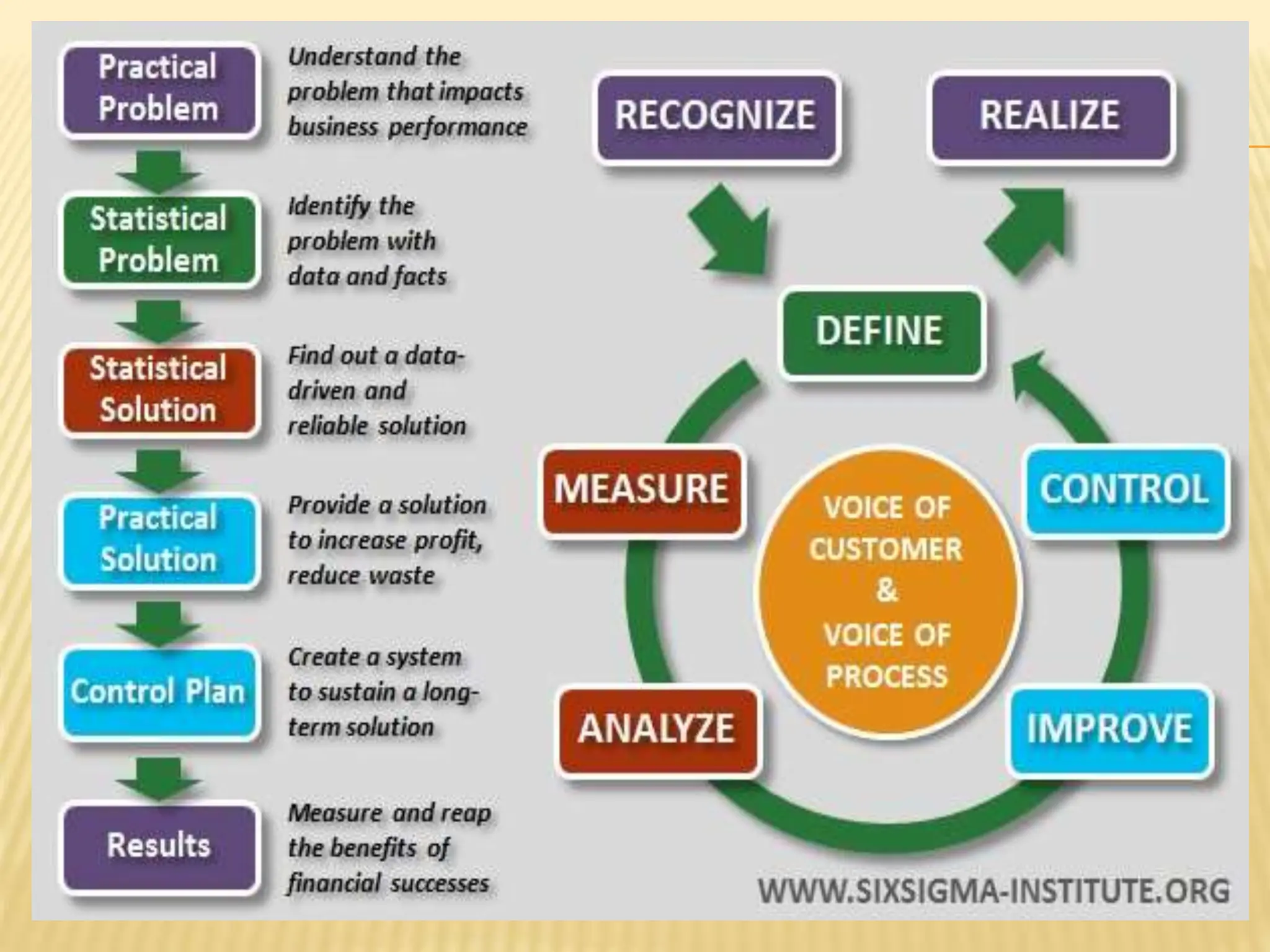
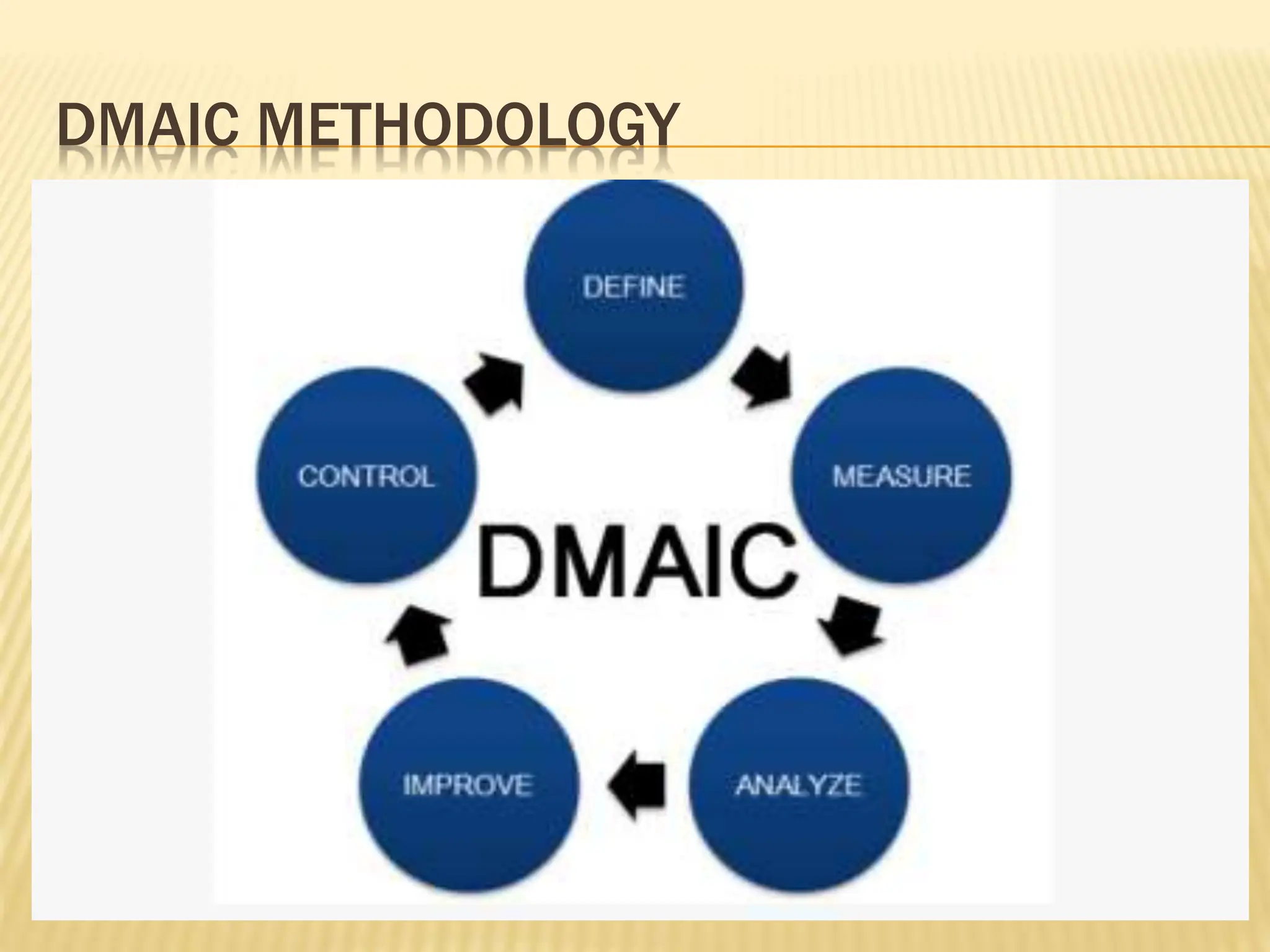
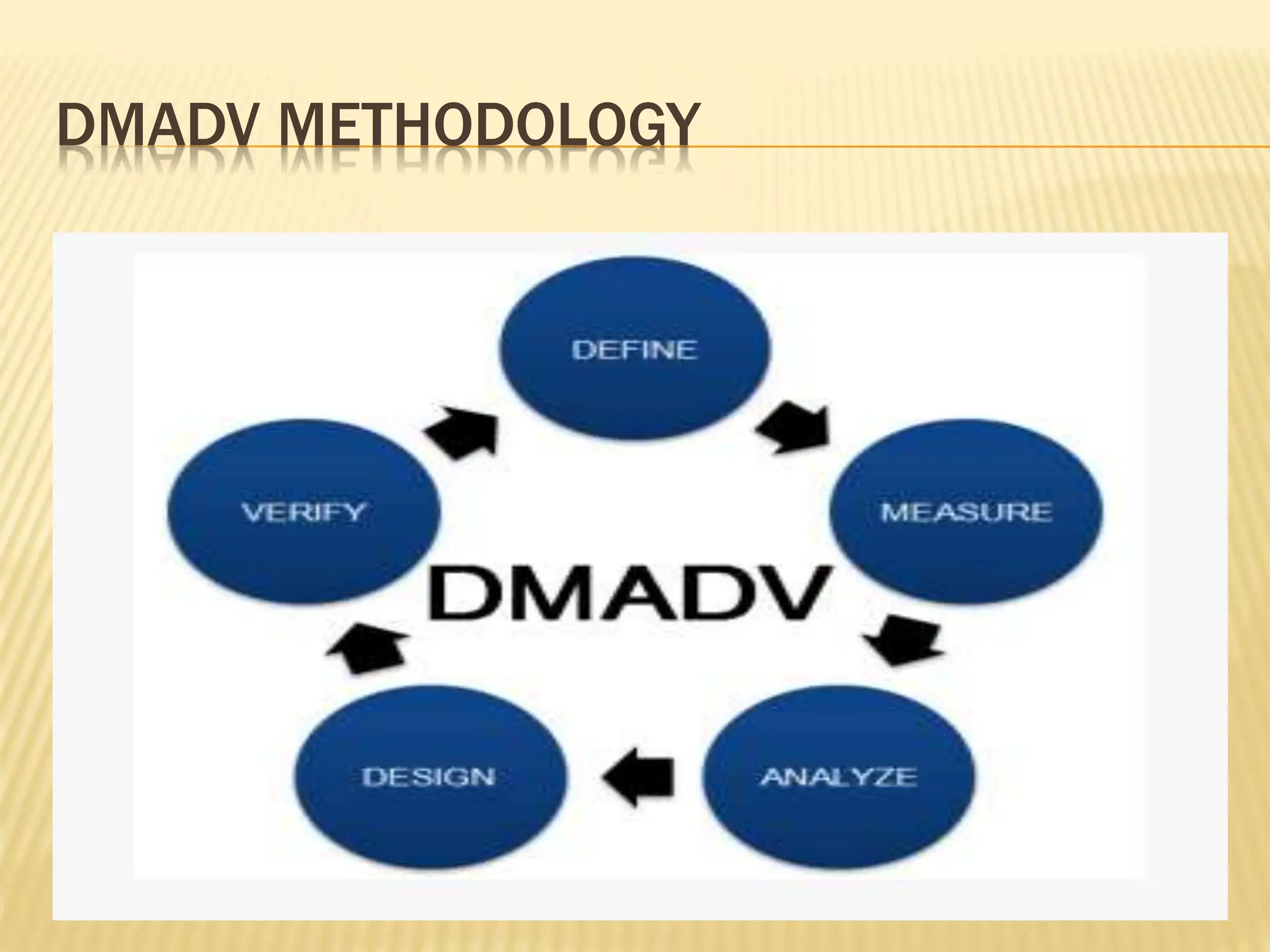
