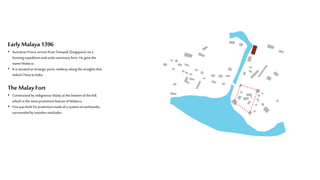
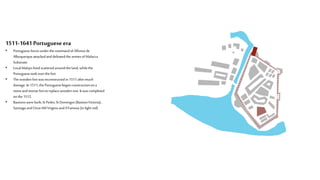
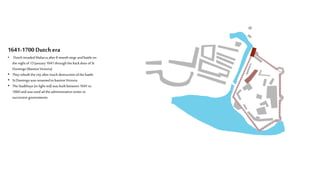
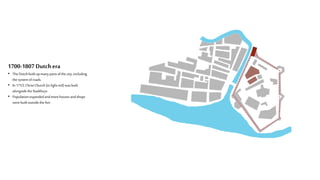
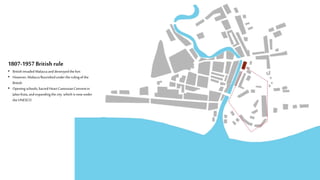
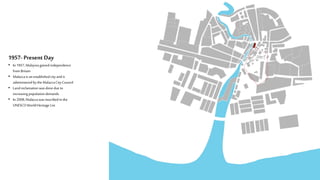
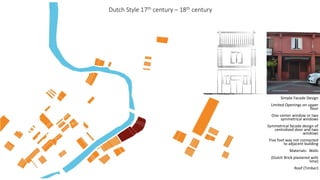
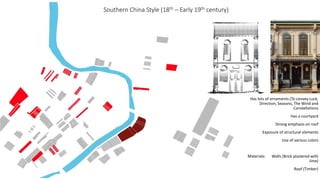
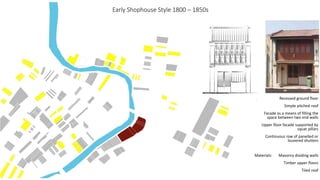
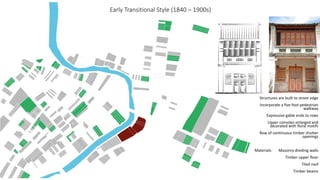
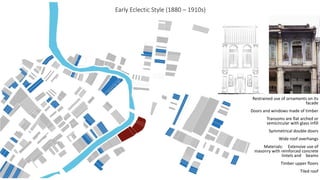
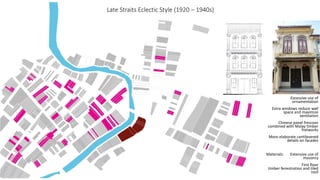
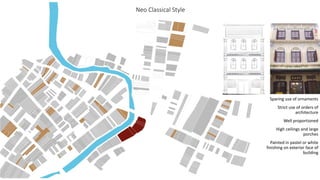
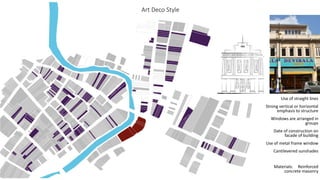
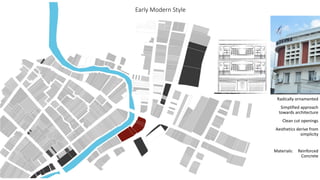
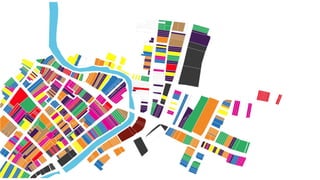
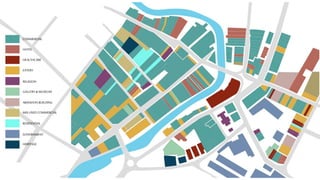
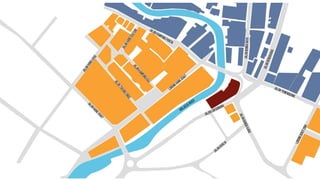
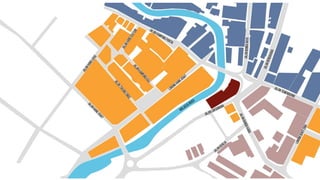
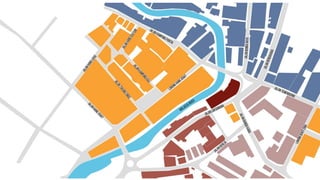
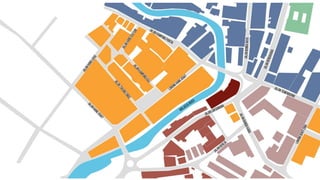
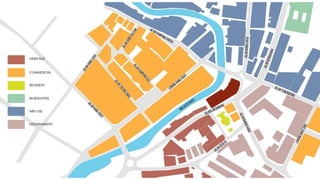
