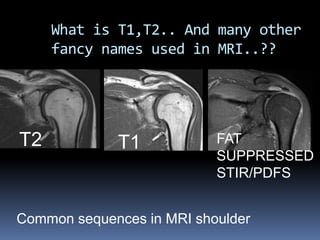
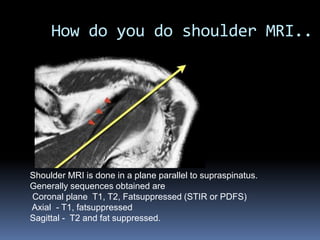
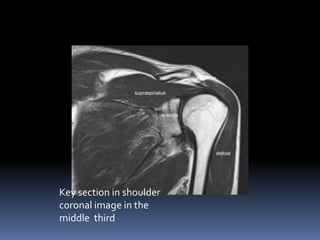
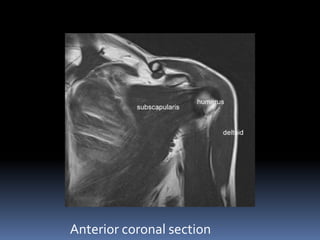
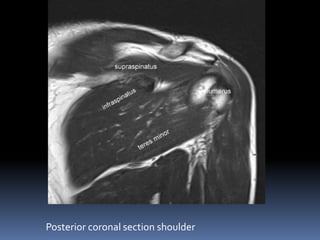
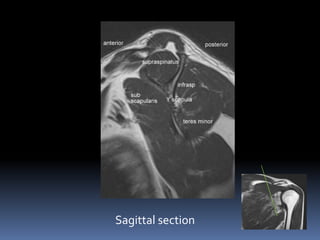
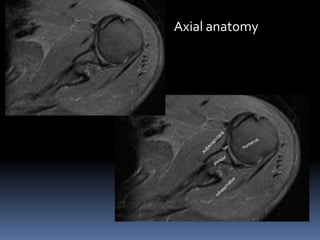
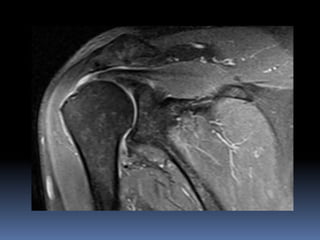
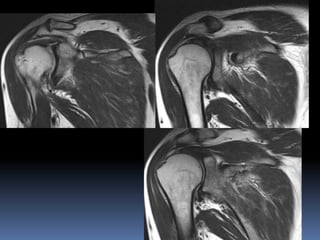
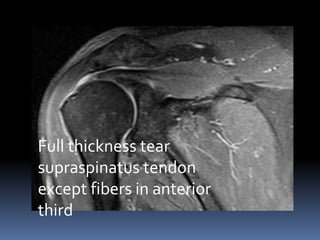
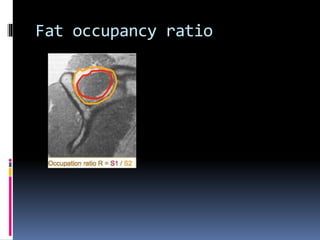
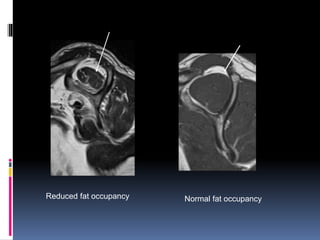
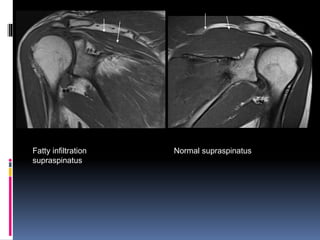
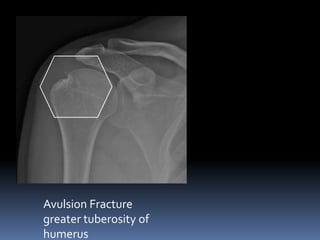
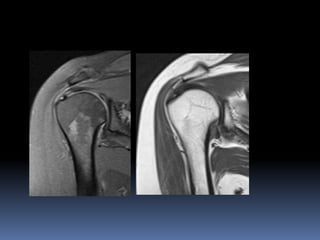
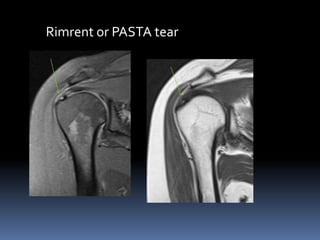
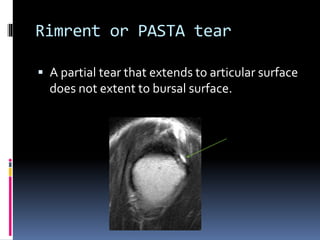
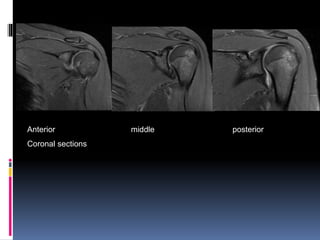
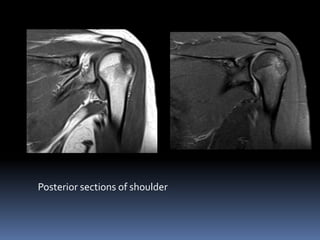