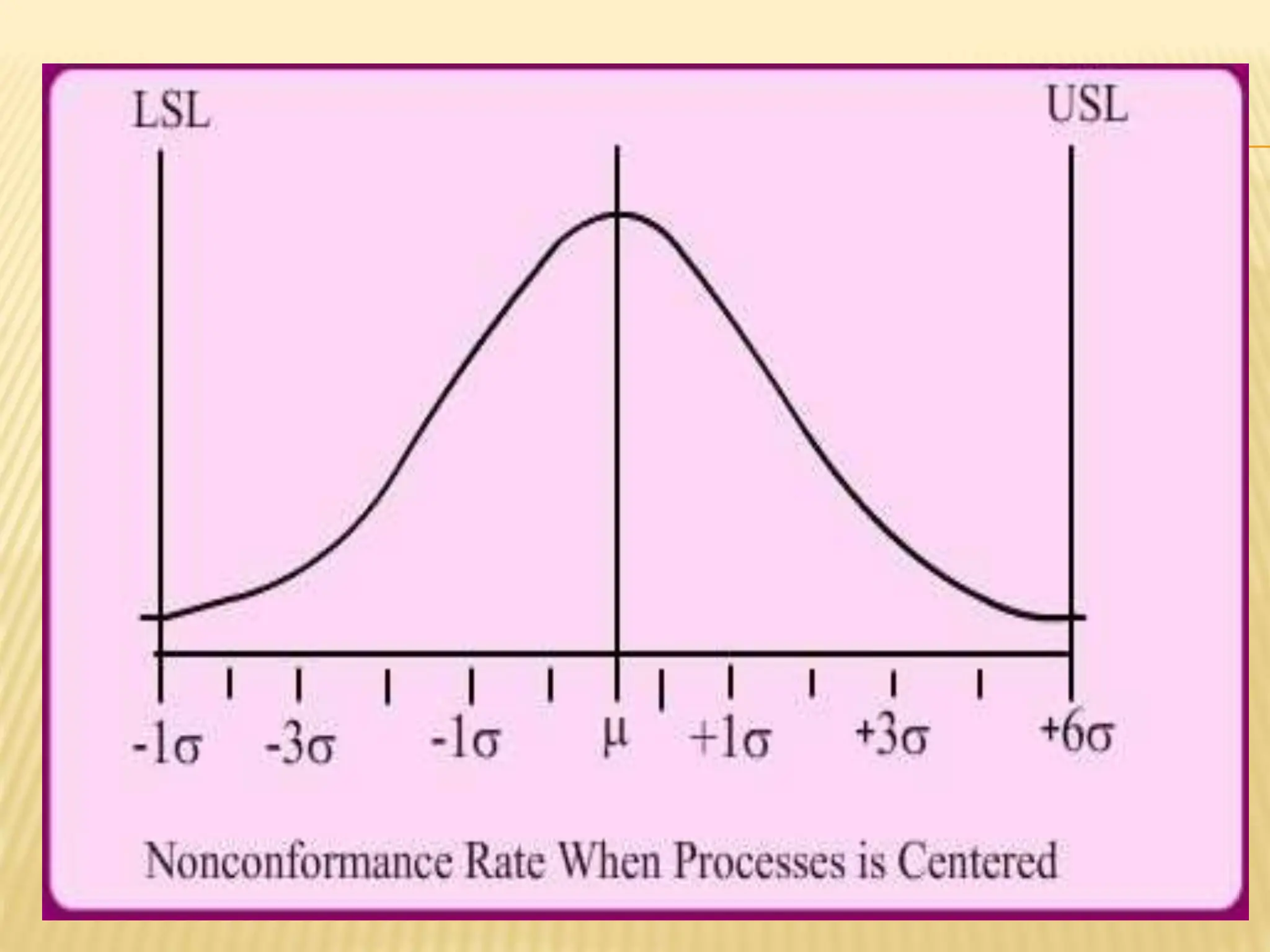
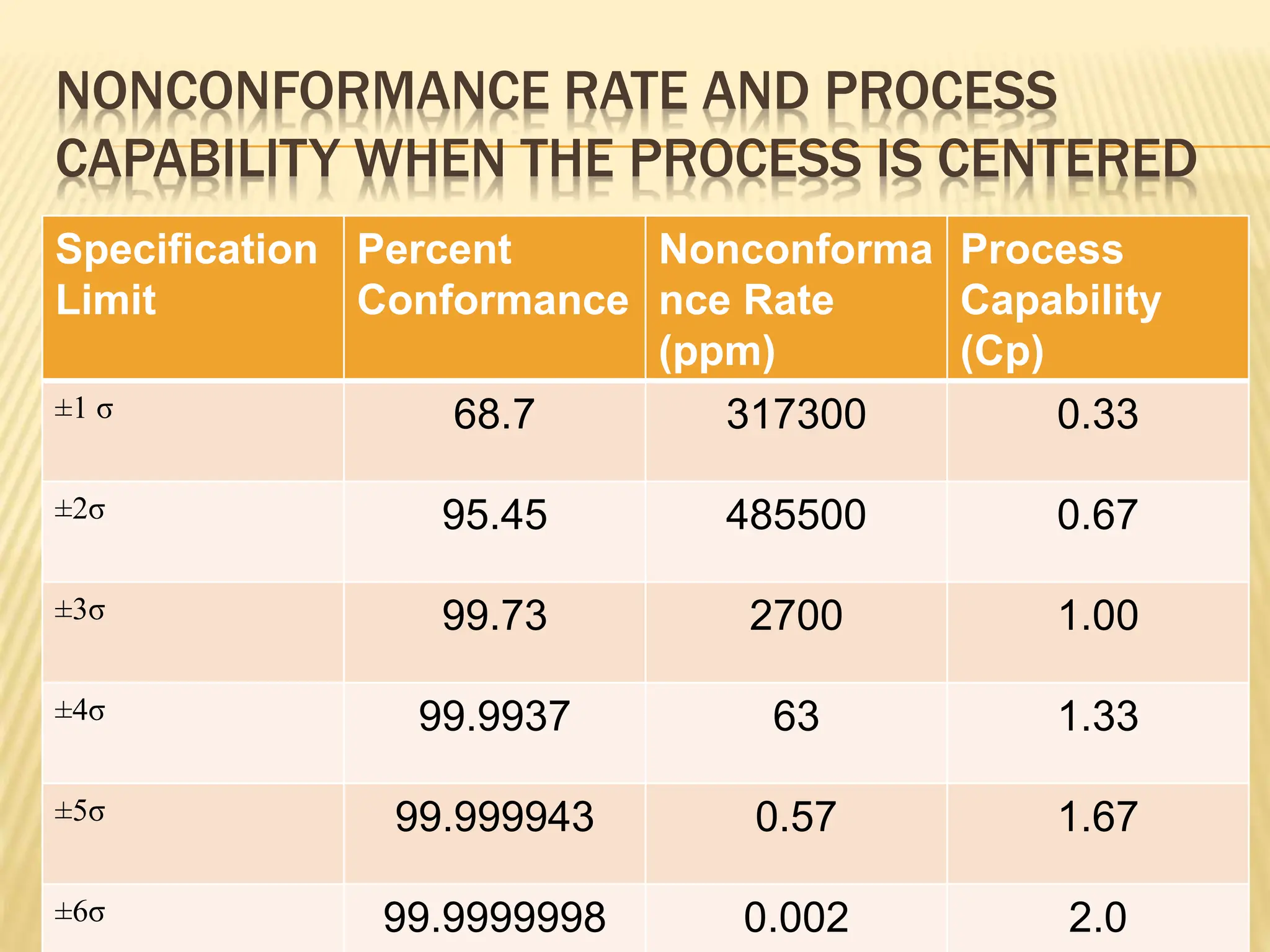
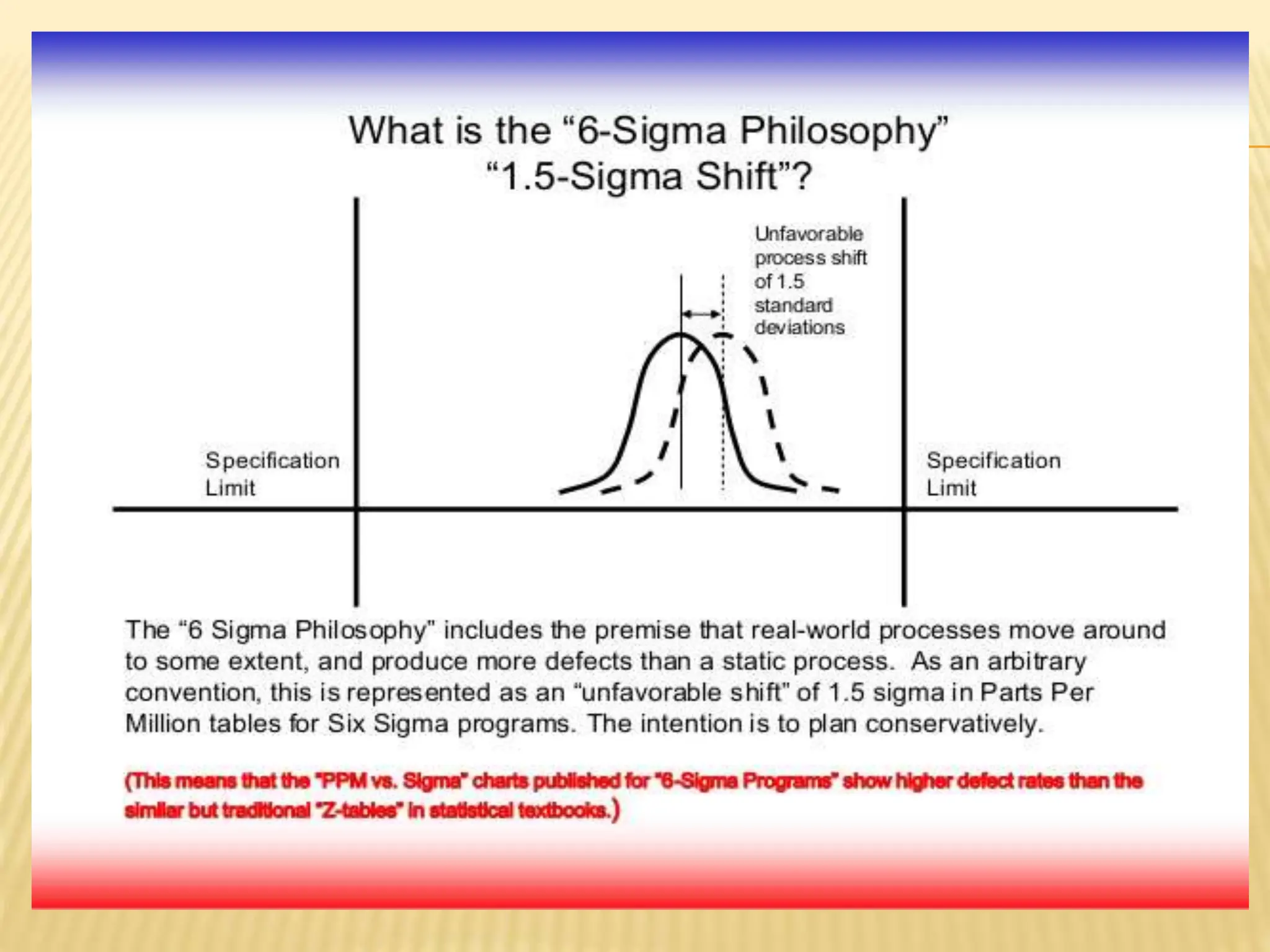
