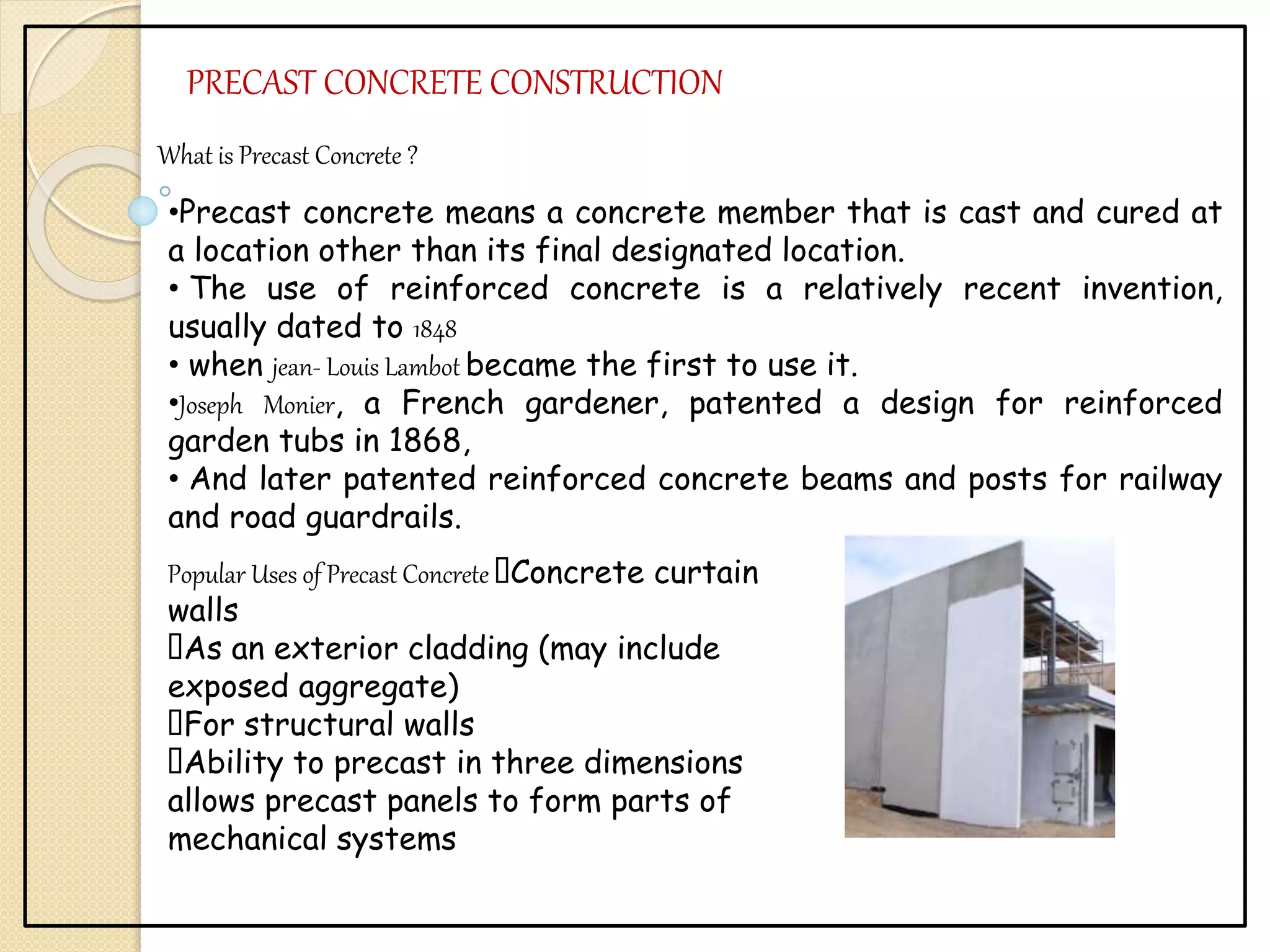
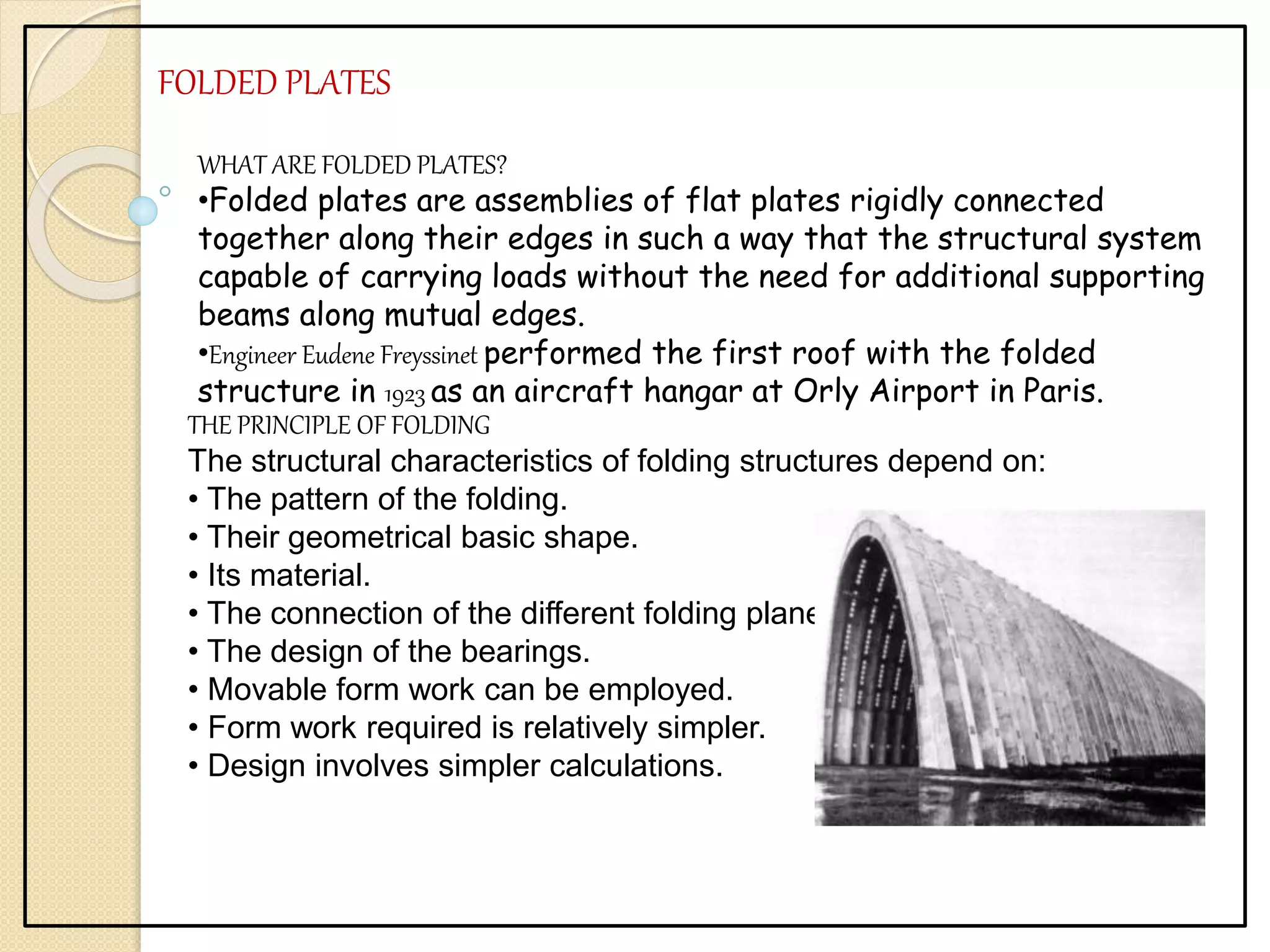
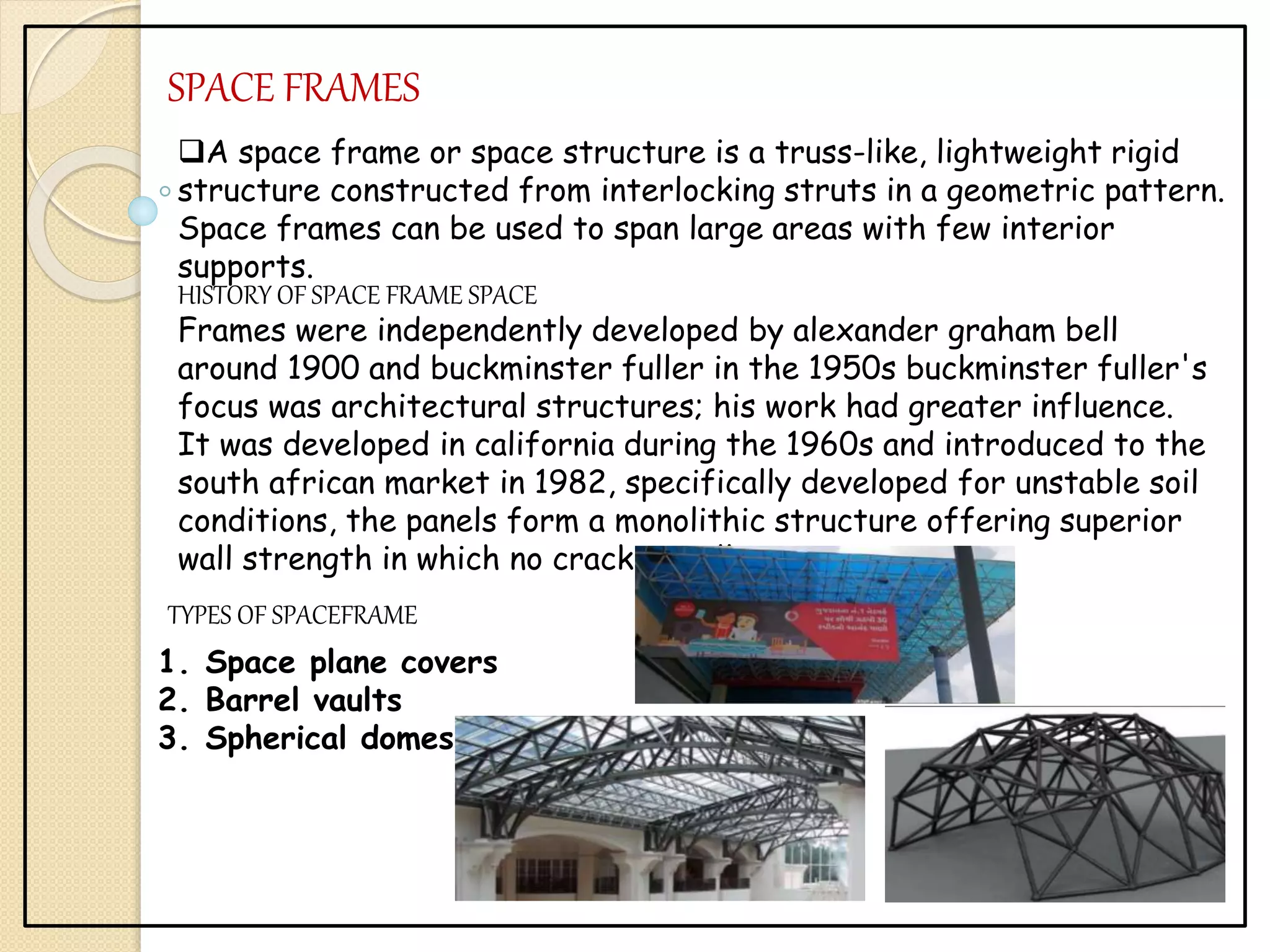
This document discusses several advanced construction technologies including precast concrete, folded plates, space frames, and shell structures. Precast concrete involves casting structural elements off-site for rapid assembly. Folded plates are rigidly connected flat plates that form structural systems without beams. Space frames are lightweight truss-like structures formed from interlocking struts. Shell structures use curved thin elements like concrete, membrane, or lattices to span large areas with few interior supports.