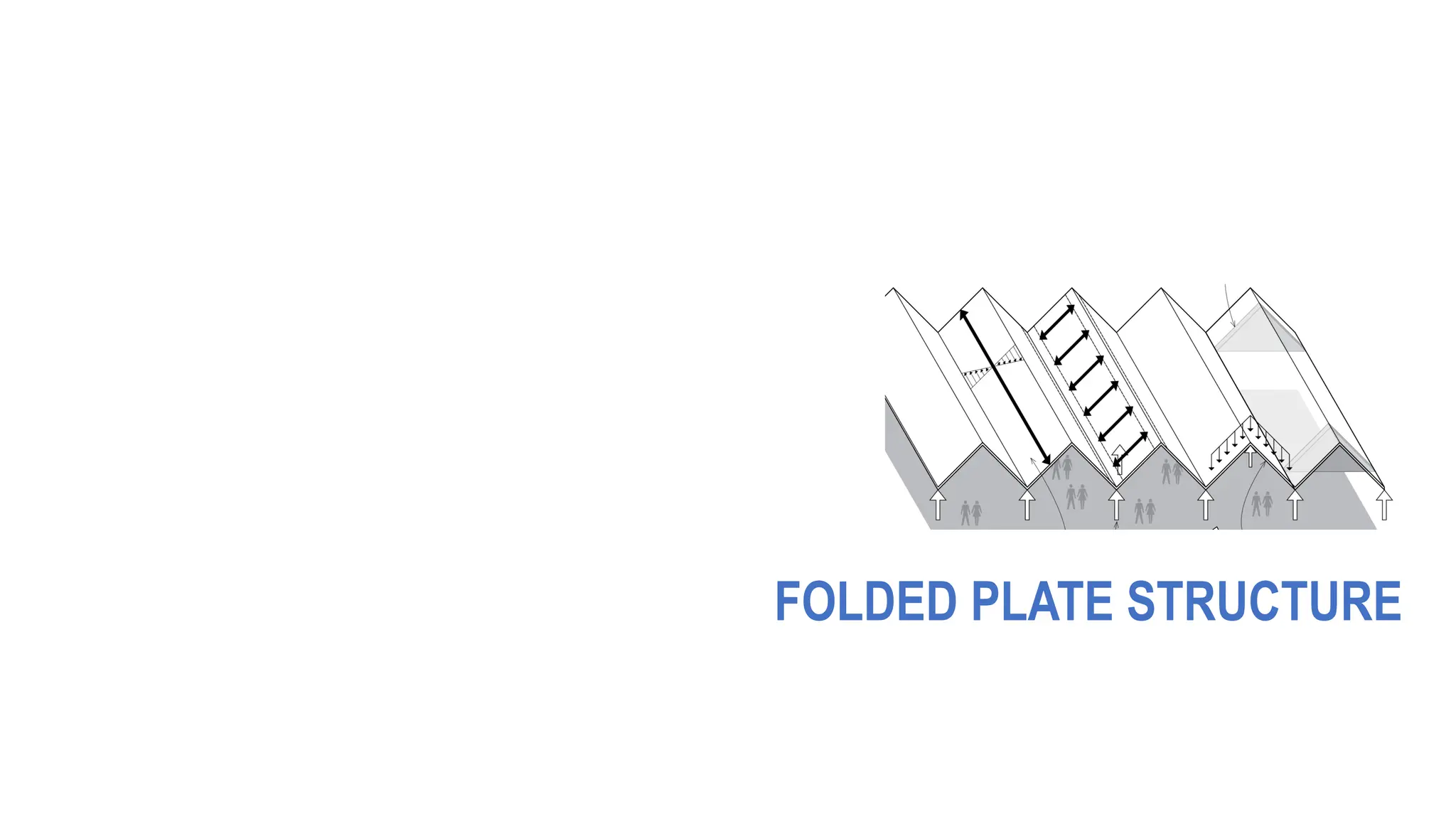
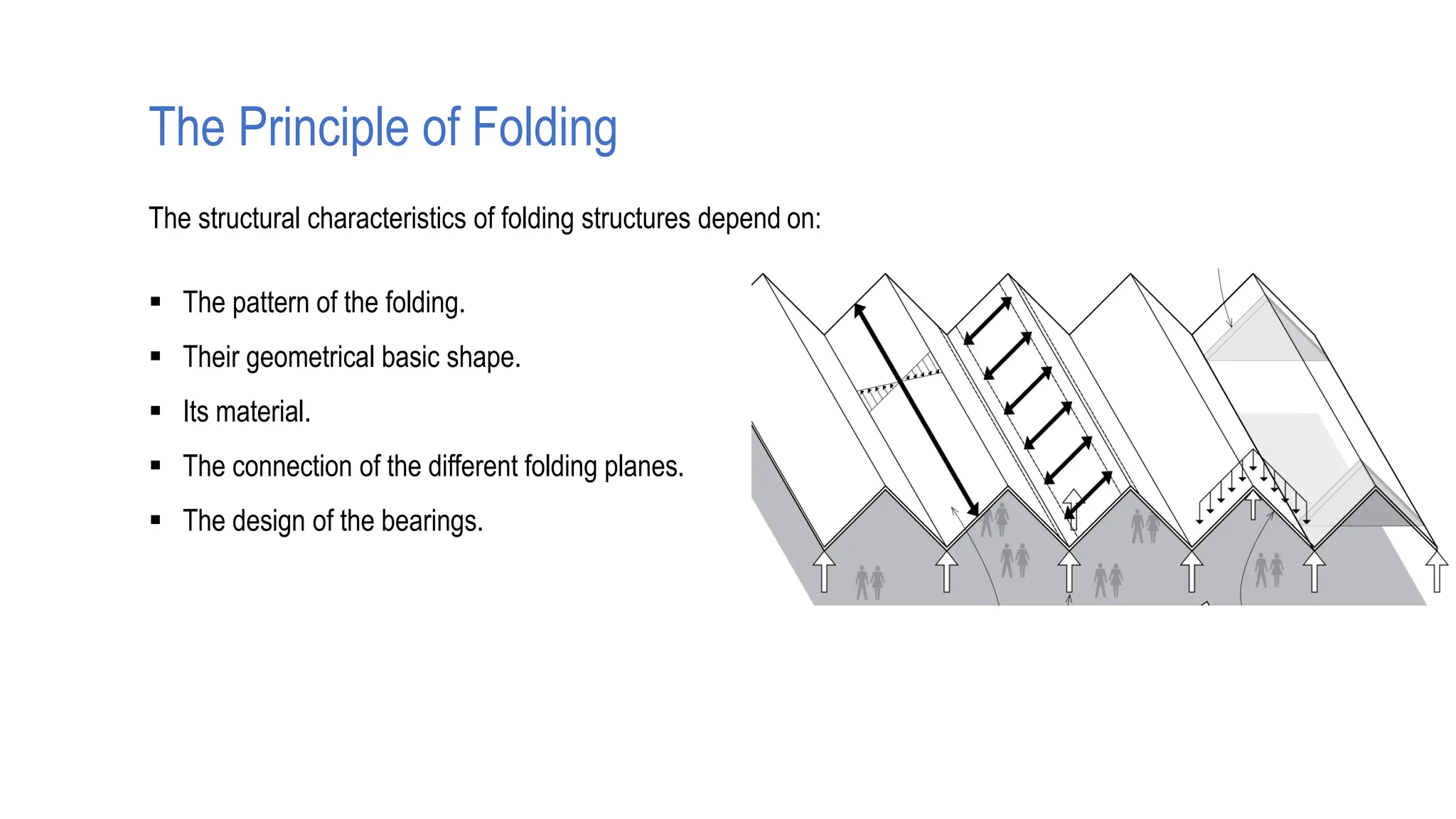
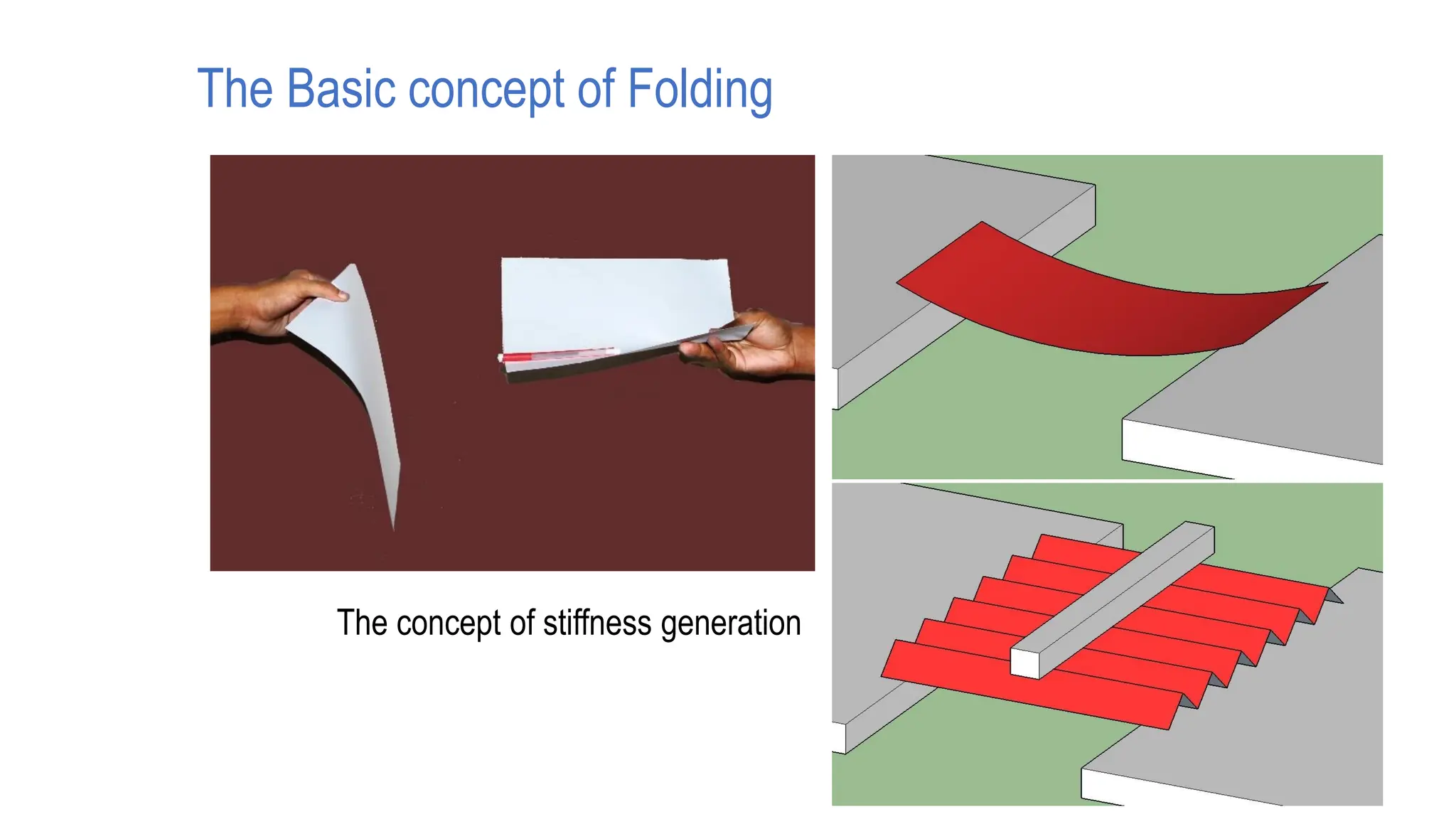
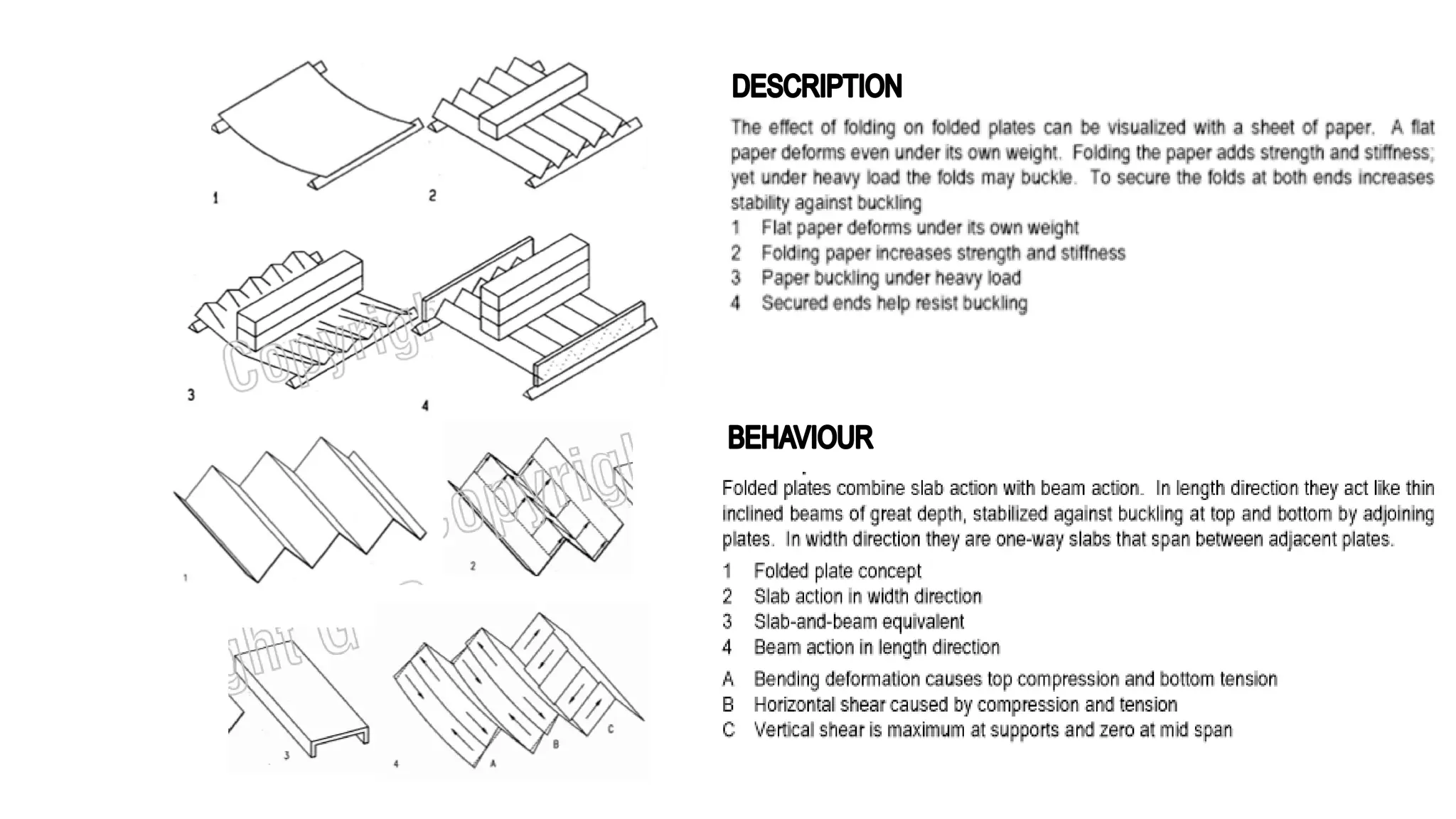