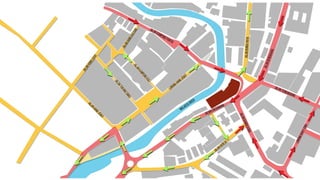
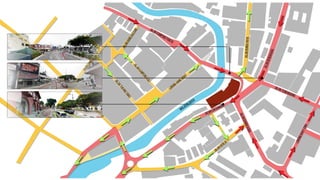
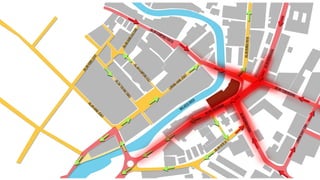
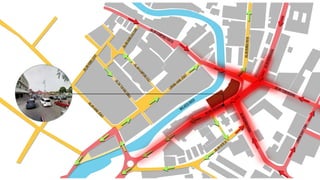
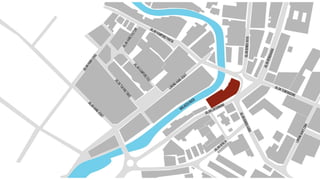
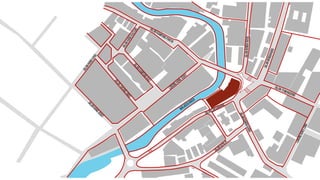
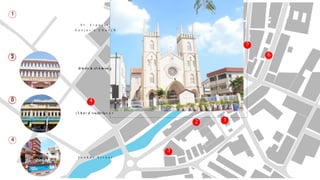
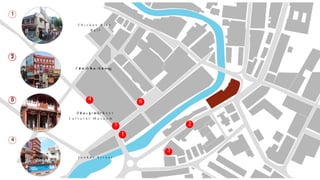
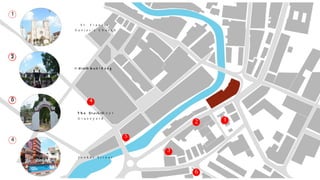
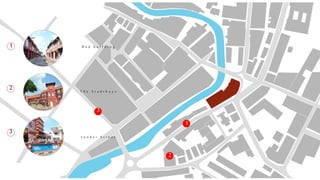
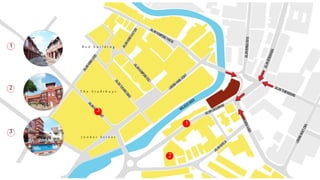
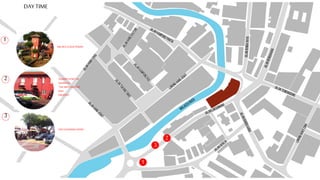
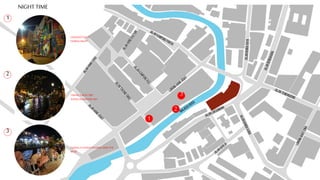
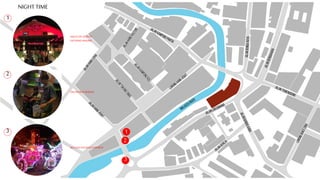
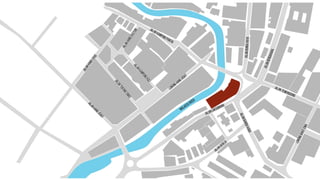
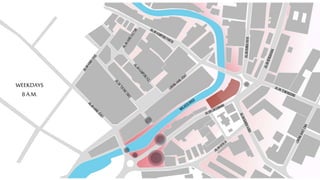
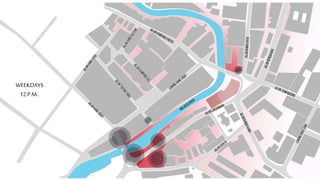
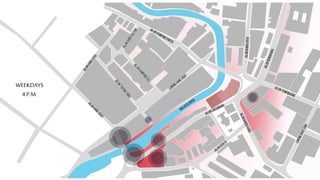
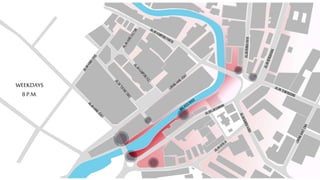
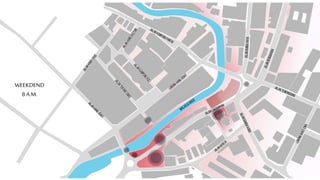
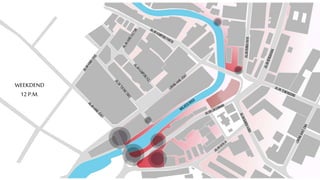
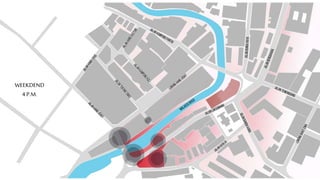
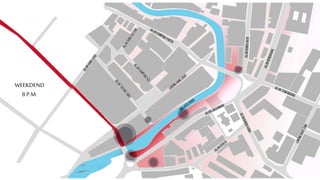
