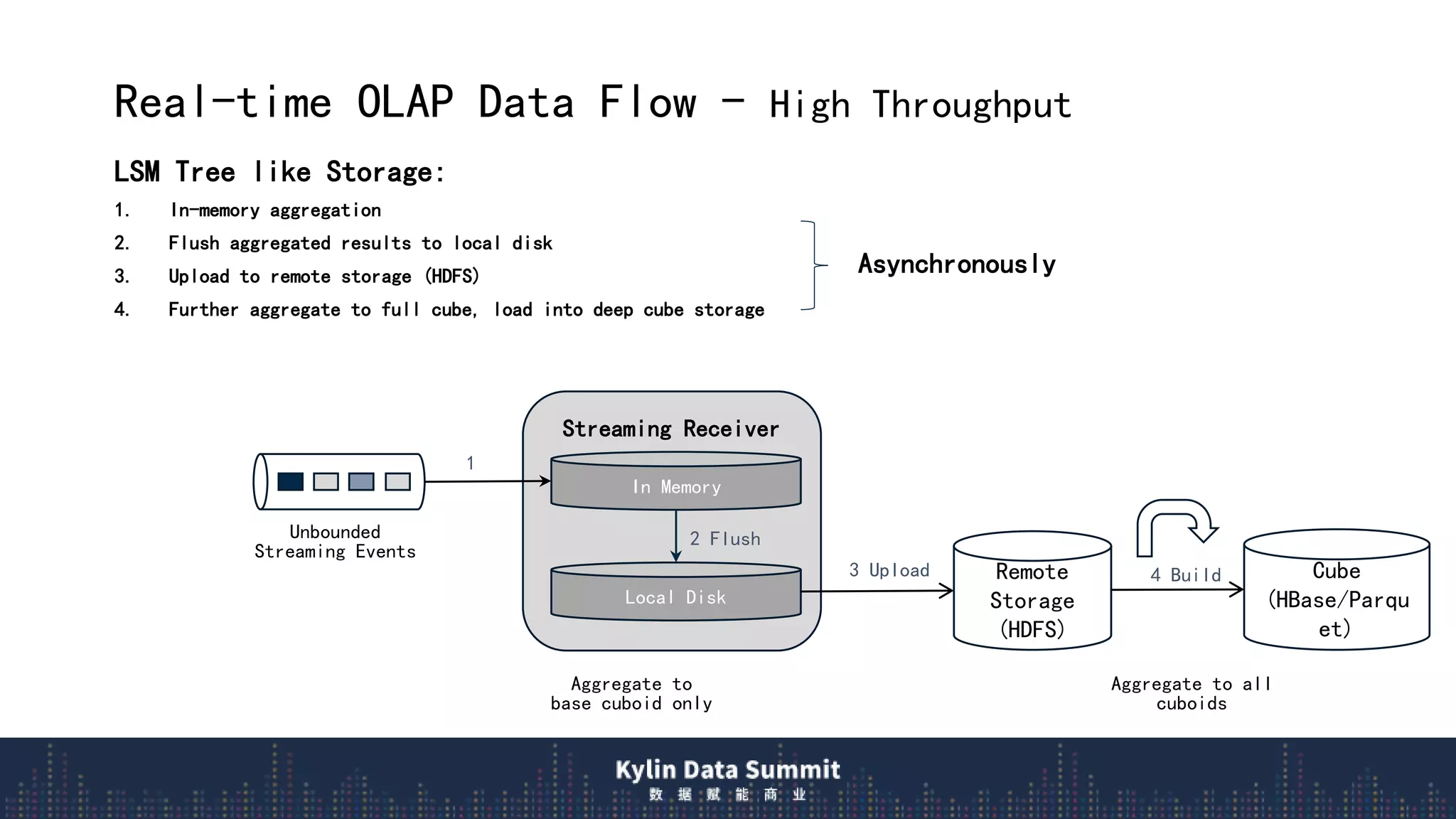
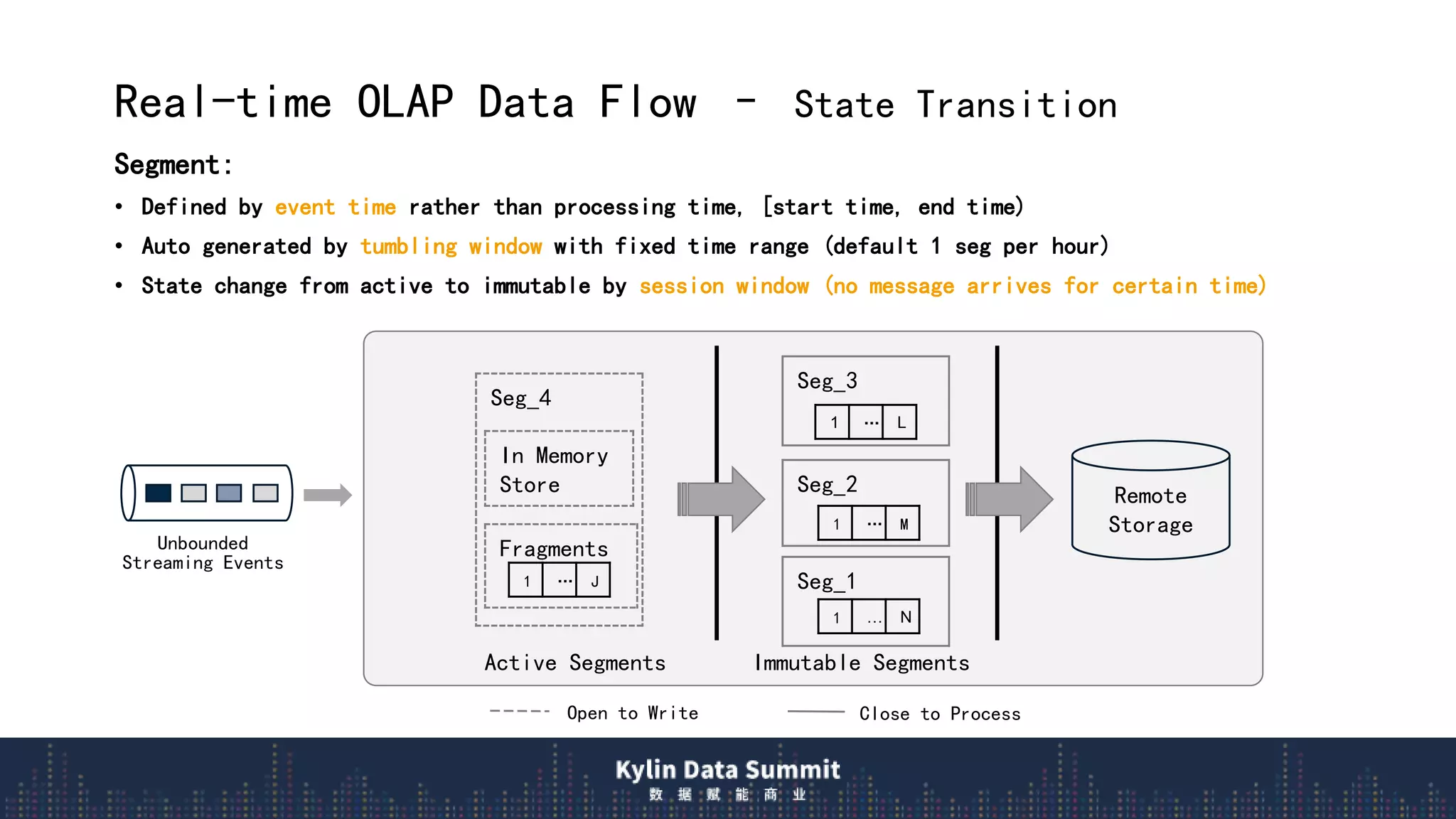