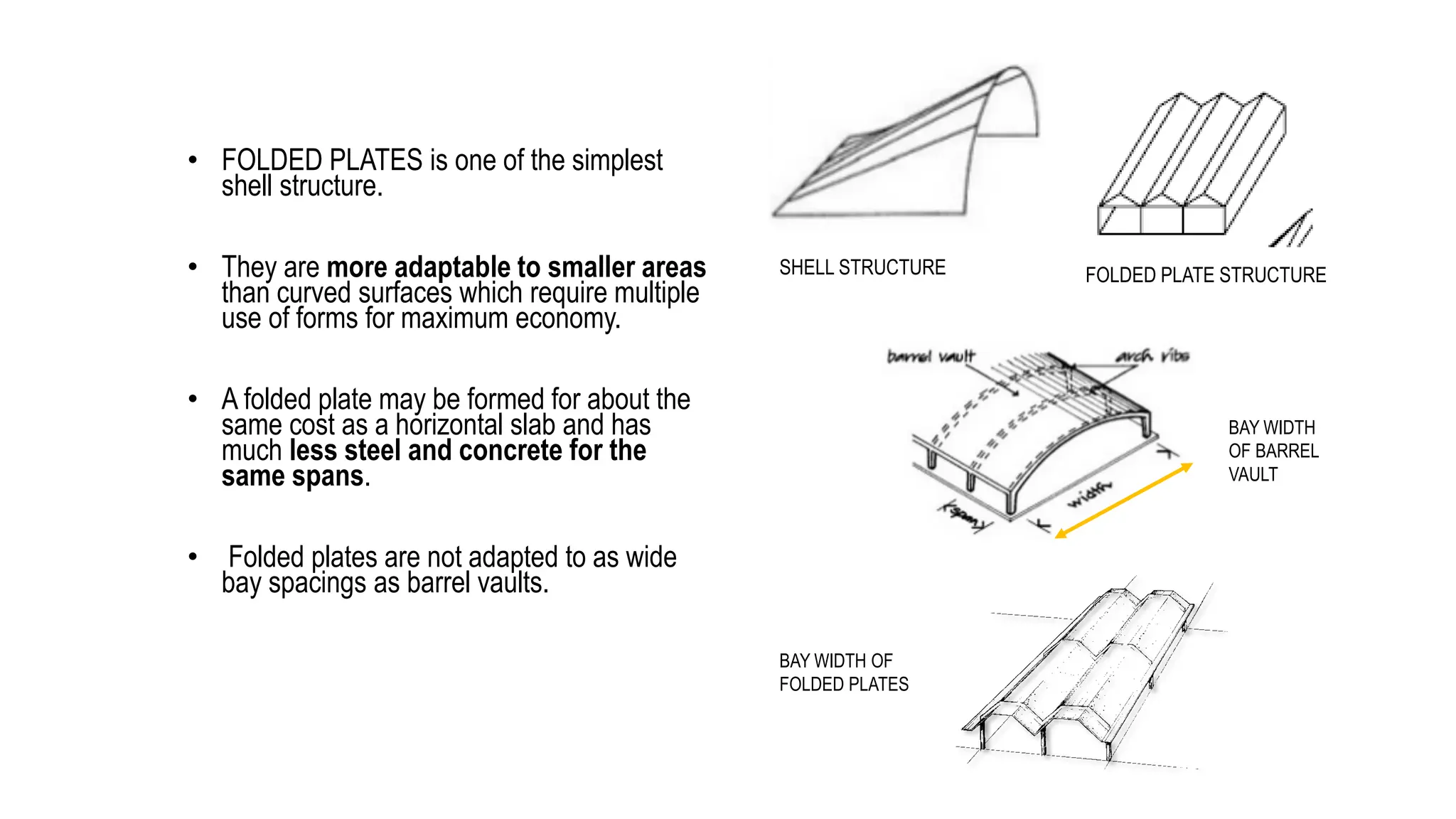
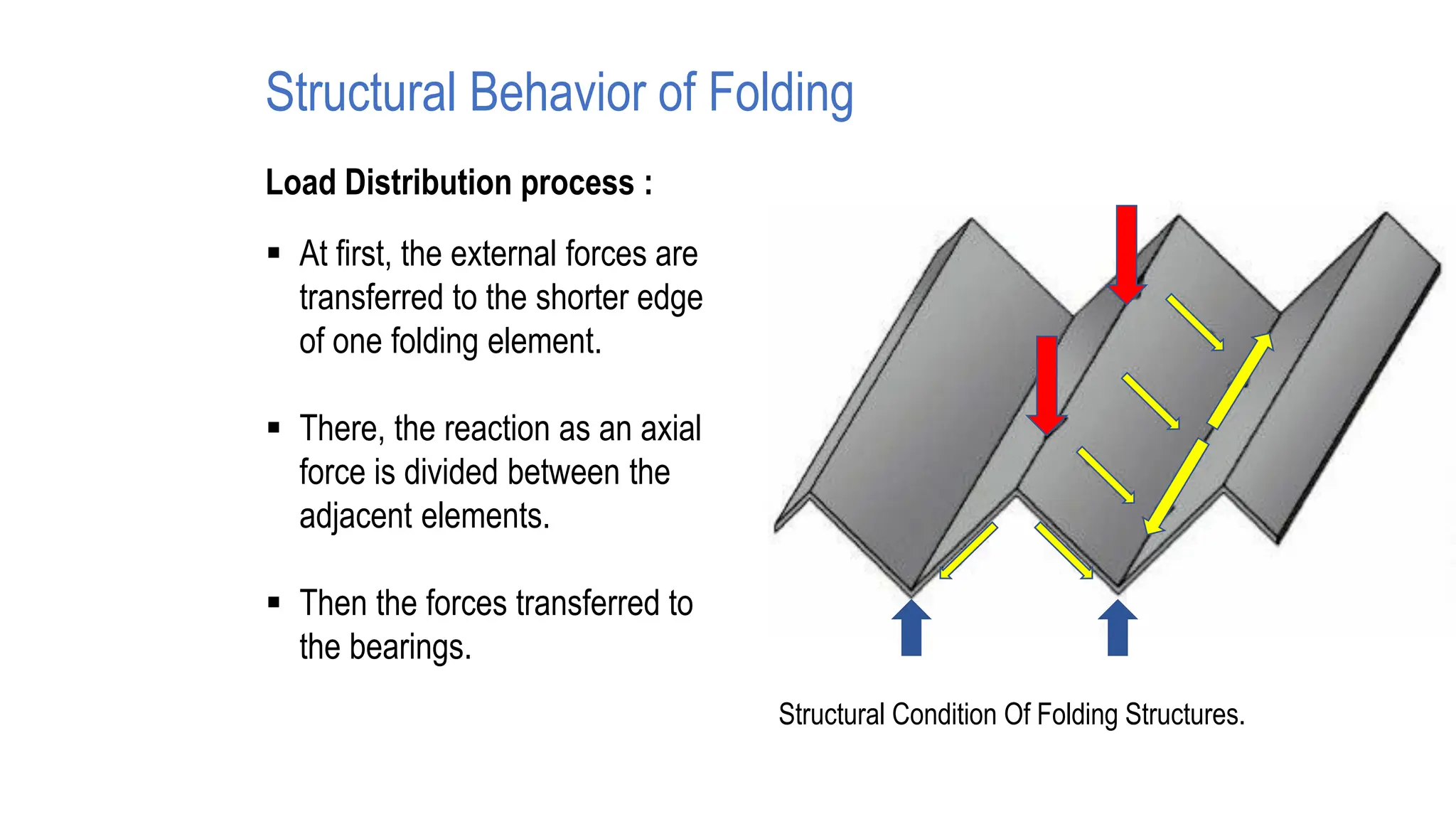
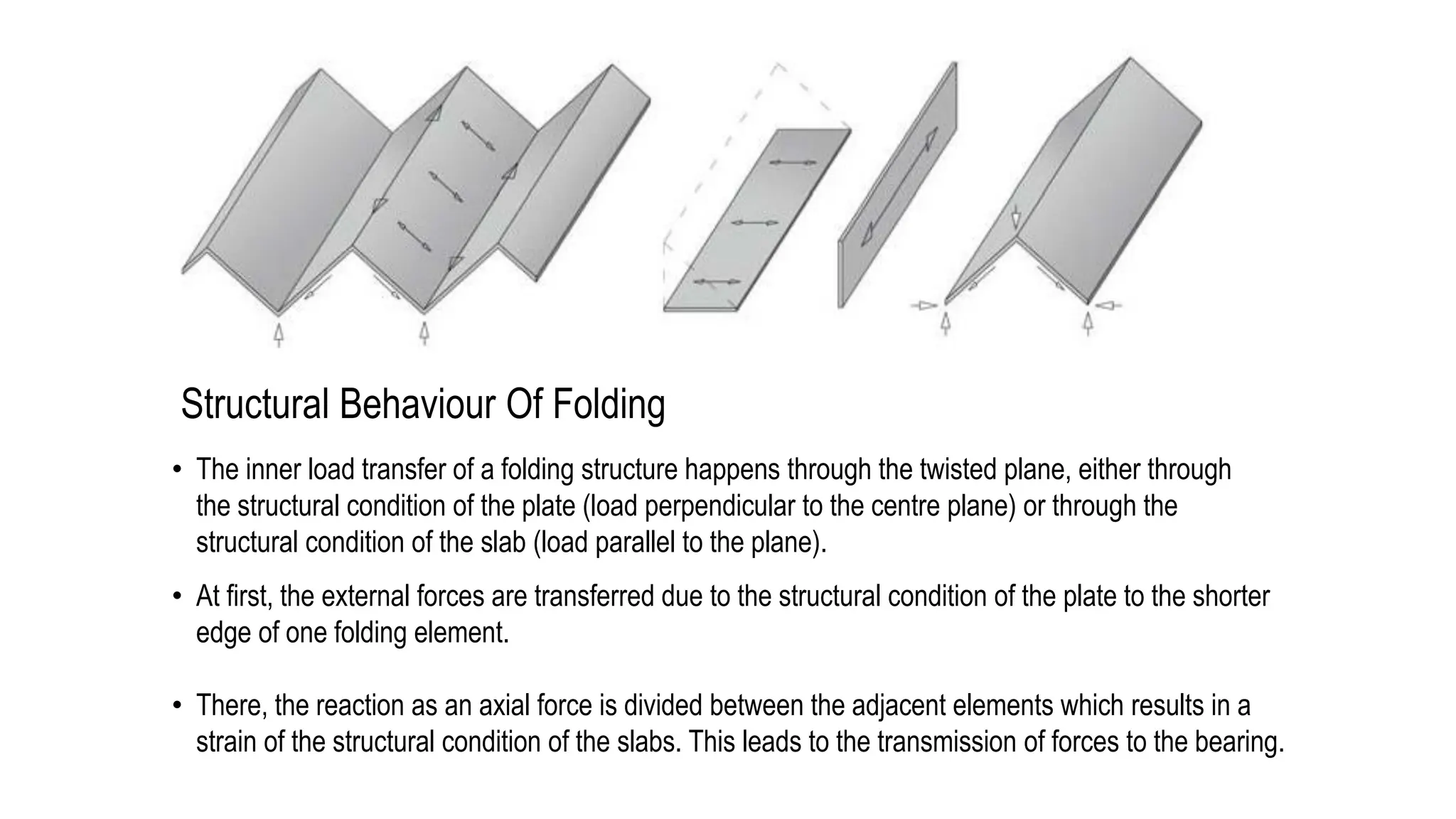
