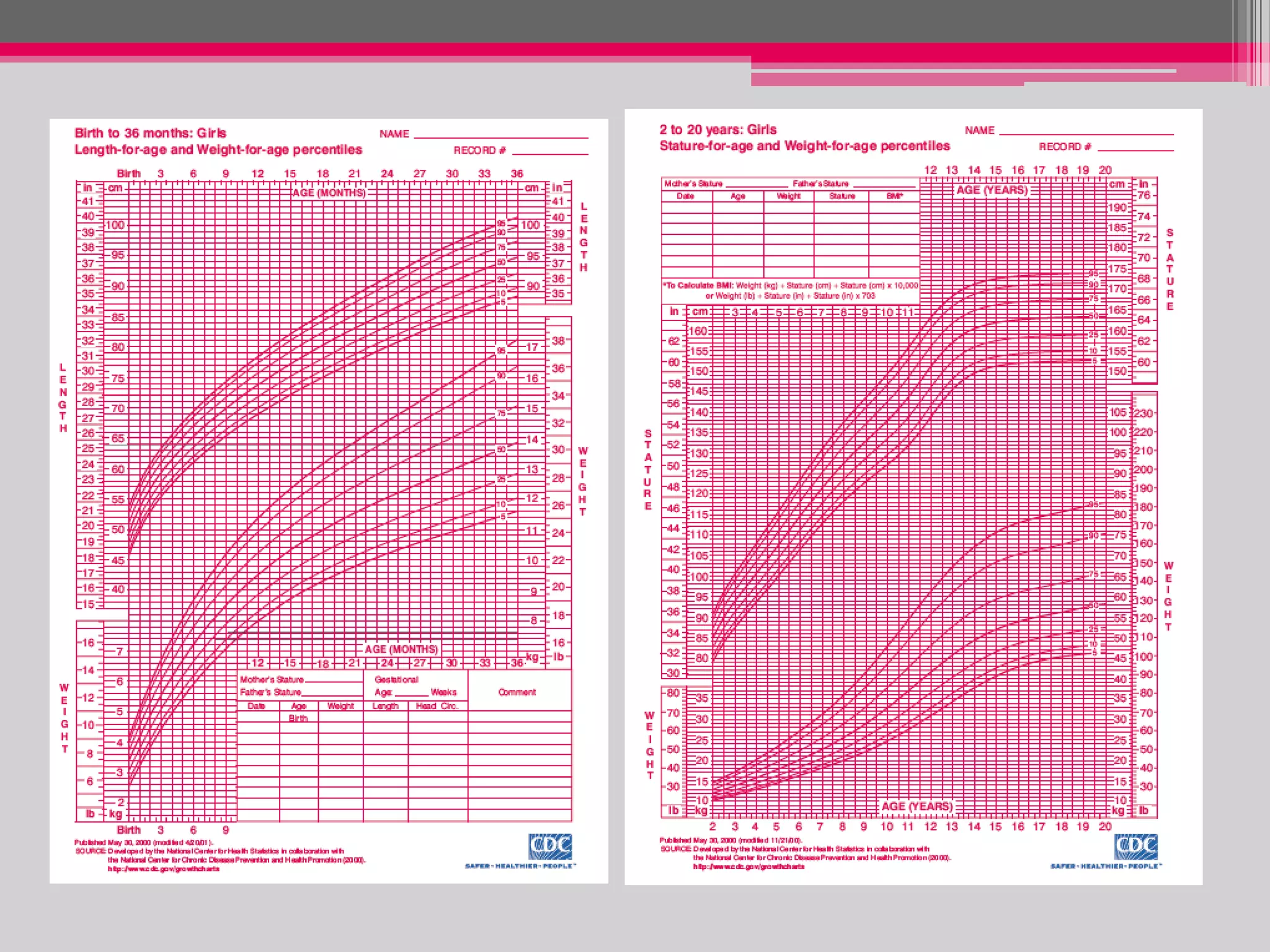
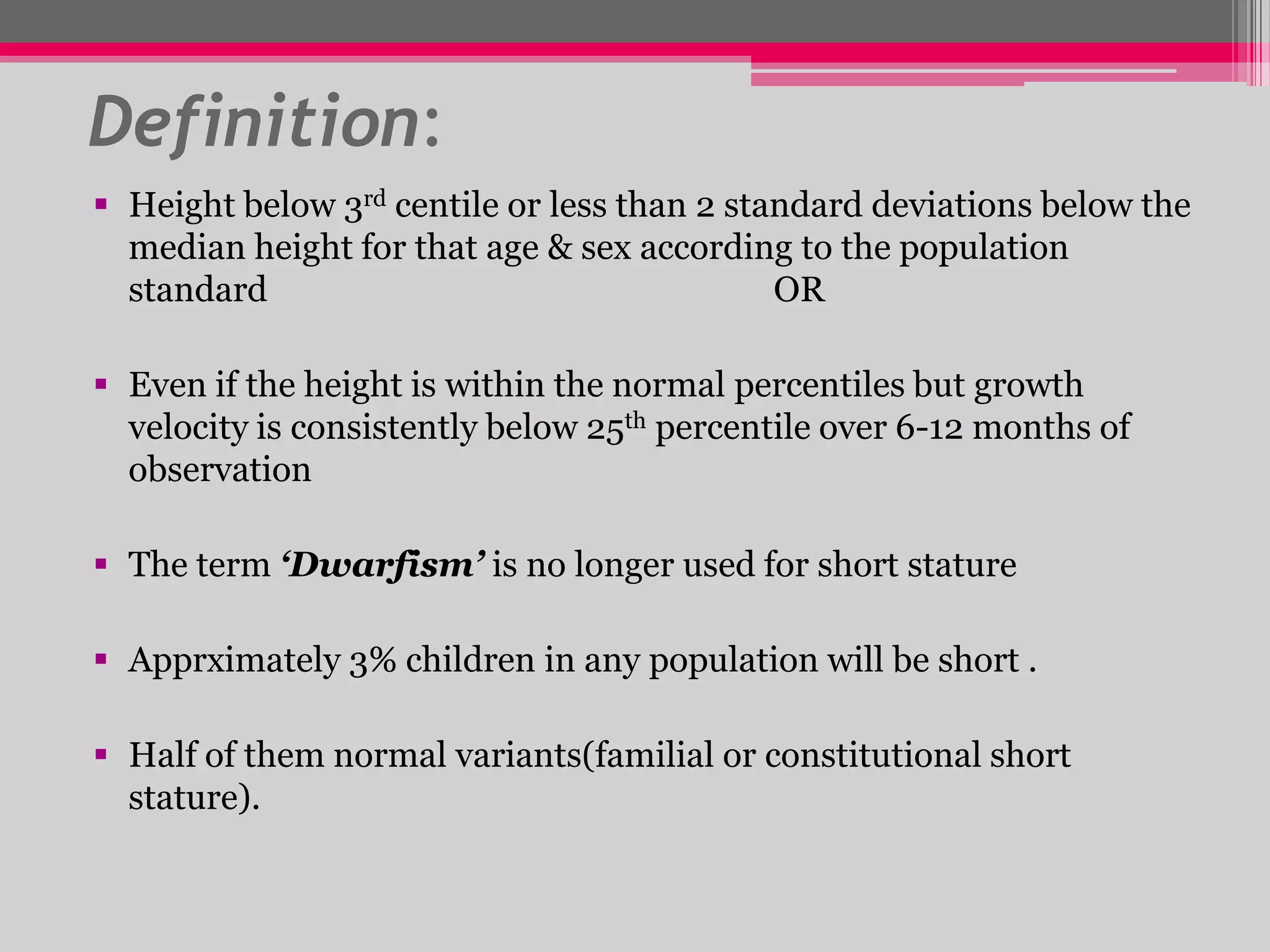
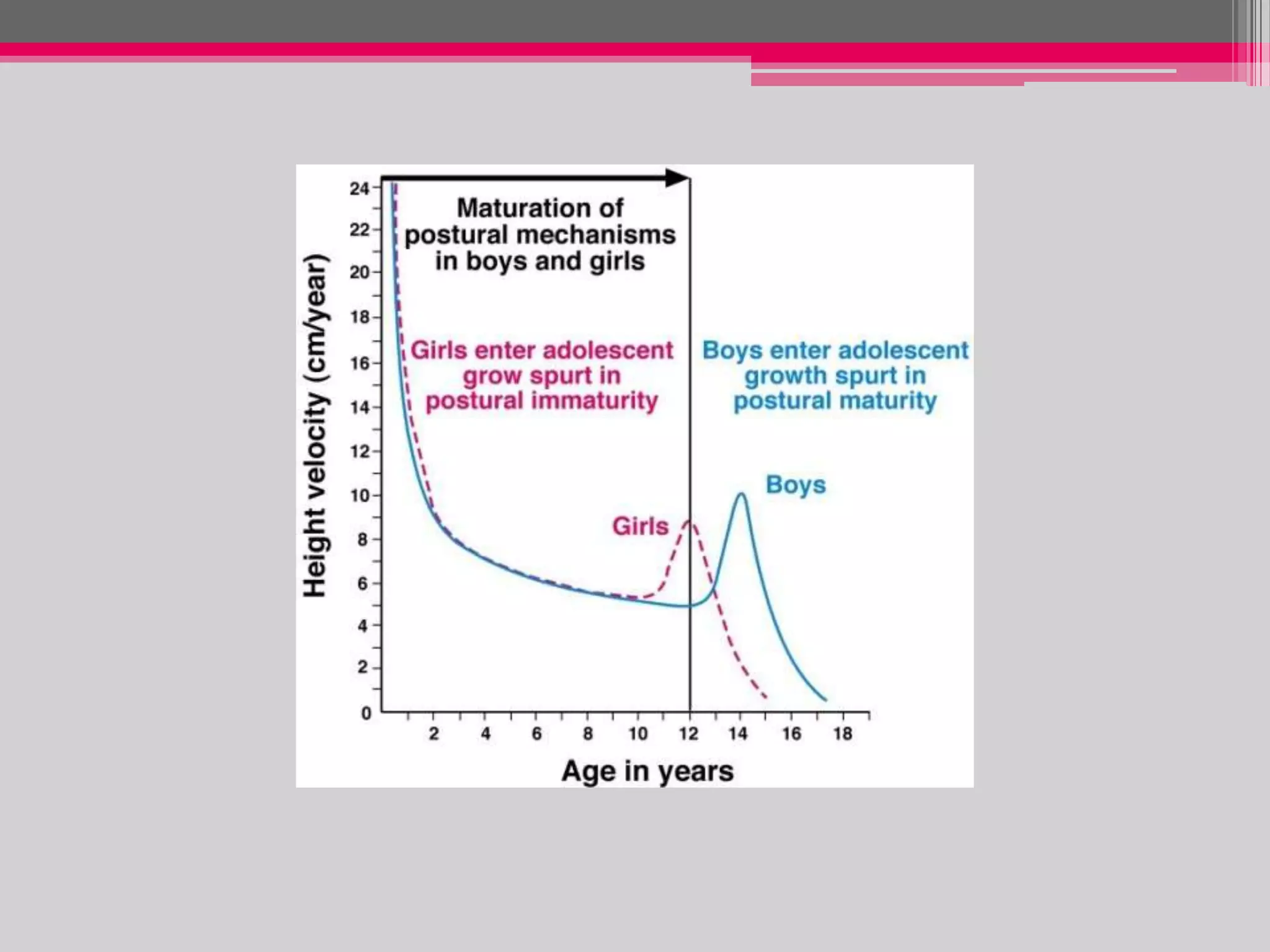
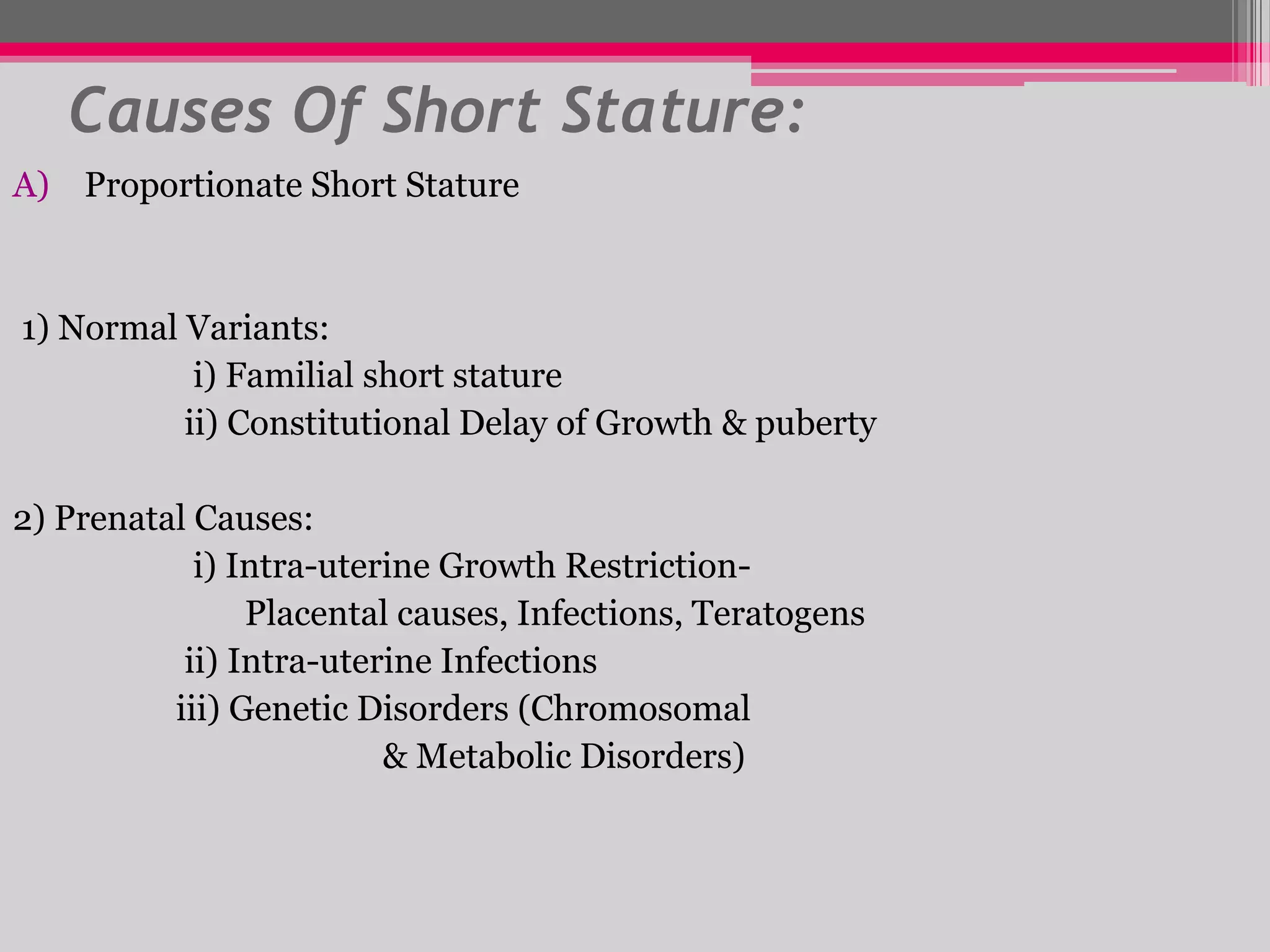