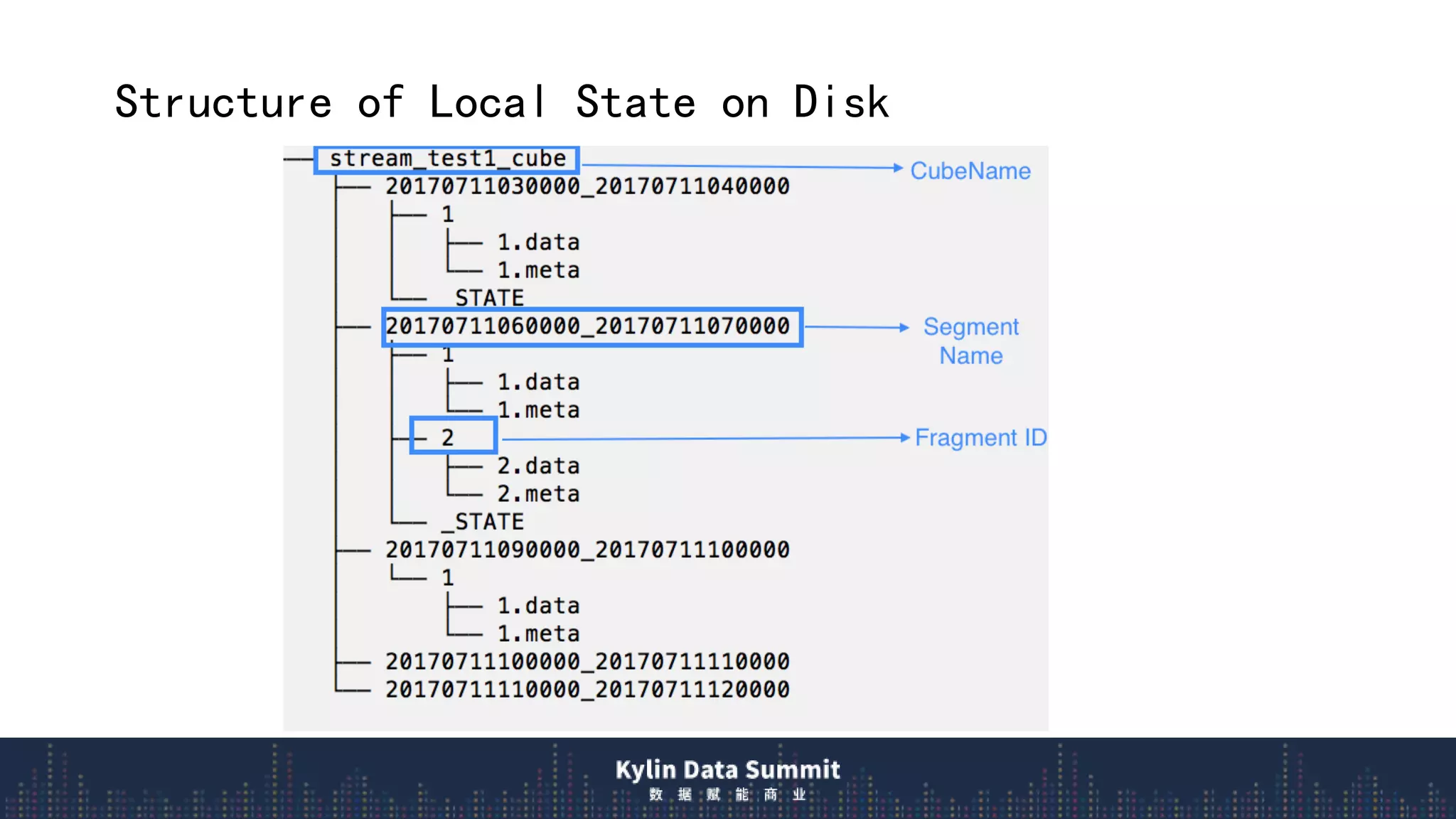
2) The data flow uses streaming receivers to aggregate streaming events in memory and flush to local disk in real-time segments before uploading to remote storage.