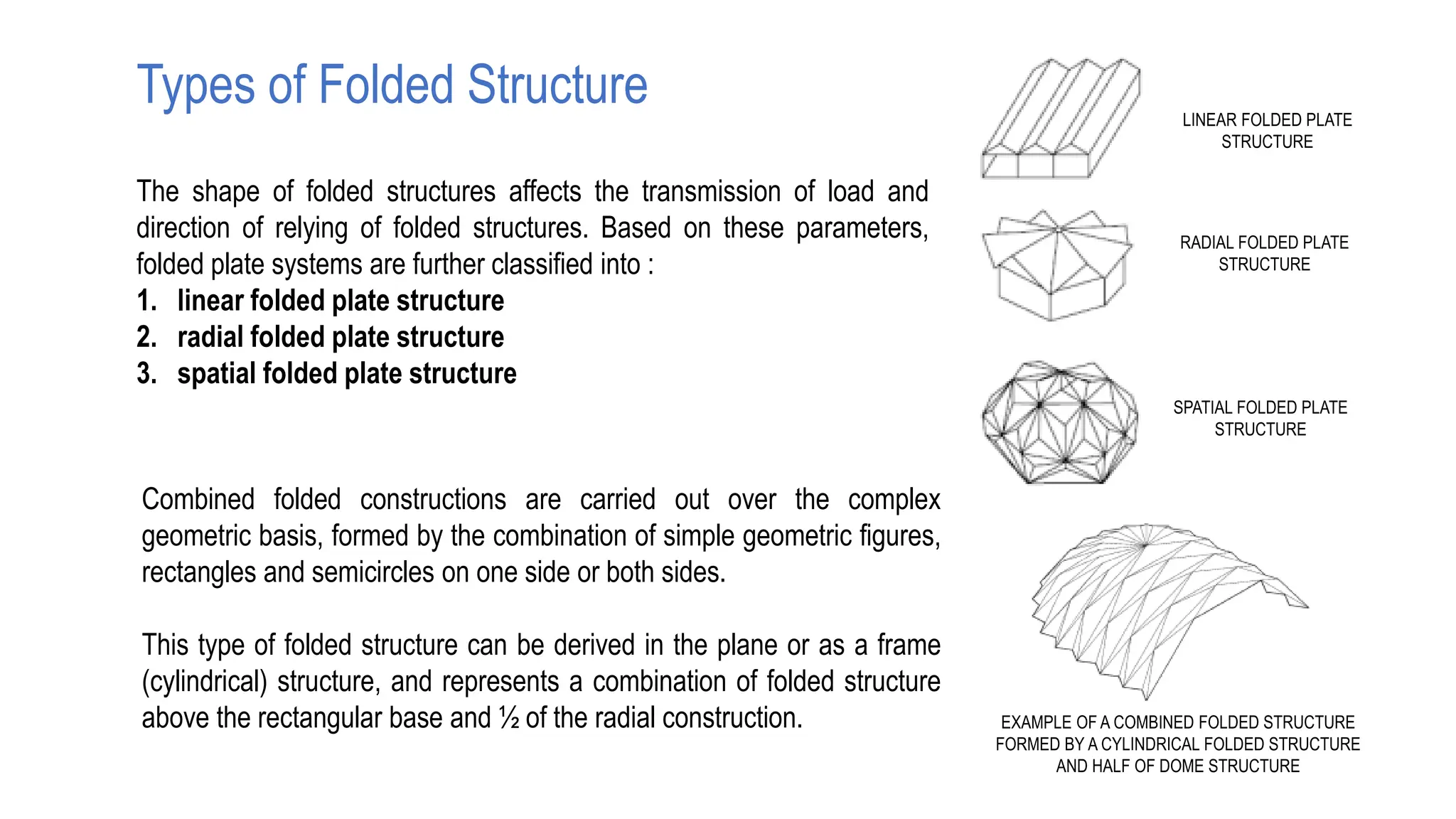
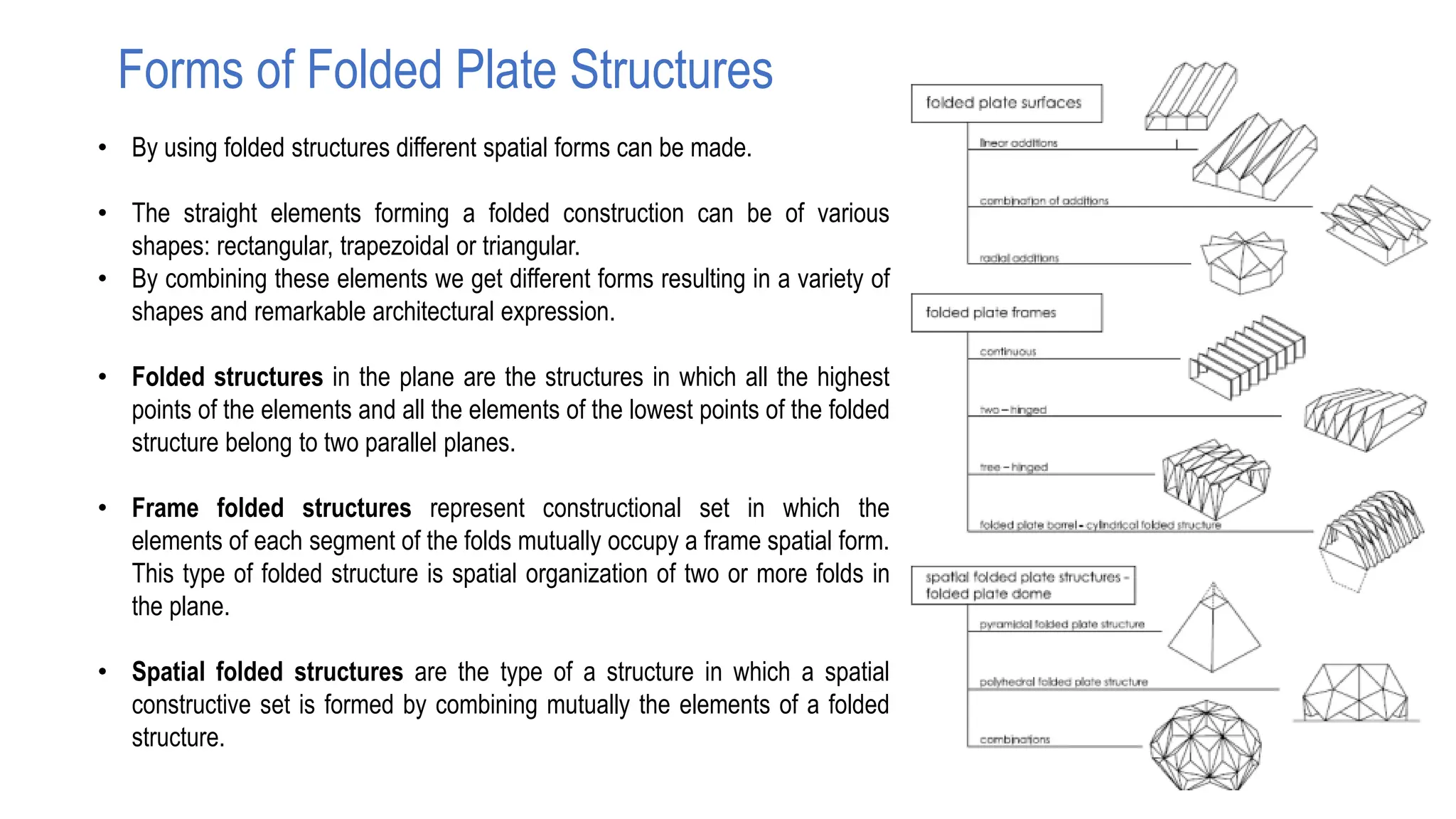
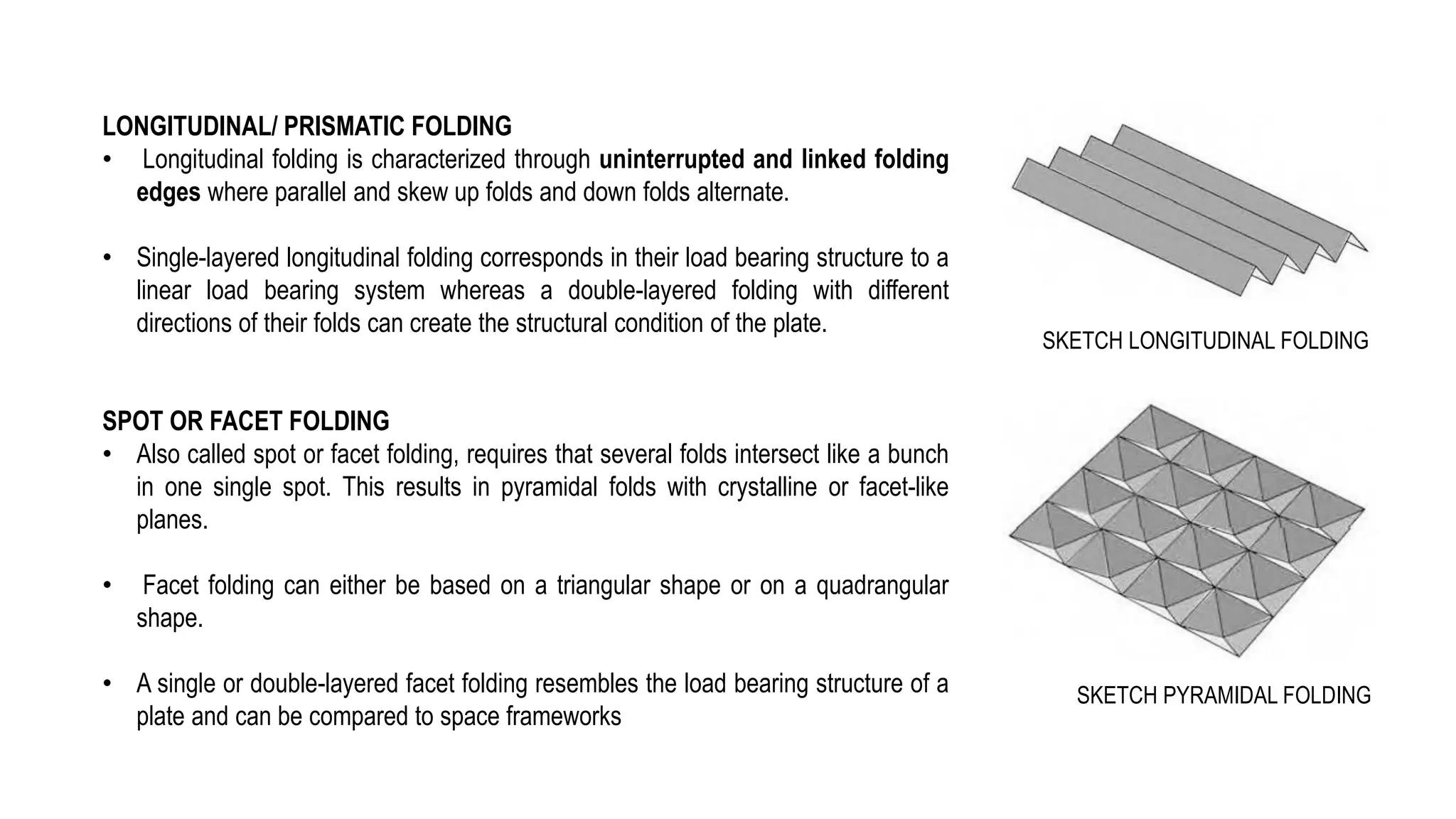
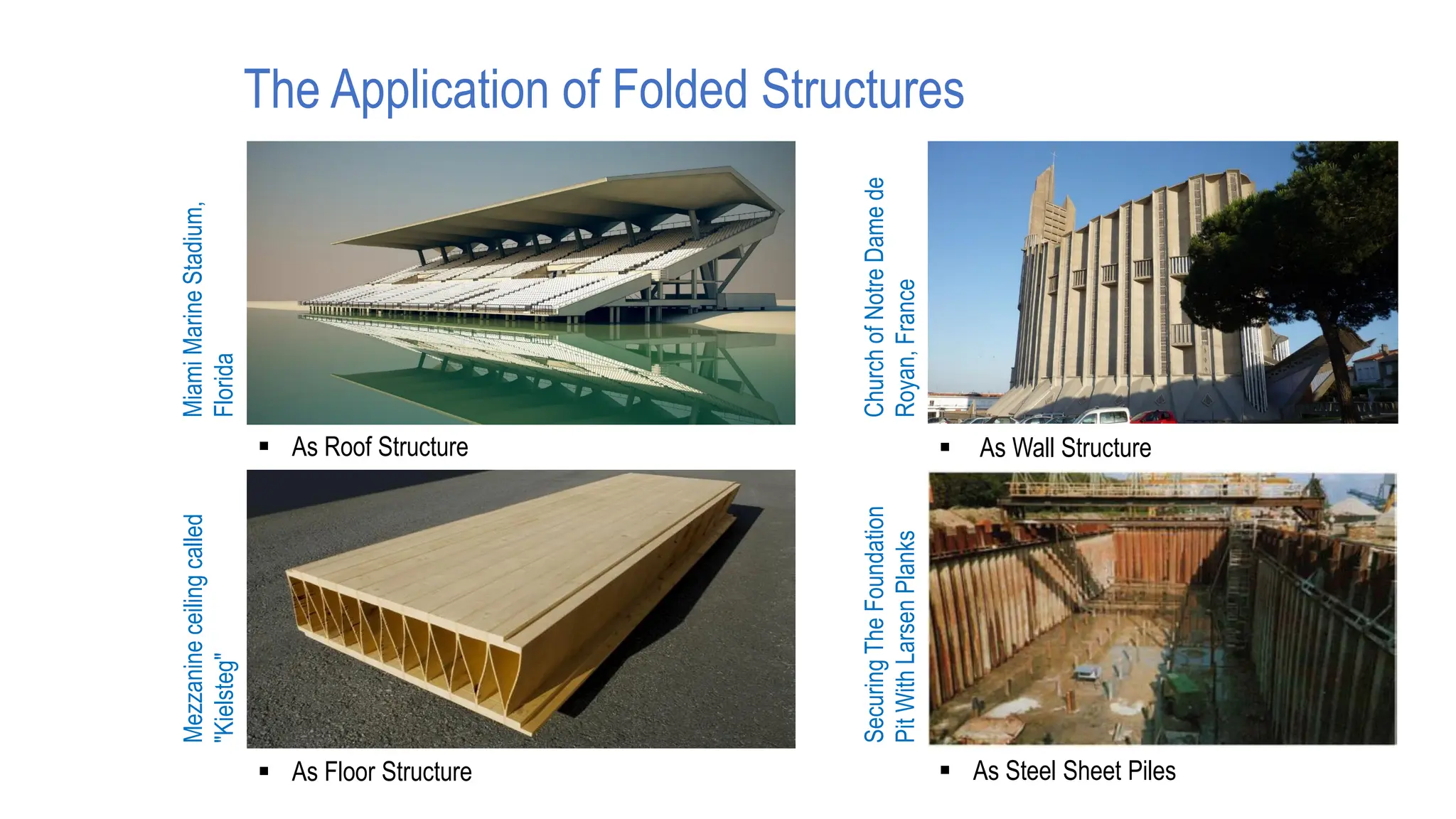