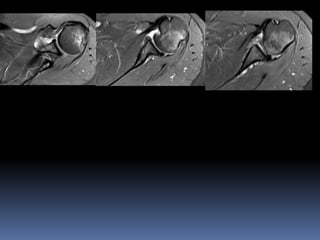
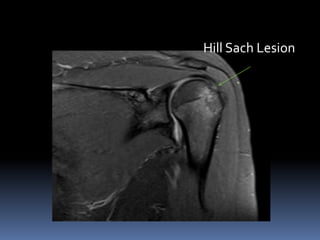
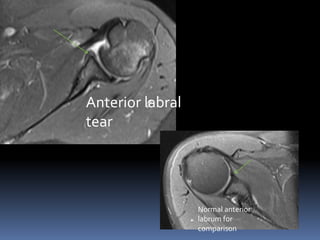
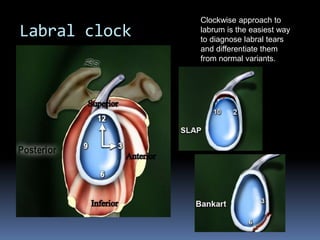
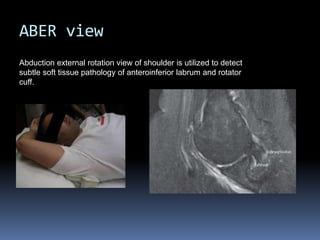
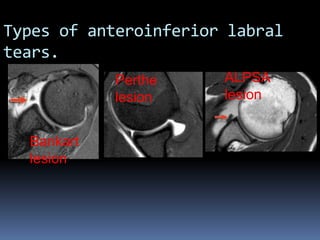
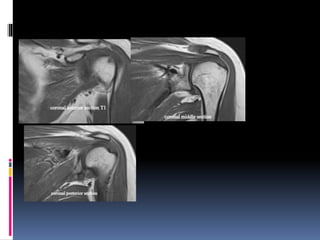
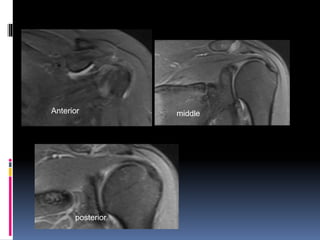
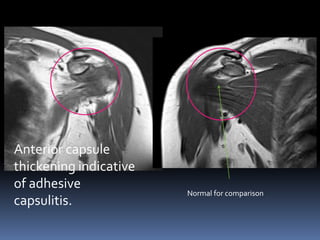
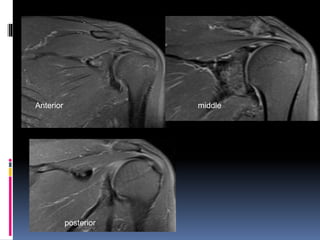
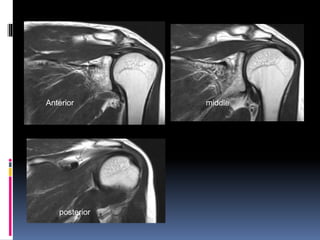
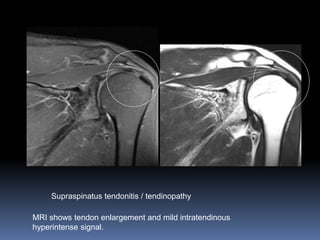
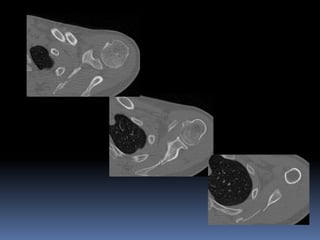
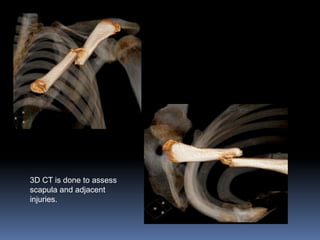
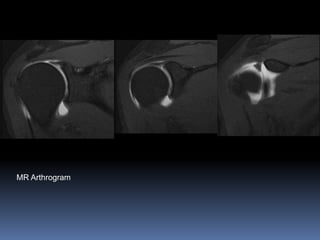
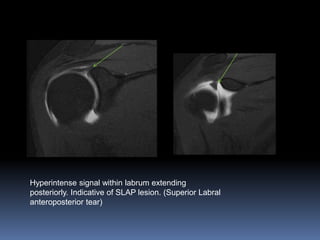
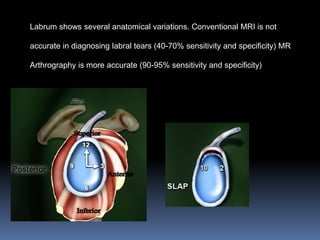
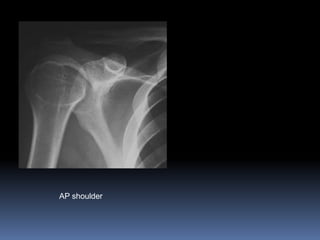
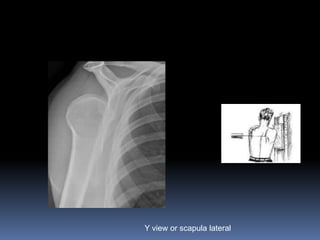
