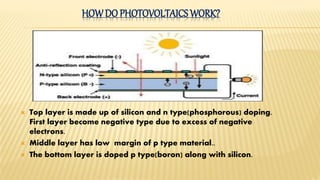
The document discusses the photovoltaic effect, defined as the generation of voltage in semiconductors when exposed to light, and provides a history of its discovery by Edmond Becquerel in 1839. It explains how photovoltaics convert sunlight into electricity, outlines different solar technologies, and highlights the advantages and disadvantages of photovoltaic systems. The text concludes with potential inquiries about photovoltaics and their practical applications.