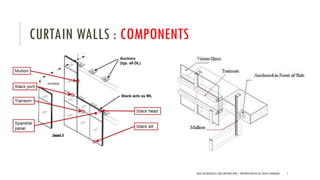
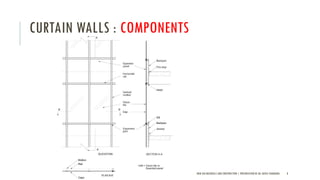
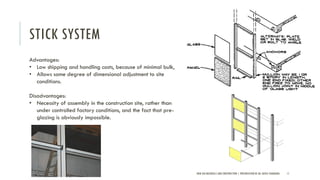
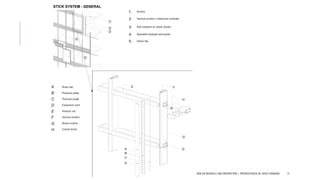
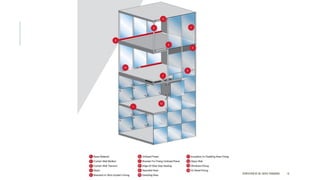
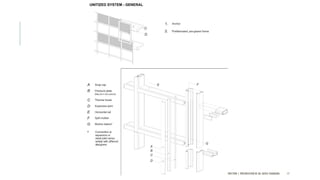
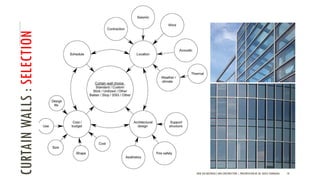
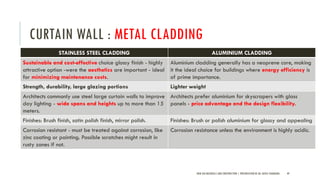
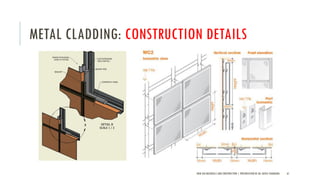
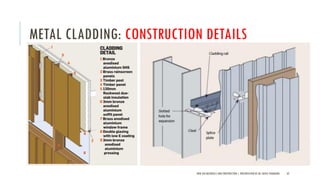
The document discusses curtain walls, which are non-load bearing exterior walls that provide aesthetics and protection from weather. Curtain walls are made of glass, steel, aluminum or other modern materials. They are assembled using stick systems where individual panels are installed, or unitized systems where entire sections are assembled in a factory. Common types include glass, metal-clad, and composite panel walls. Materials like glass, aluminum, stainless steel, copper and brass are used for their durability, flexibility, corrosion resistance and aesthetic qualities in curtain wall construction.