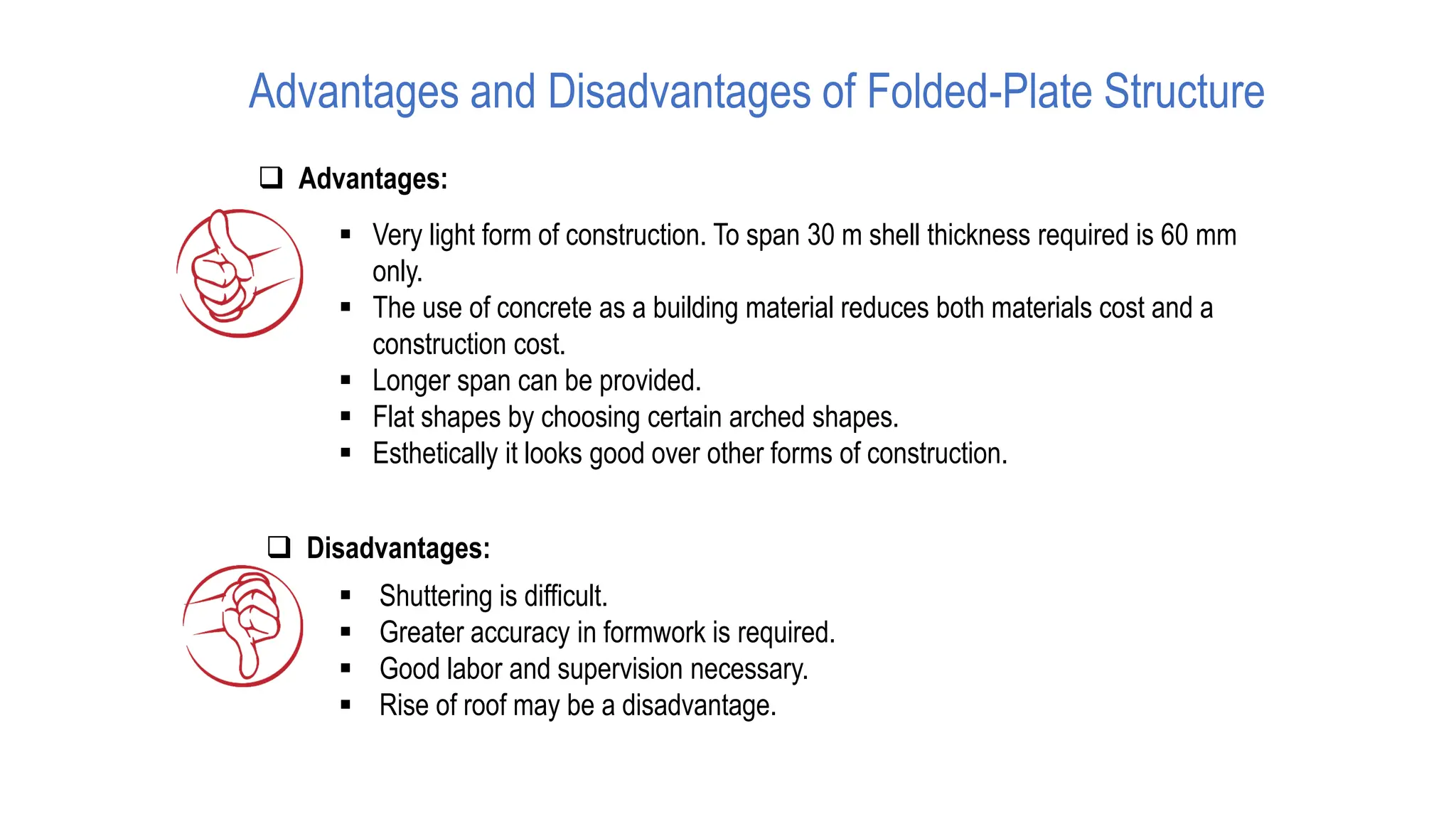
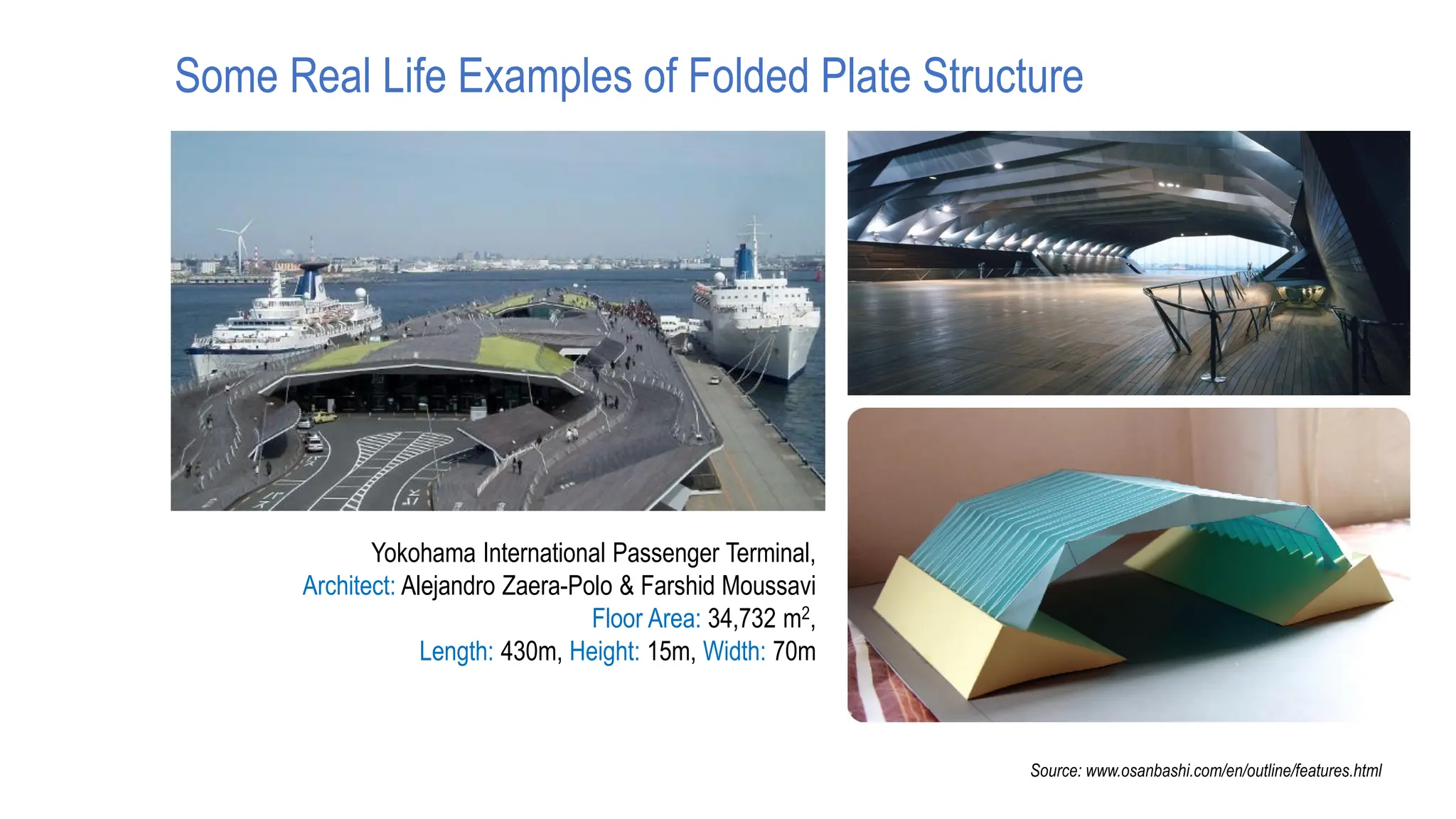
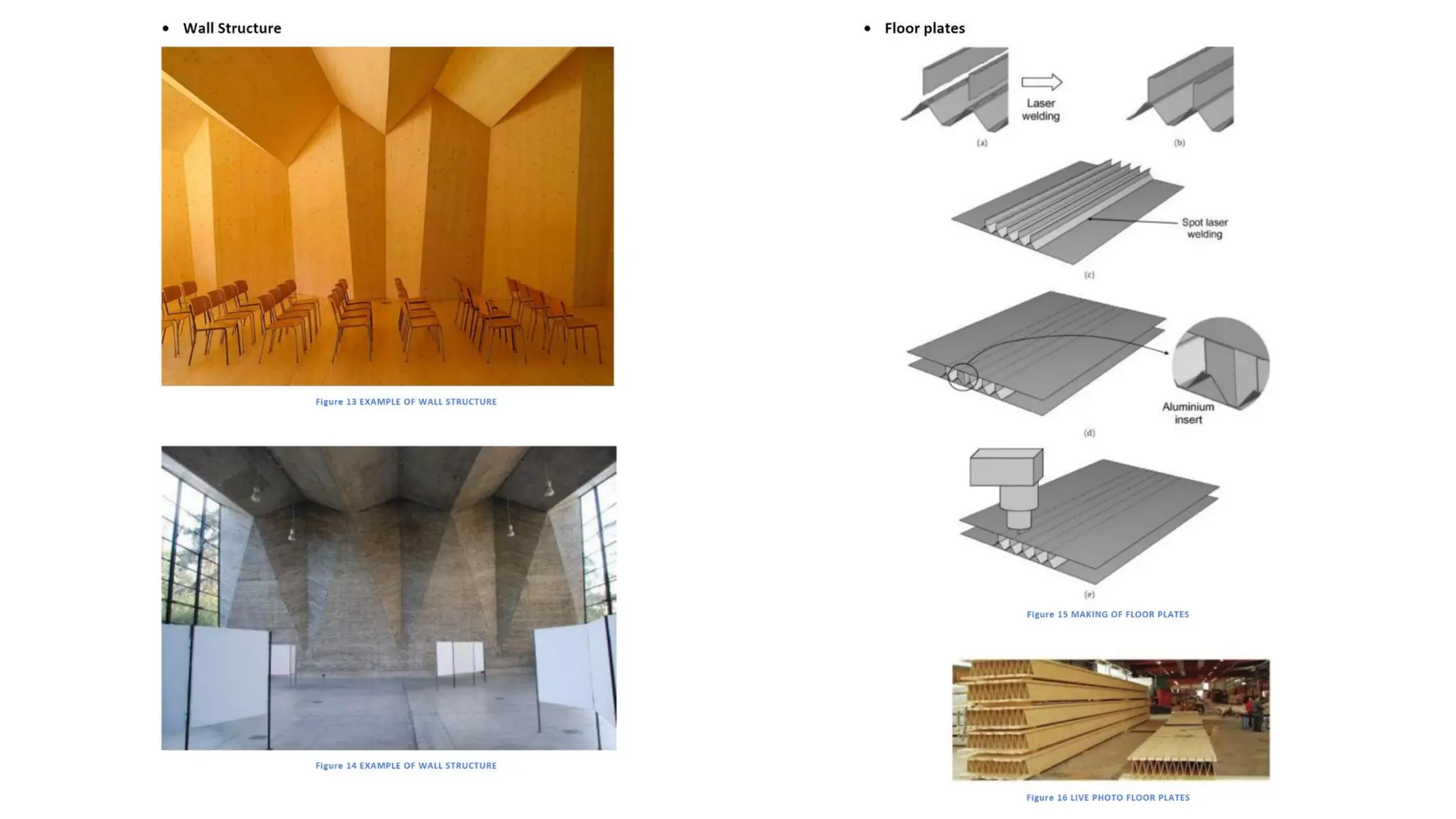
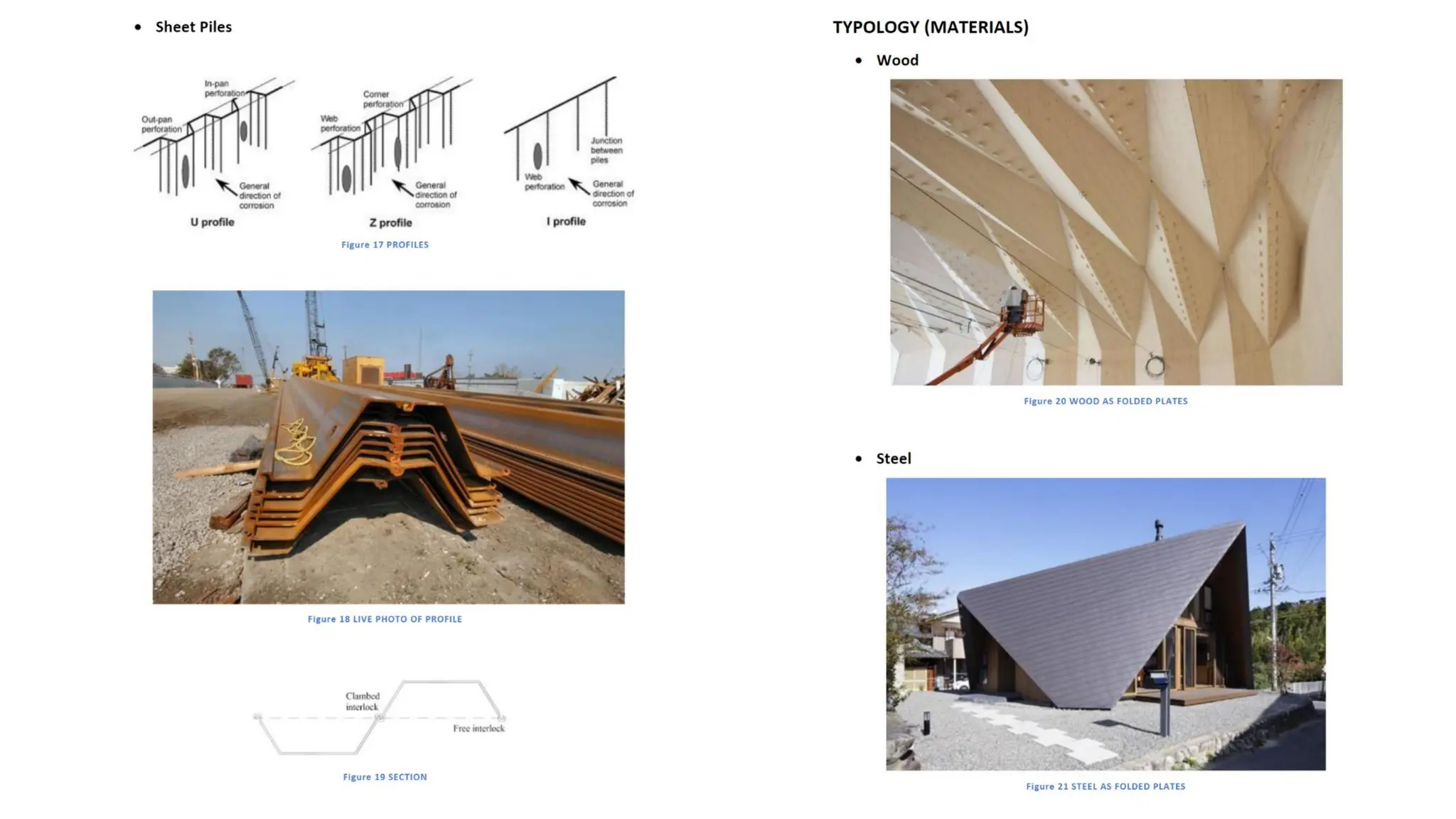