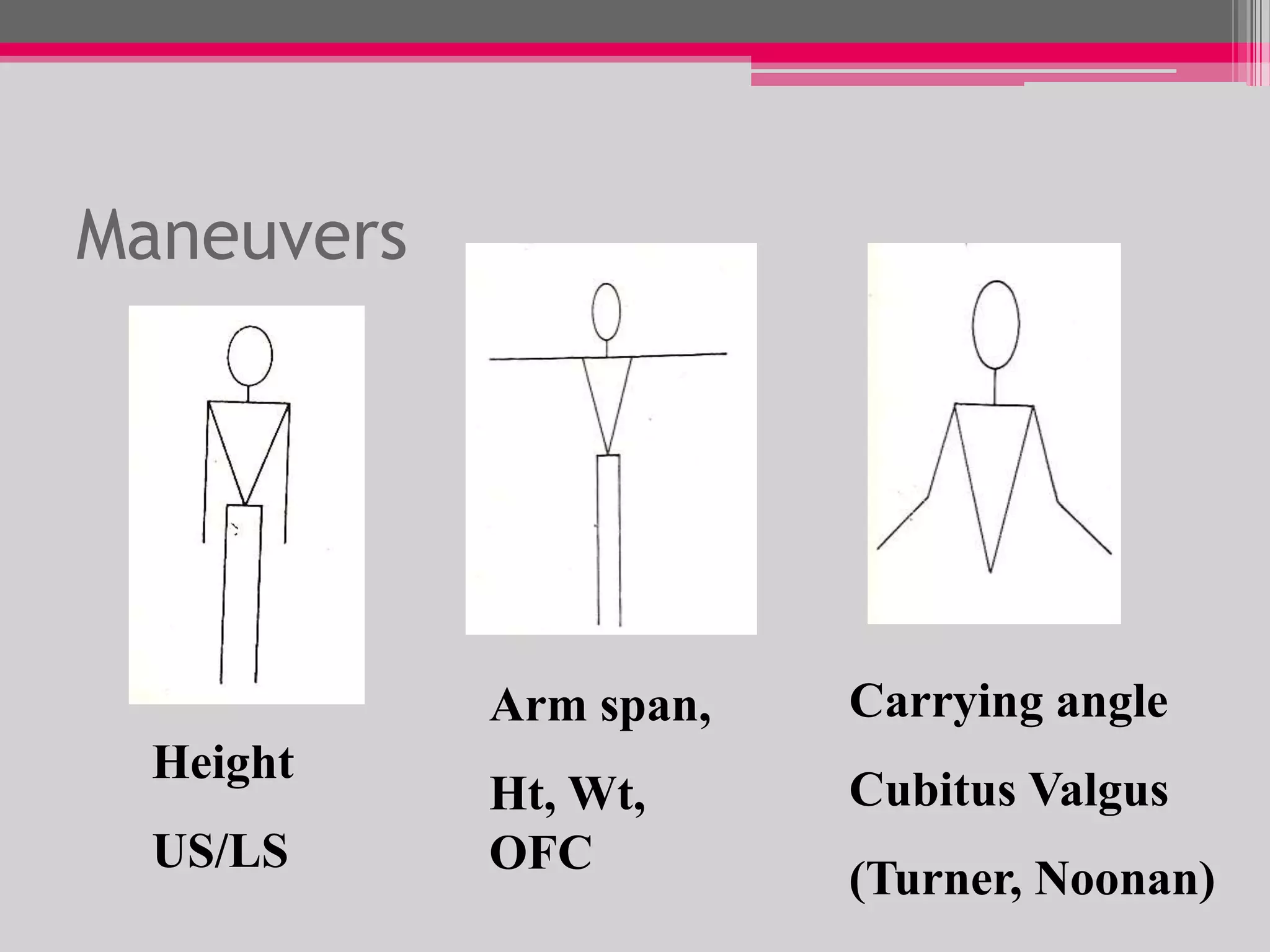
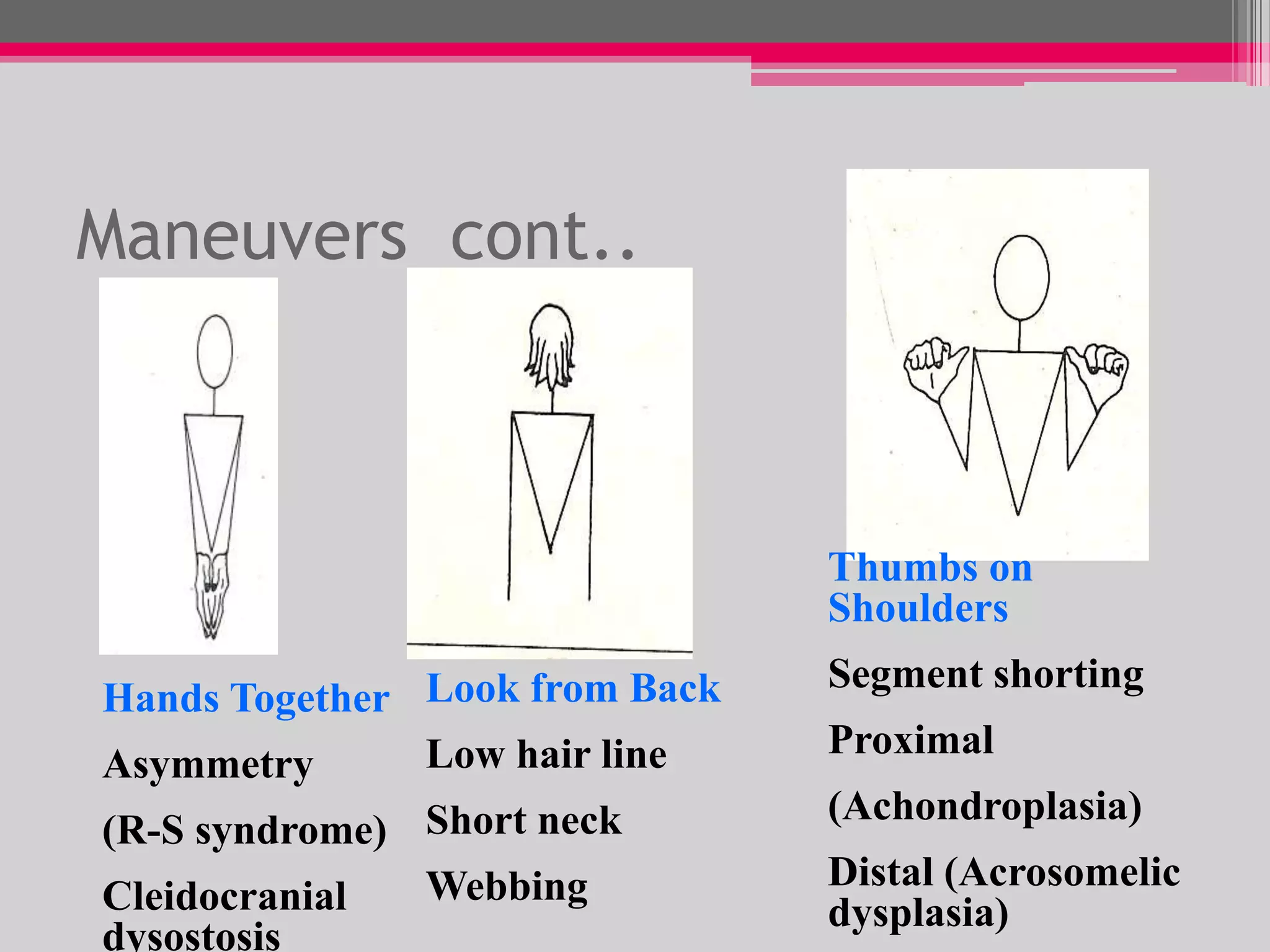
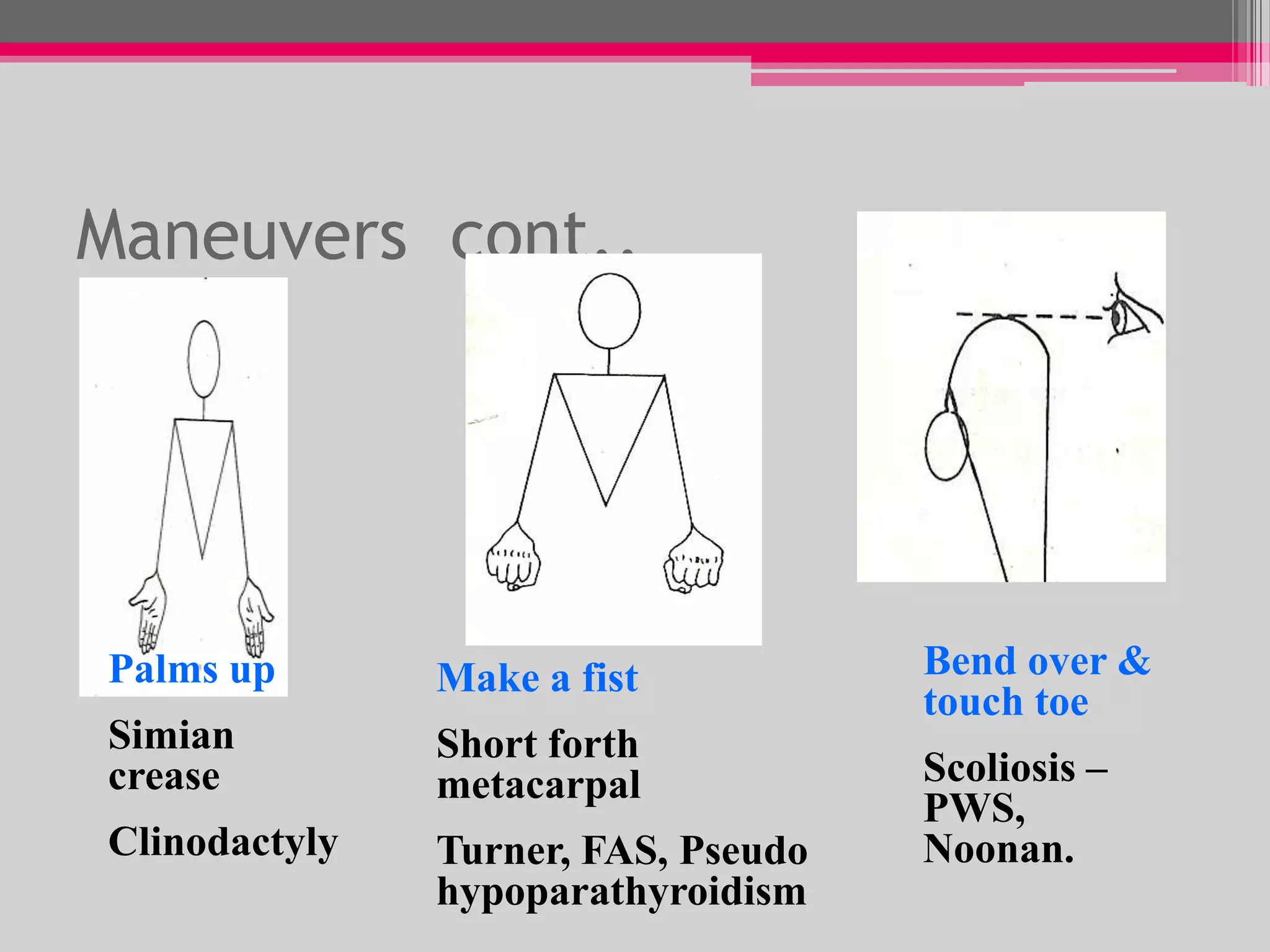
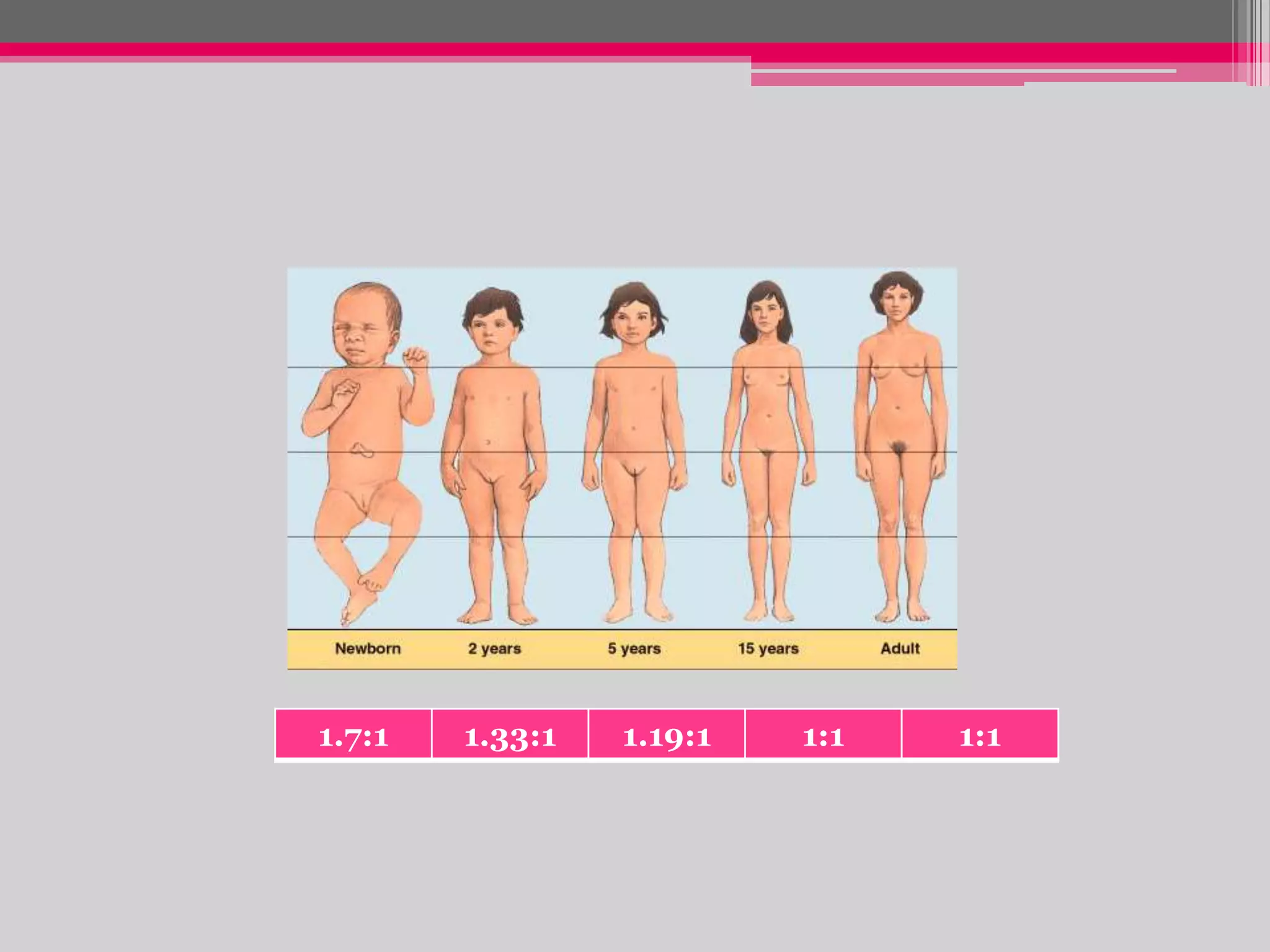
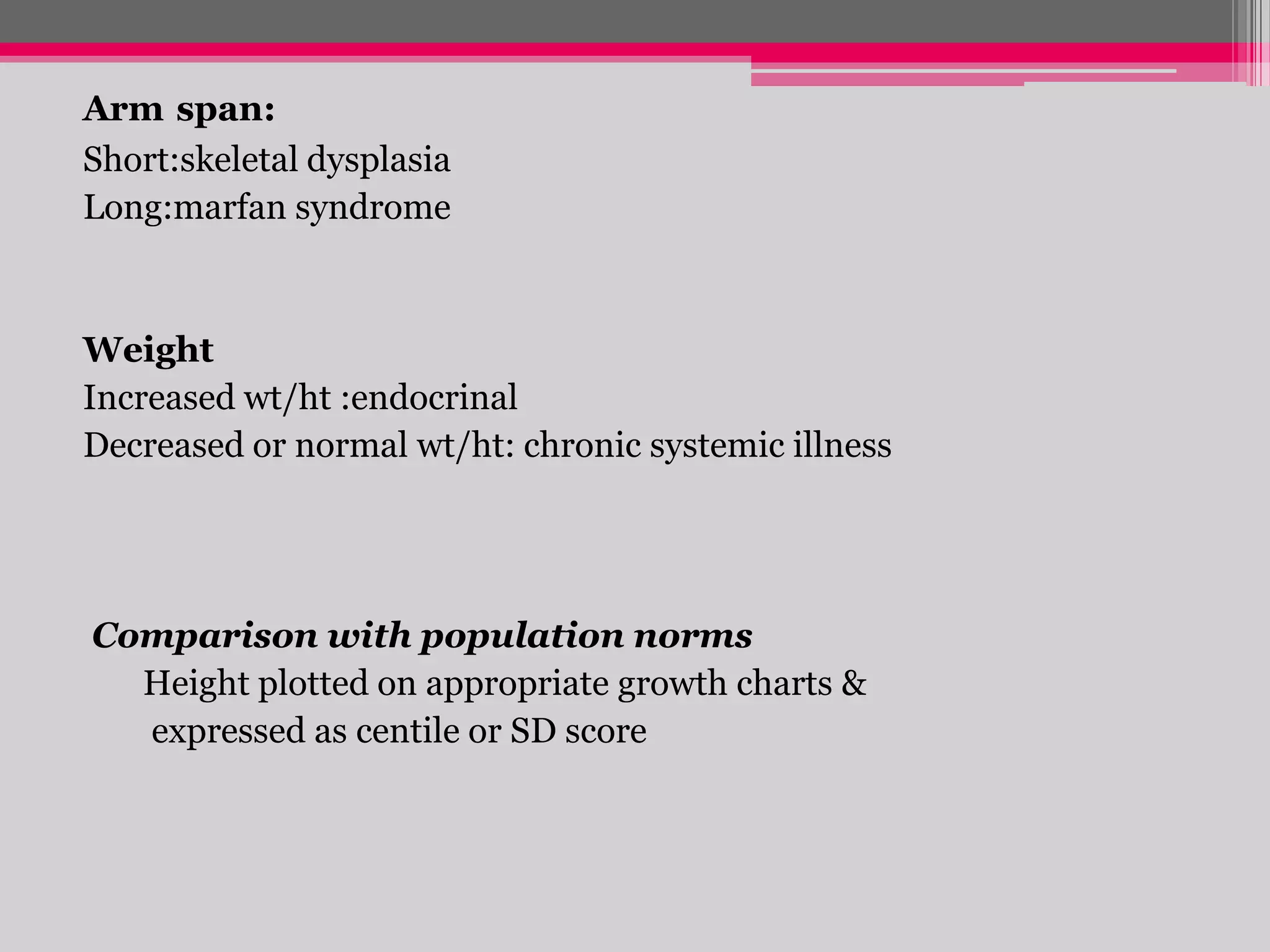
