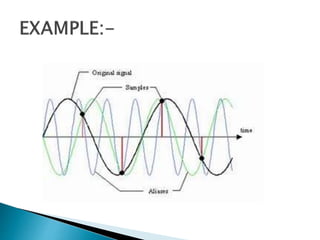
Aliasing occurs when a high frequency signal appears as a low frequency after sampling. It can happen when sampling audio signals over time (temporal aliasing) or patterns in images spatially. Aliasing happens because sampling acts as a low-pass filter, and the Nyquist sampling criterion states the sampling frequency must be at least twice the highest frequency to avoid aliasing. An anti-aliasing filter before sampling can restrict the bandwidth to satisfy the sampling theorem, but a real filter cannot perfectly block frequencies and some aliasing may still occur, so systems often oversample to ensure accurate reconstruction. An ideal anti-aliasing filter completely passes frequencies below the cutoff and cuts off those above, but a physical filter has a transition band where signals