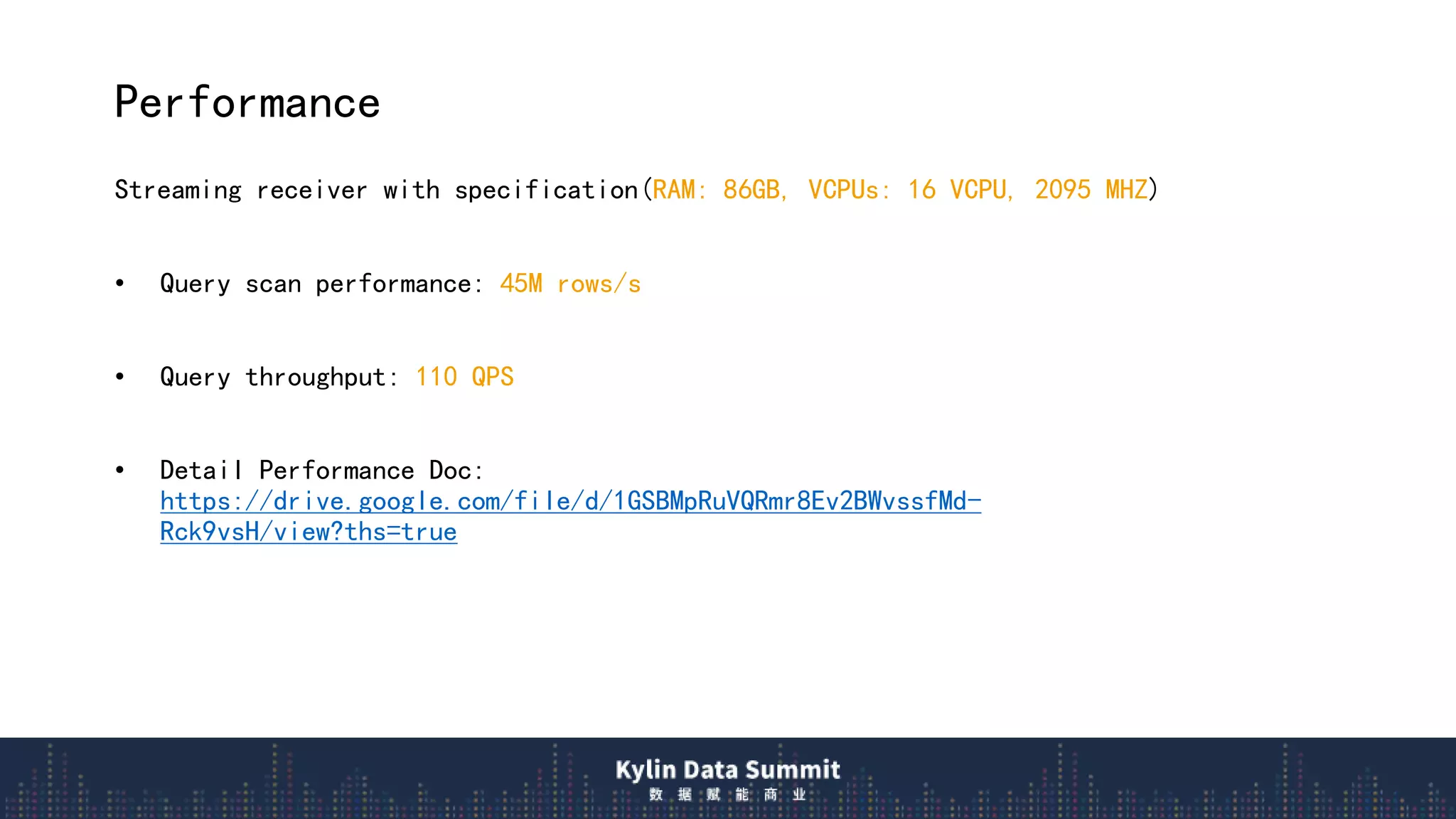
3) The query flow scans local real-time segments for low latency before querying remote historical data, providing millisecond responses over trillions of rows.