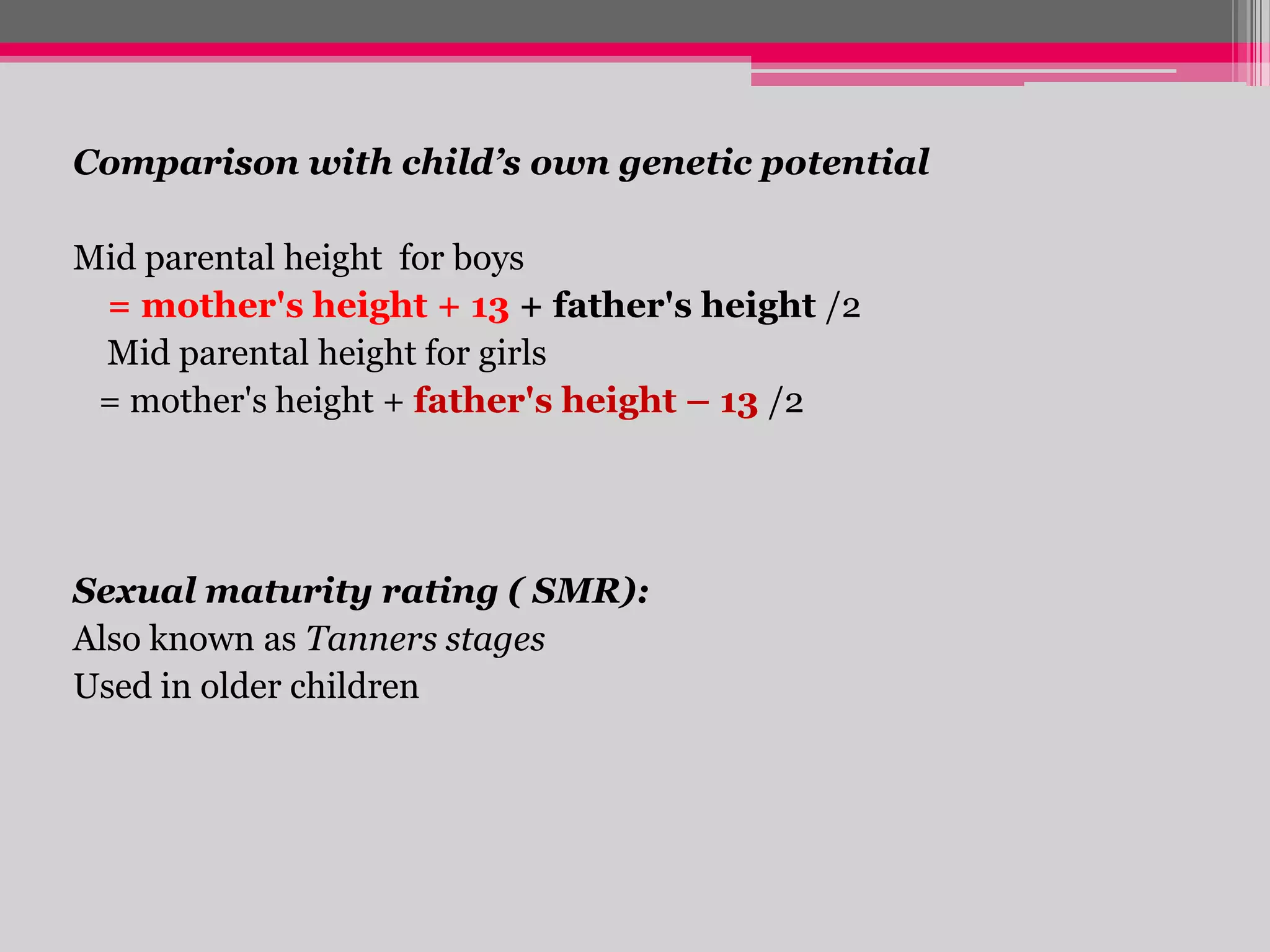
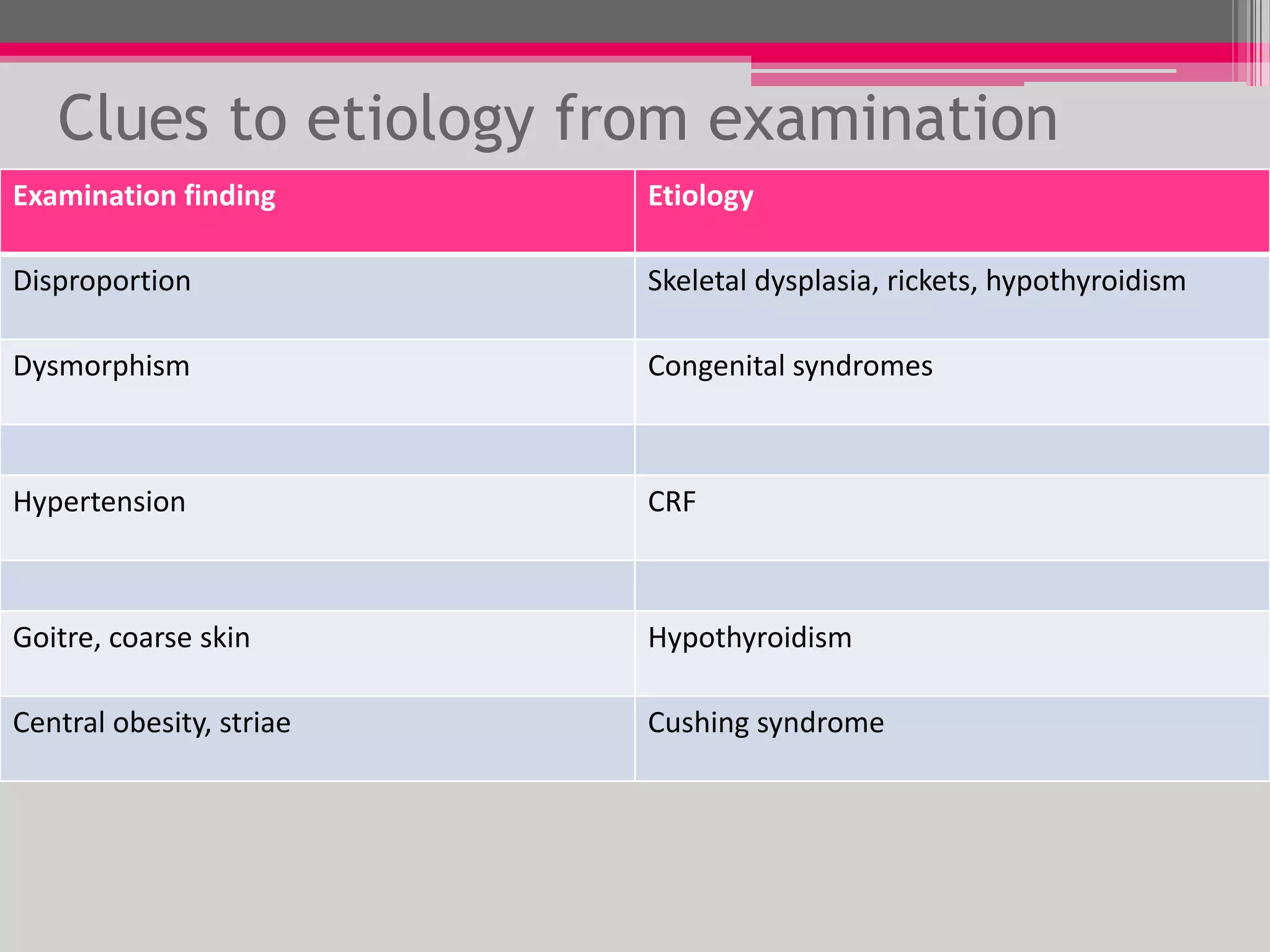
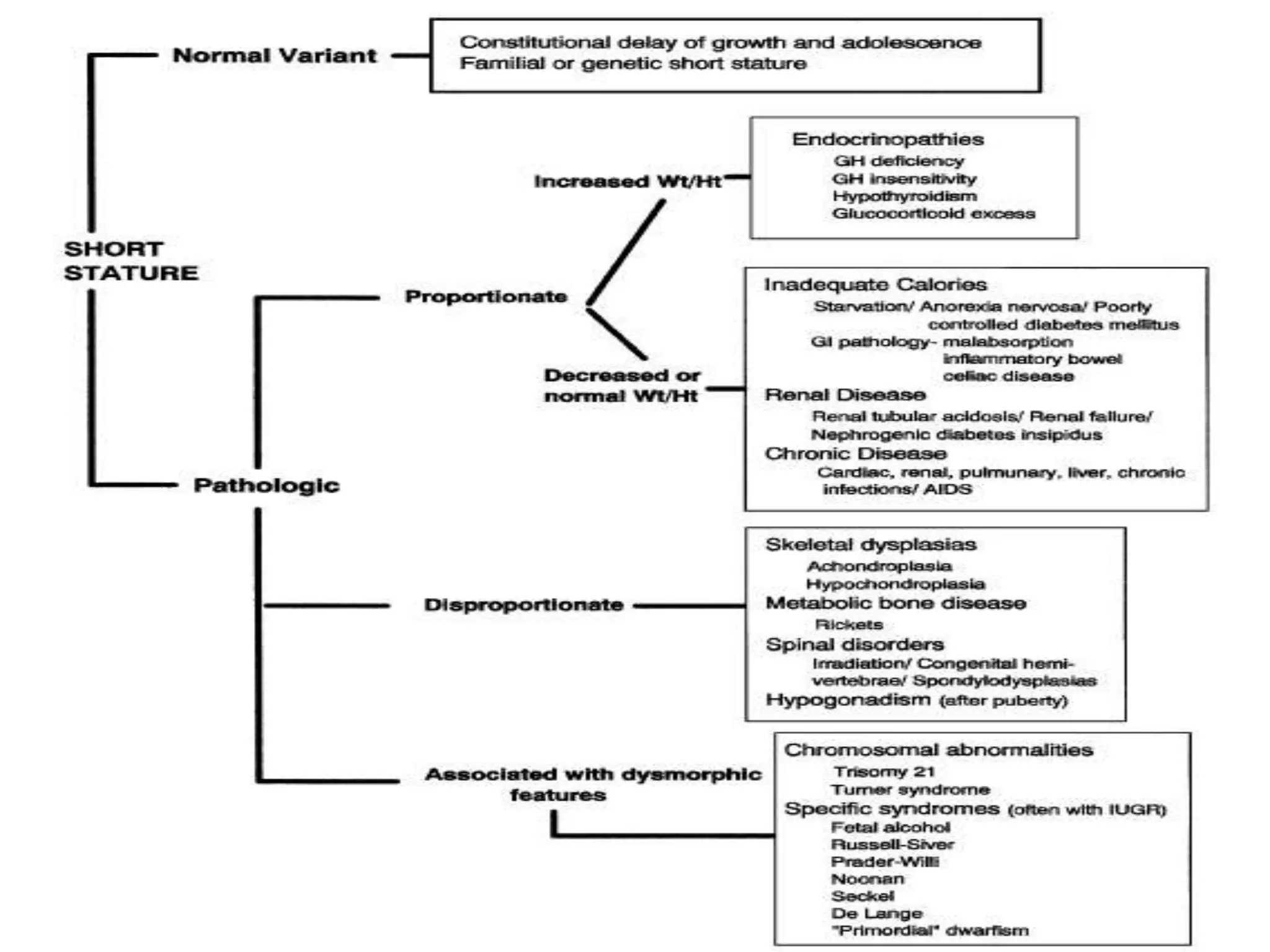
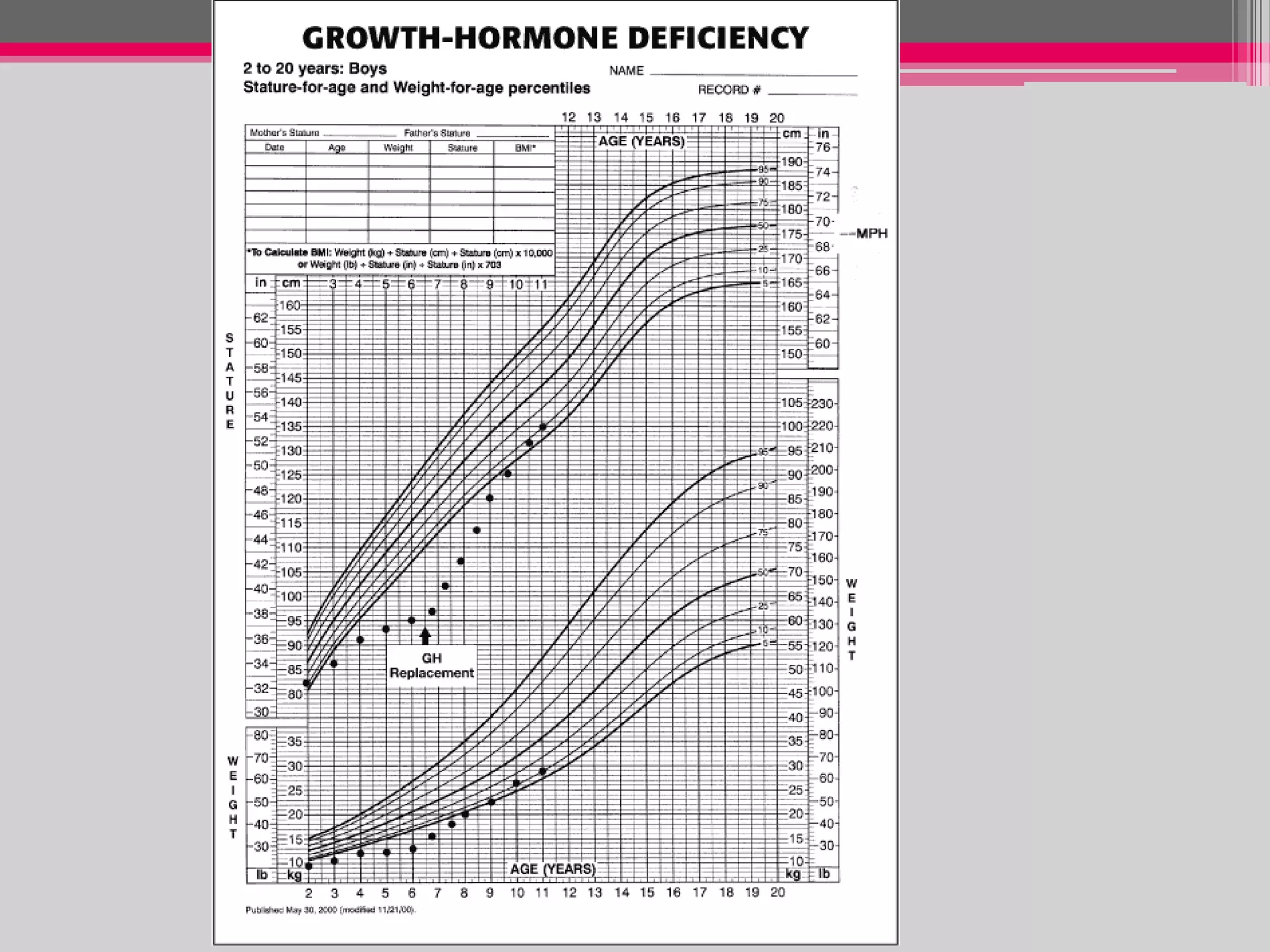