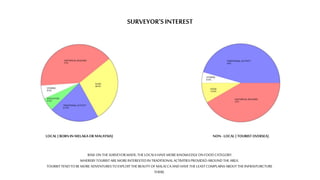
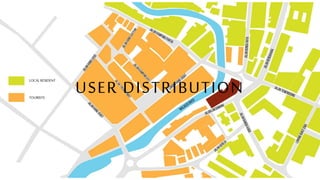
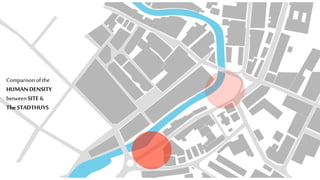
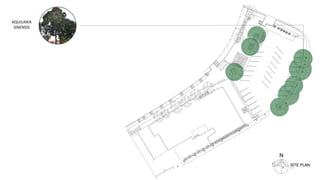
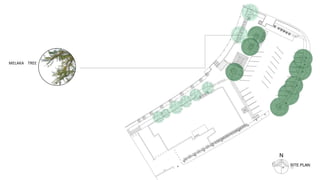
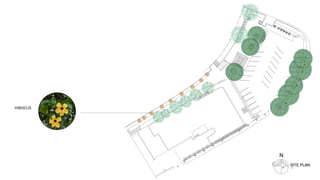
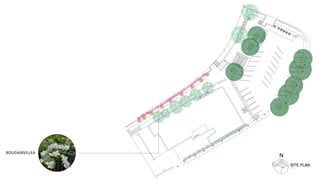
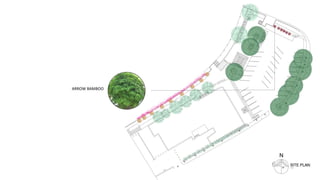
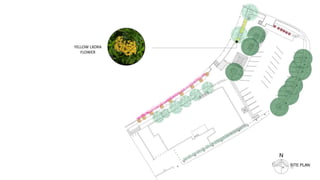
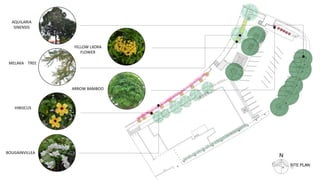
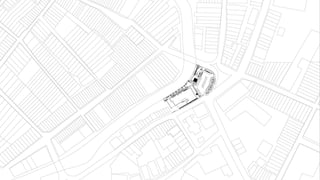
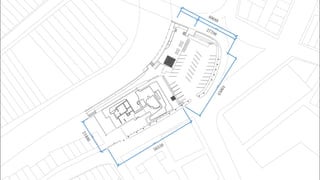
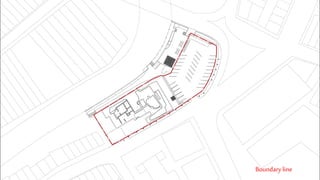
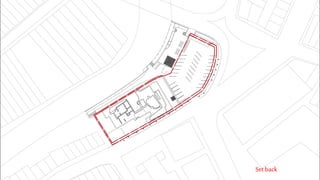
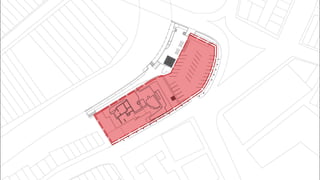
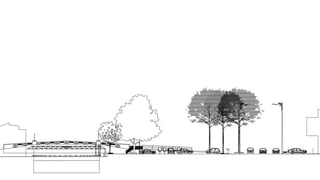
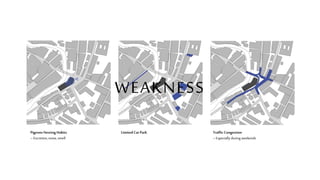
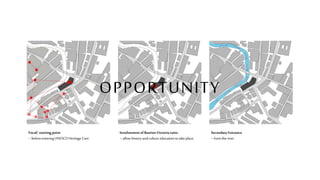
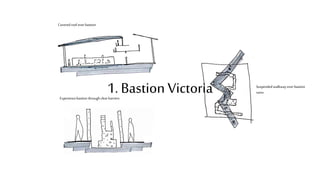
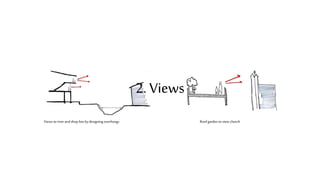
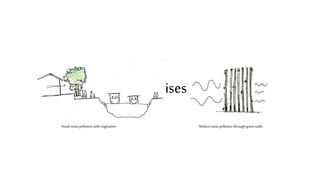
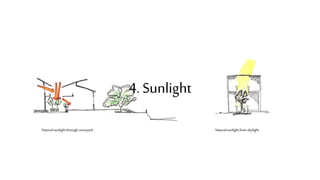