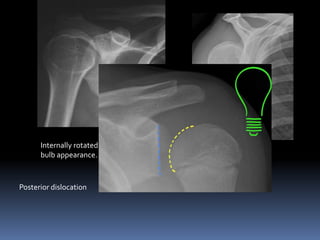
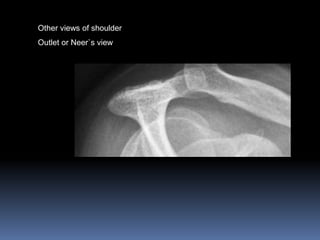
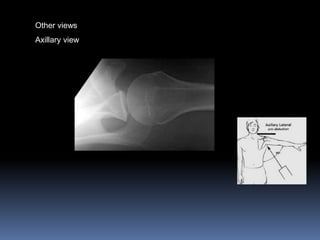
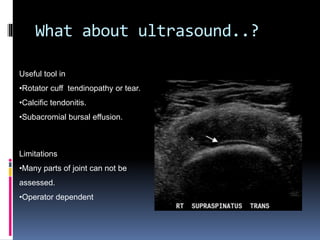
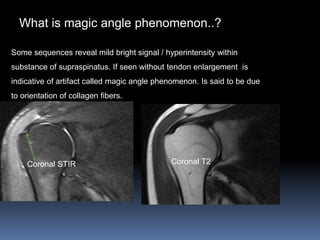
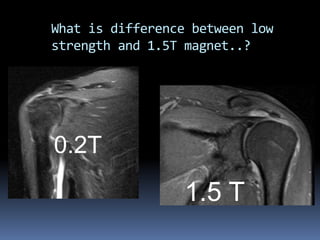
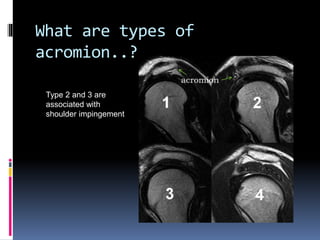
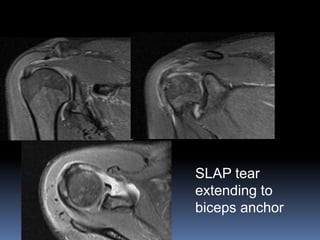
This document discusses MRI of the shoulder joint. It provides information on common MRI sequences used for the shoulder, key anatomical sections imaged, and various pathologies that can be seen. Example cases are presented to demonstrate common injuries like rotator cuff tears, labral tears, fractures, and adhesive capsulitis. The importance of correlating MRI findings with arthroscopy is emphasized given the potential for asymptomatic findings on MRI.