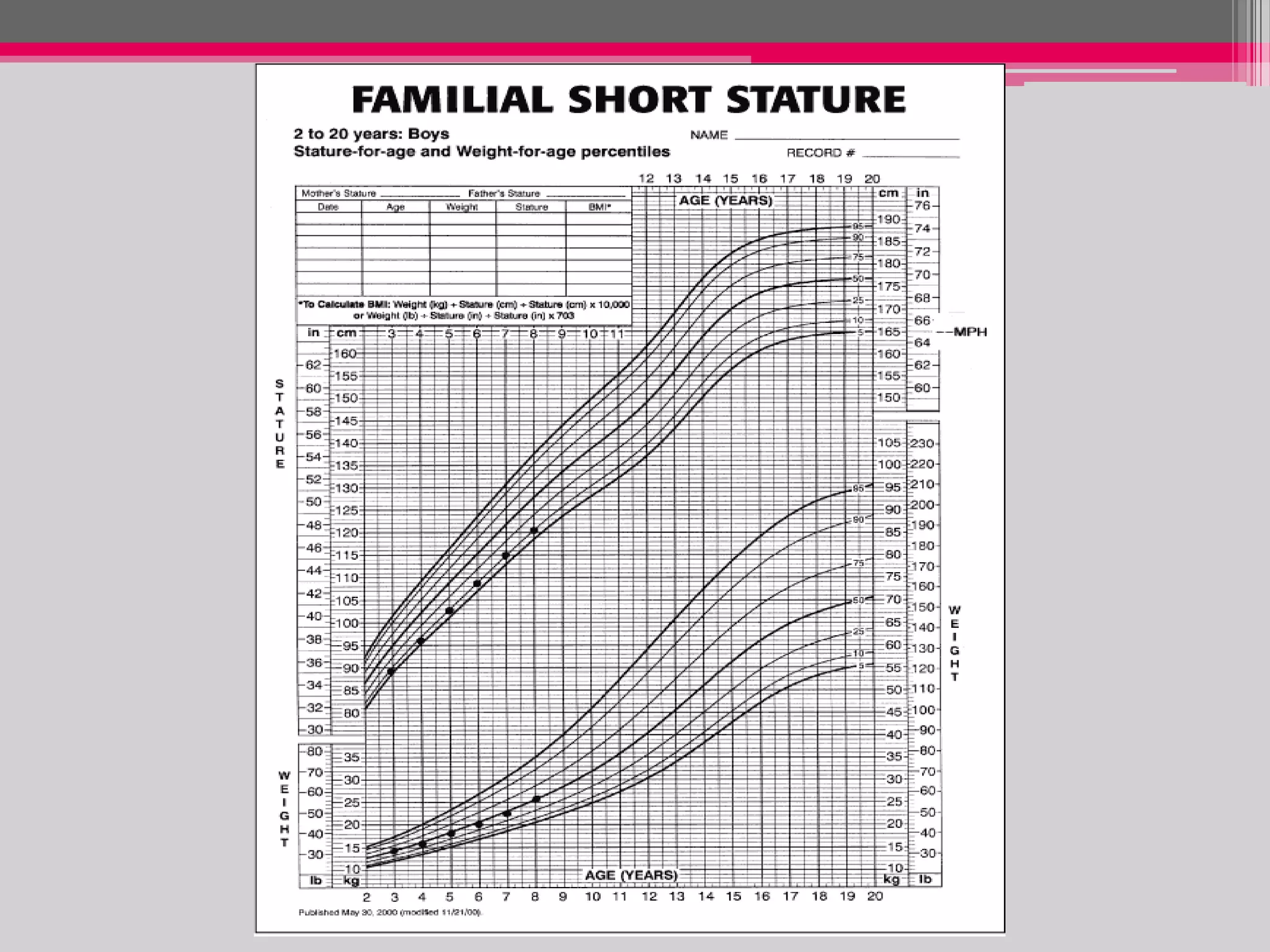
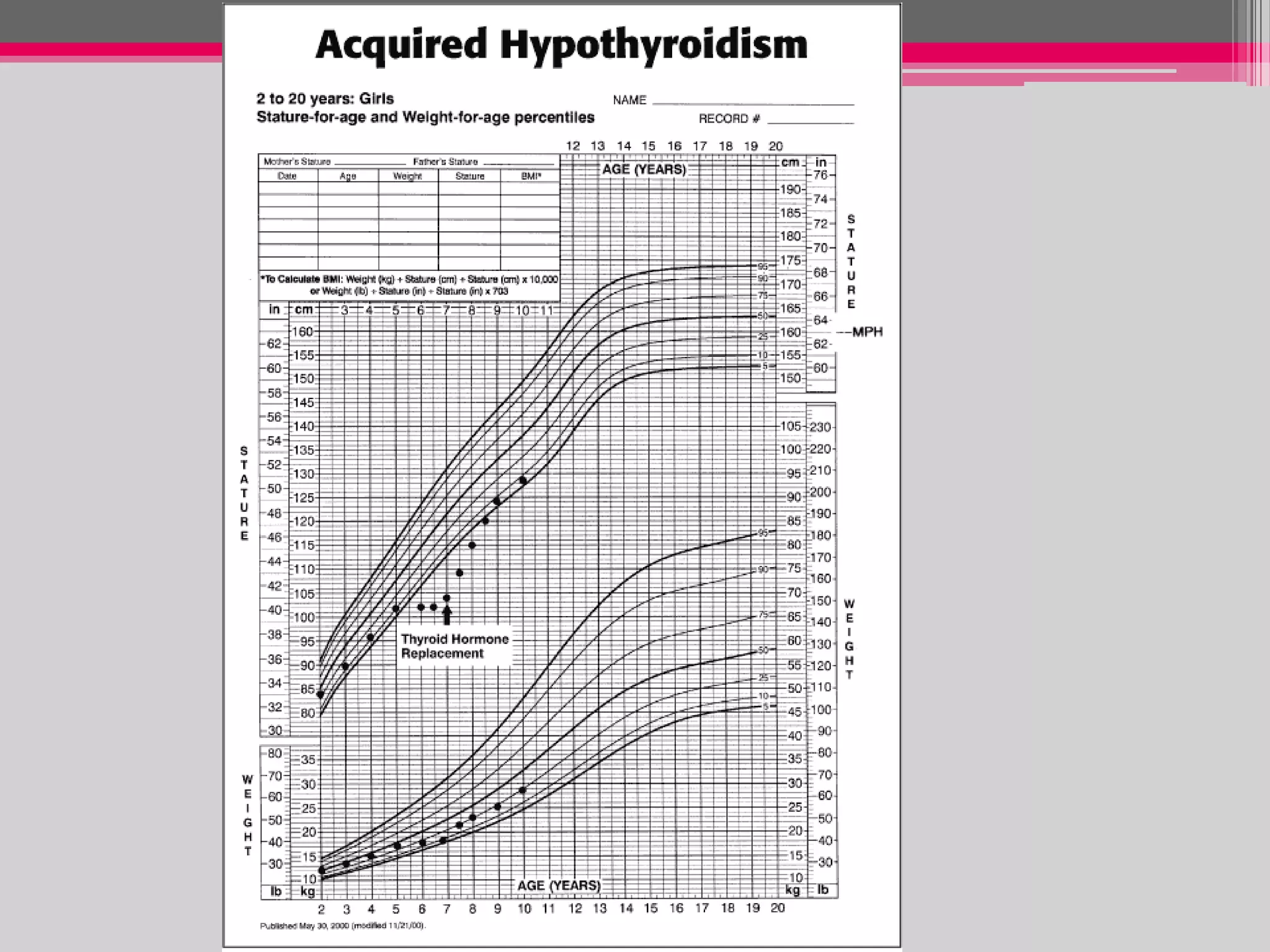
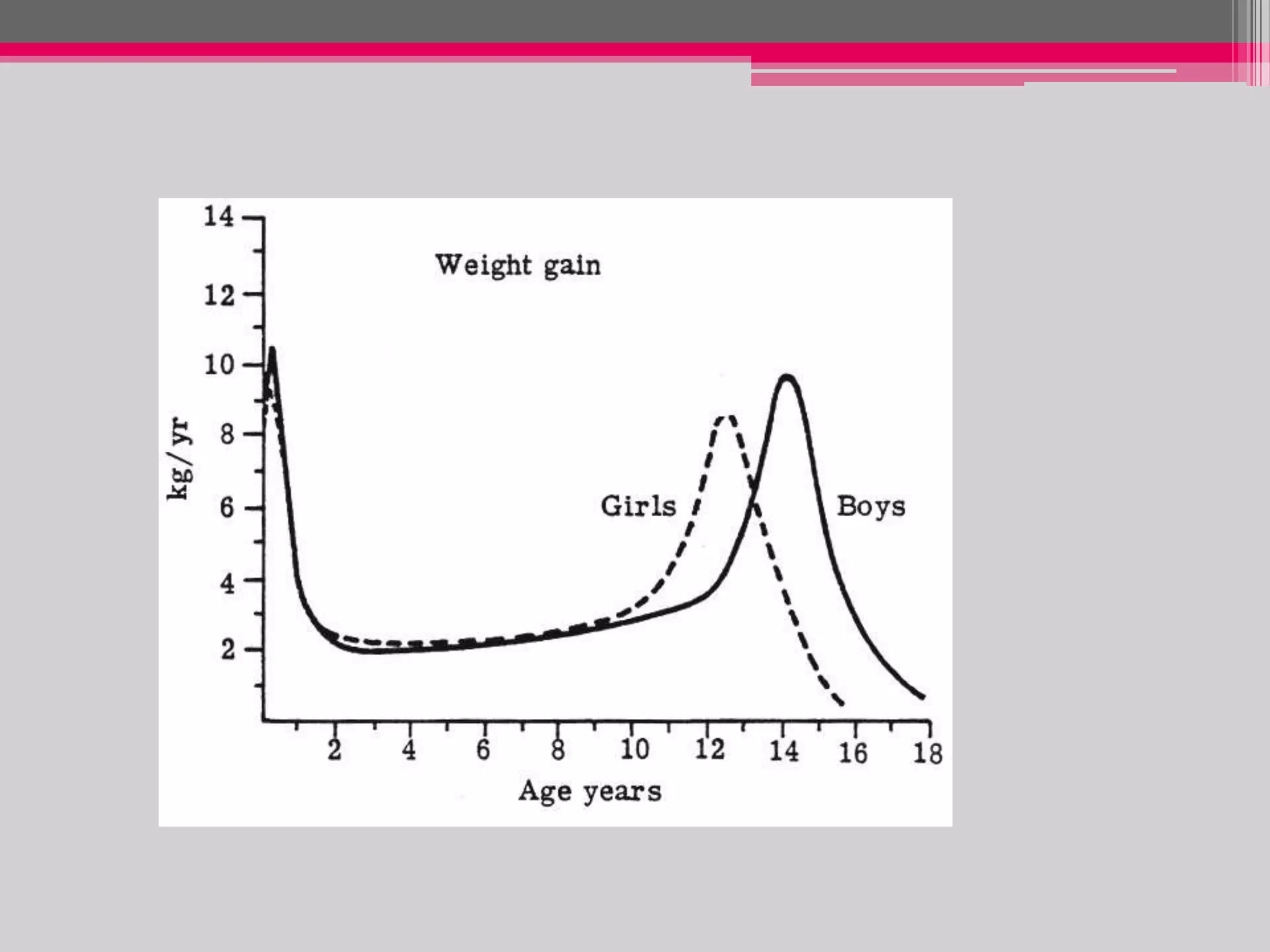
This document provides an overview of the approach to evaluating and managing short stature in children. It defines short stature and outlines normal growth patterns. Common causes of short stature include familial short stature, constitutional delay of growth, prenatal issues, malnutrition, chronic illness, and endocrine disorders. A thorough history, physical exam including growth measurements and Tanner staging, and screening lab tests can provide clues to identify underlying causes. Further testing may include bone age, thyroid function, genetics, celiac serology, and growth hormone stimulation if initial workup is normal. Management depends on the specific cause but may include diet, supplements, growth hormone therapy, or surgery.