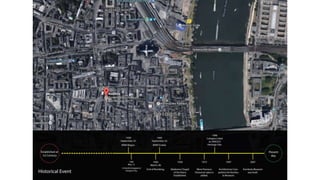
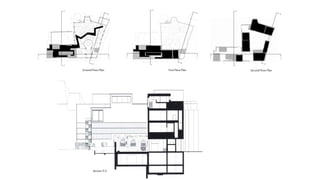
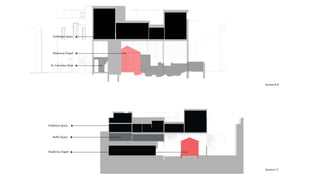
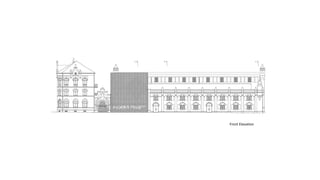
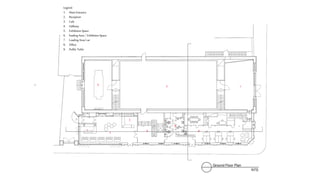
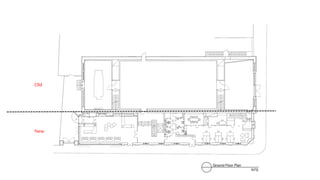
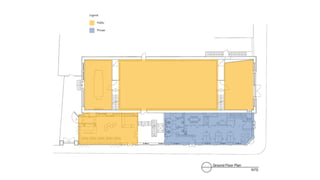
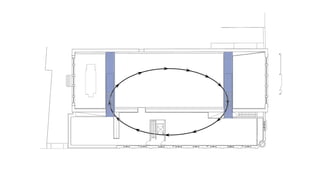
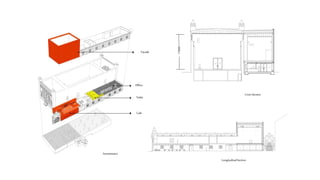
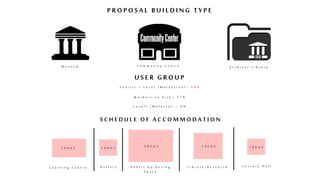
This document provides a history of Melaka from 1396 to present day. It begins with a Sumatran prince seeking sanctuary in Melaka and establishing the city. It then discusses the construction of the Malay fort for protection. It outlines the Portuguese, Dutch, and British rule over Melaka from 1511 to 1957 when Malaysia gained independence. Architectural styles that developed during each period are also described. The document concludes with sections on land use, vegetation, and landmarks in Melaka.