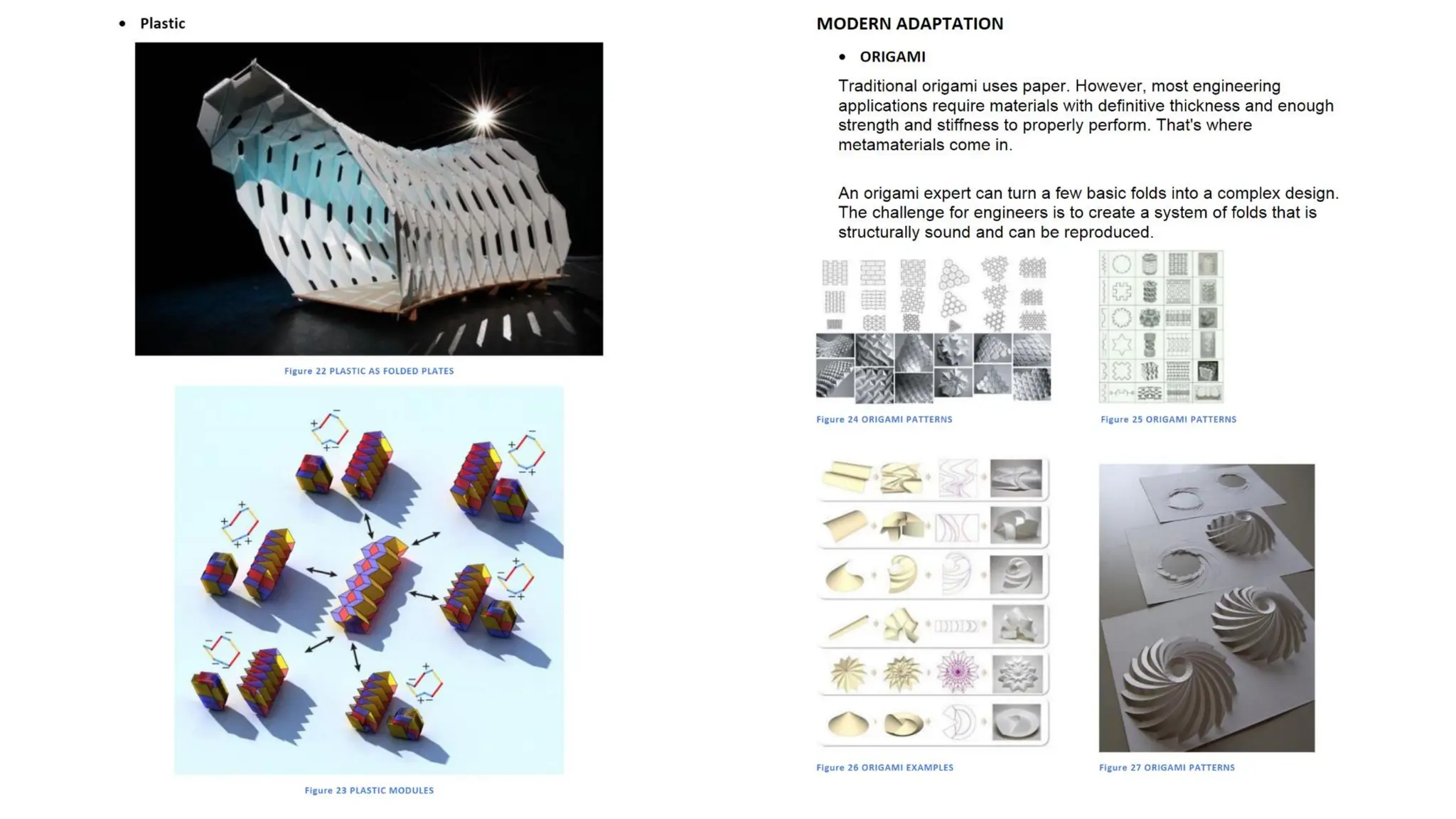
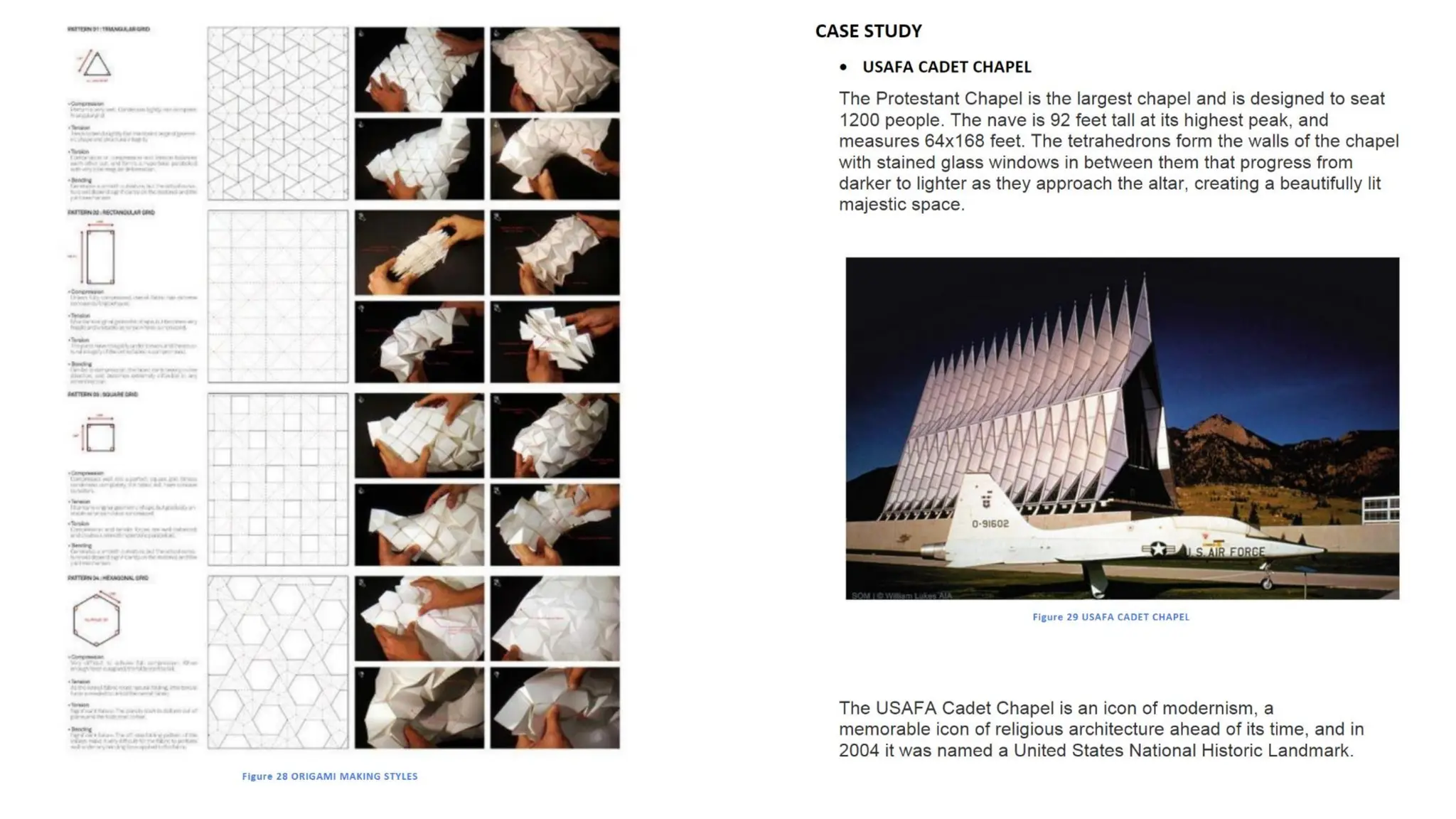
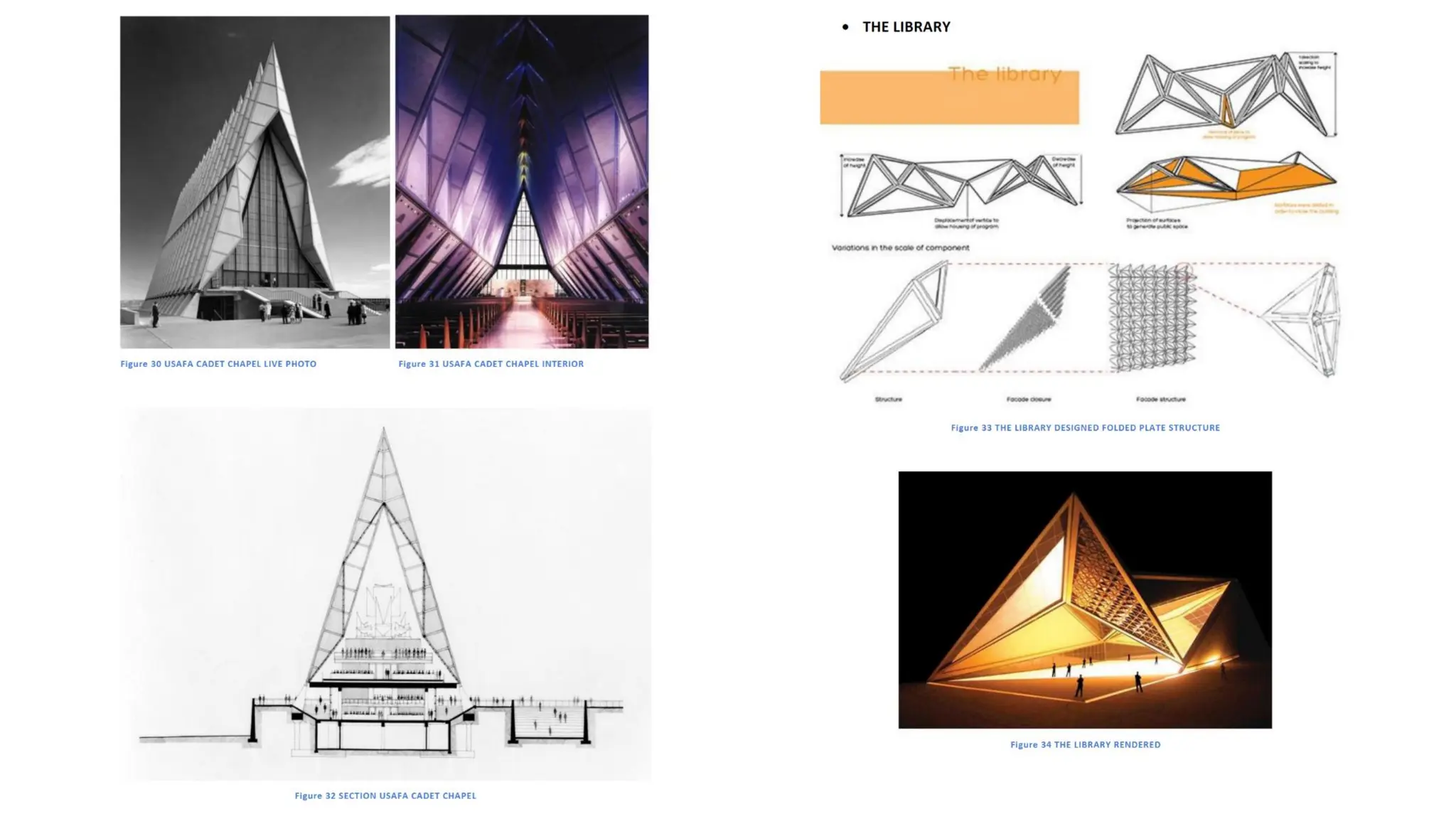
Folded plate structures consist of flat plates connected along their edges to form a structural system capable of carrying loads without additional beams. They were inspired by folding patterns in nature. There are different types including linear, radial, and spatial folding based on the shape and load distribution. Folded plates are lighter than other shell structures but require accurate formwork. Examples of their use include roofs, walls, floors, and foundations.