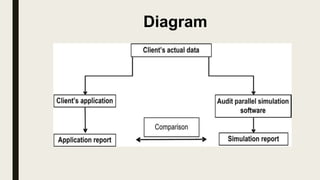
Parallel simulation involves an auditor writing a program to replicate part of a client's application system and processing actual client data through audit software. The auditor compares the output from the simulation to the client's actual results. Parallel simulation allows auditors to verify transaction processing and client results. It is one technique auditors use to obtain evidence on the quality of records produced by client systems. The auditor must understand the client's application and develop a simulation that accurately replicates client processes.