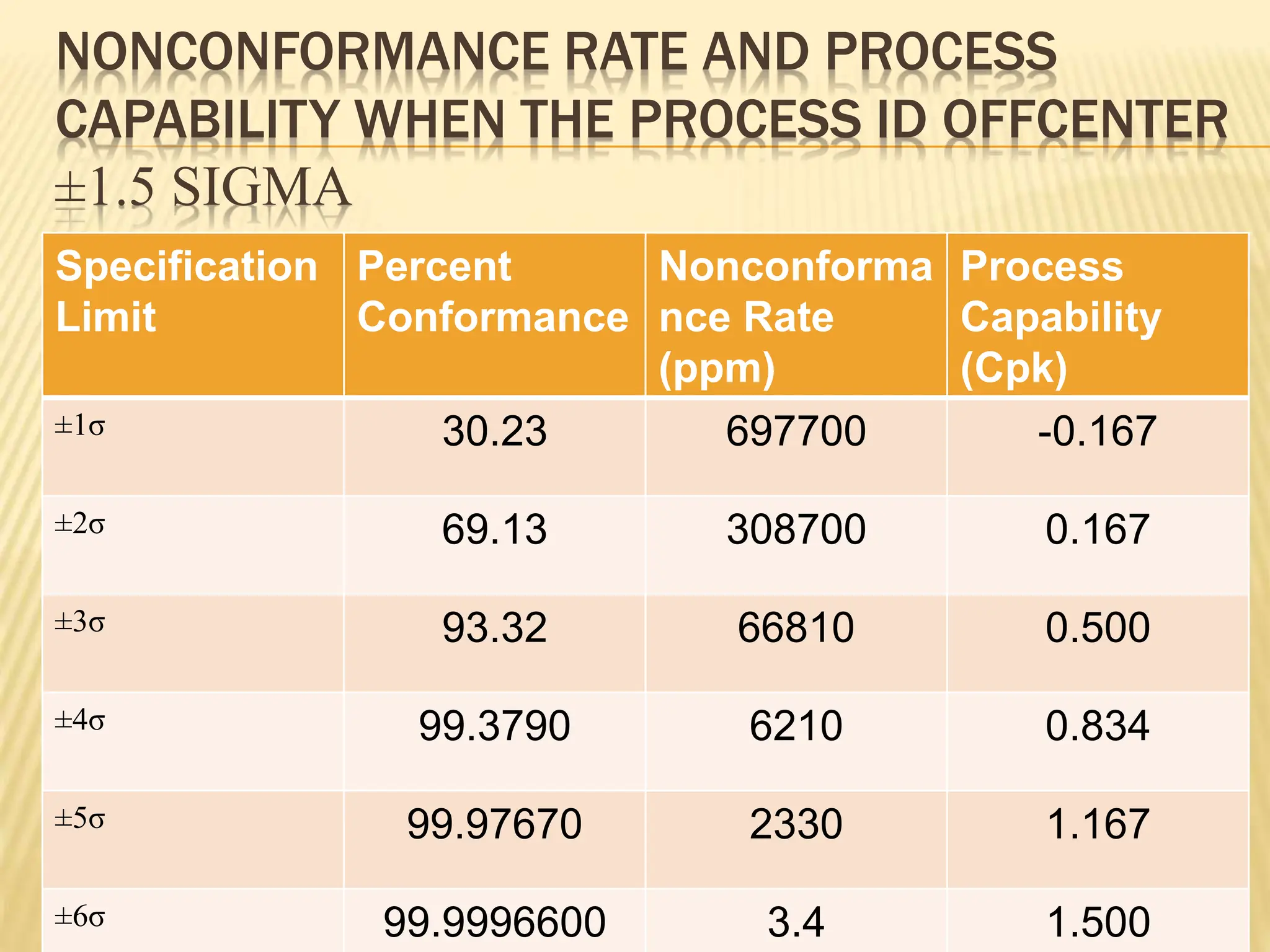
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology for process improvement that aims to reduce defects. It follows the DMAIC cycle of define, measure, analyze, improve, and control. The methodology was developed by Motorola in the 1980s and focuses on minimizing process variation to produce no more than 3.4 defects per million opportunities. Projects use belts ranging from Green to Black to Master Black Belt to implement Six Sigma techniques and achieve a process capability of 1.5 or better. While effective for large companies, Six Sigma can be difficult for small businesses to implement due to infrastructure and training costs.