Embed presentation
Download to read offline
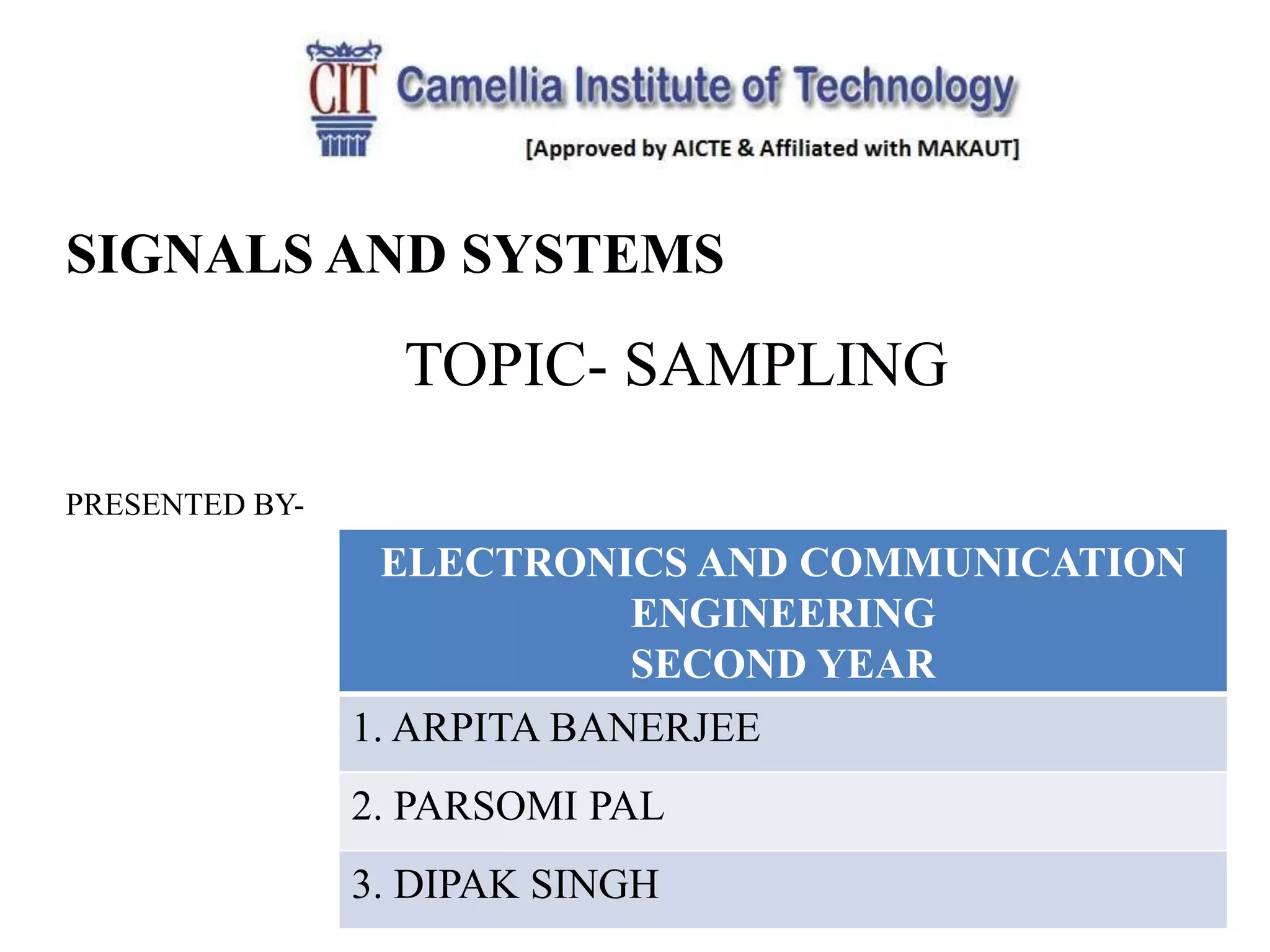


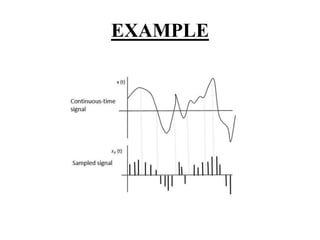
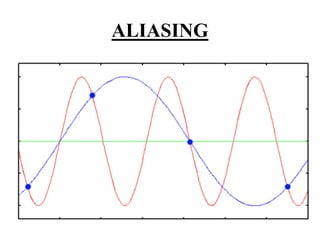




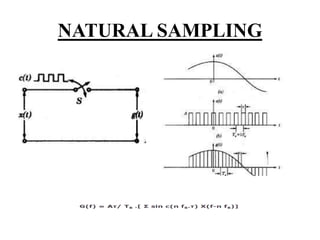
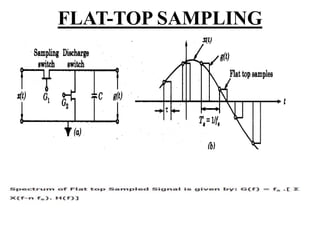
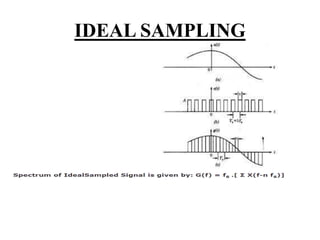


This document discusses sampling in signals and systems. It defines sampling as measuring the instantaneous values of a continuous-time signal in discrete form. It describes concepts like aliasing, decimation, the Nyquist rate, the Nyquist theorem, and the aperture effect. The Nyquist theorem states that a signal can be reproduced if sampled at a rate greater than twice the maximum frequency. It also discusses types of sampling like natural sampling, flat-top sampling, and ideal sampling.












