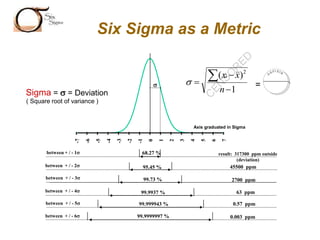
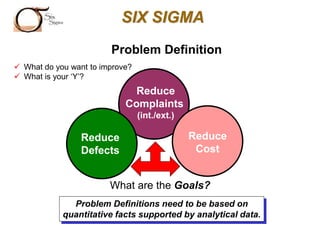
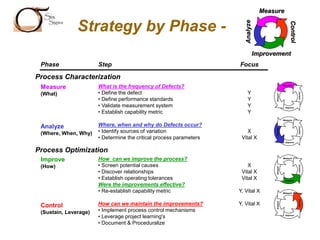
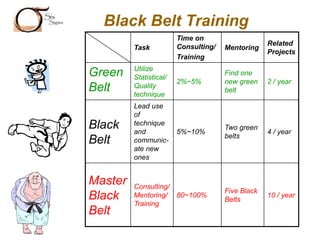
The document outlines the Six Sigma methodology as a problem-solving approach aimed at improving organizational performance by enhancing key process metrics and customer satisfaction. It emphasizes a customer-focused philosophy, the importance of employee engagement, and the need for rigorous data analysis and statistical tools to identify and eliminate defects. Additionally, it describes the DMAIC framework (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) for managing Six Sigma projects, highlighting strategies for continuous improvement and operational excellence.