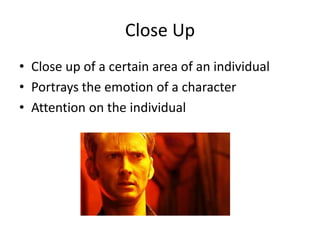
This document defines and describes various shot types and camera movements used in filmmaking. It discusses low angle, high angle, and mid-shots used to portray characters. It also covers canted angles, bird's eye views, close ups, follow/over the shoulder shots, and point of view shots. Long shots, establishing shots, and extreme close ups are also defined. Finally, it lists common camera movements like pans, tilts, dolly zooms, arcs, zooms, tracks, crabbing/sideways, and crane shots.