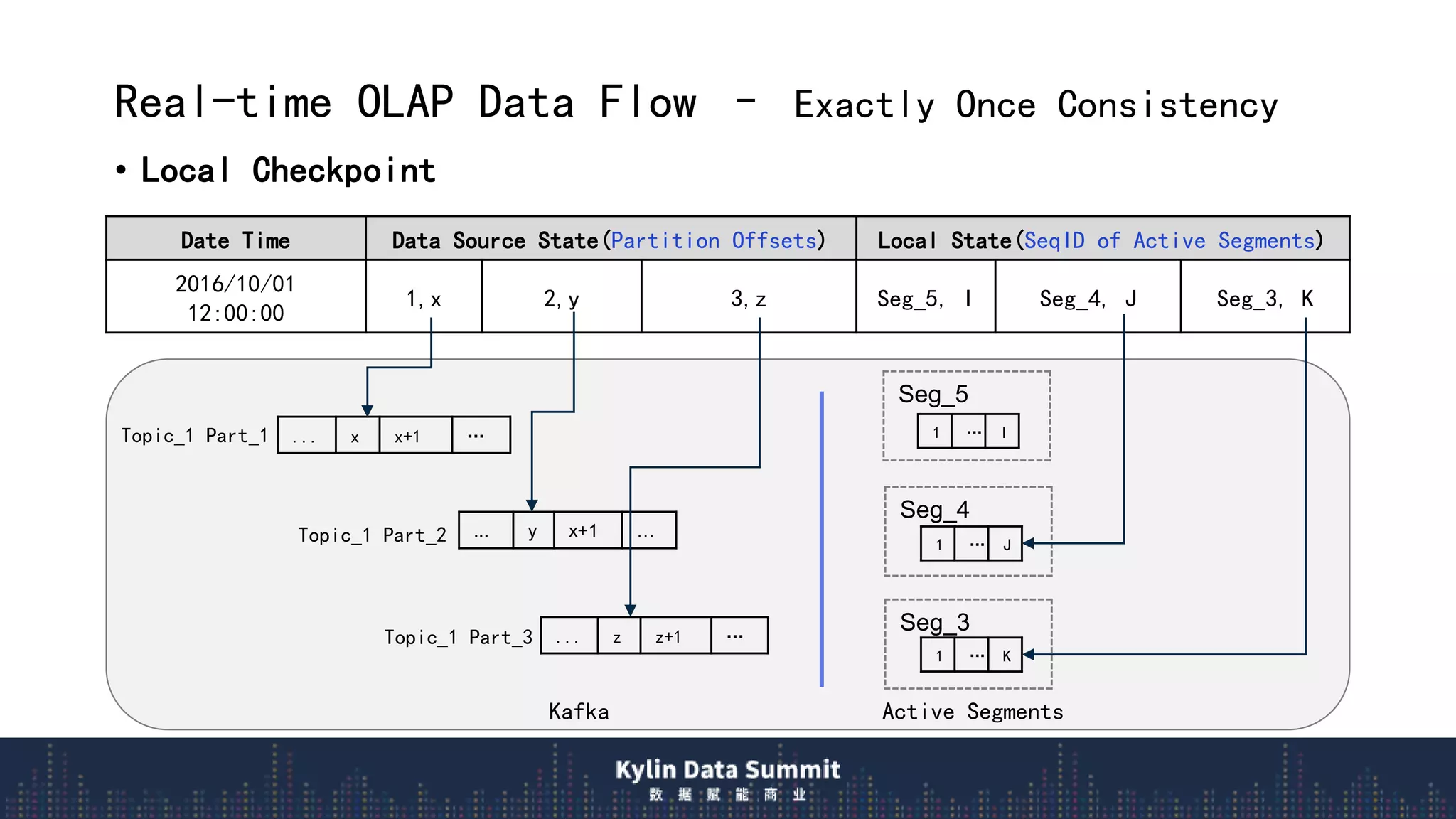
![Real-time OLAP Data Flow – Exactly Once Consistency
• Remote Checkpoint
o Checkpoint is saved to Cube Segment metadata after HBase segment be built
“segments”:[{…,
"stream_source_checkpoint": {"0":8946898241, “1”: 8193859535, ...}
},
]
o The checkpoint info is the smallest/earliest partition offsets on the streaming receiver
when real-time segment is sent to full build.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/realtimeolaparchitectureinapachekylin3-190808052428/75/Realtime-olap-architecture-in-apache-kylin-3-0-10-2048.jpg)