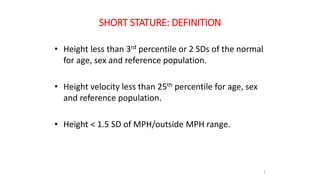
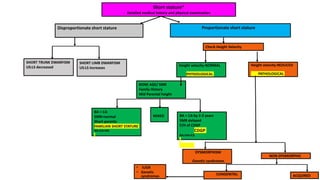
1. Short stature is defined as a height less than the 3rd percentile for age, sex and population or more than 2 standard deviations below the mean height.
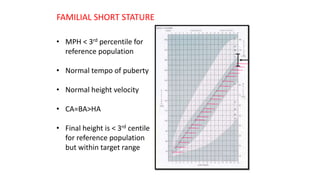
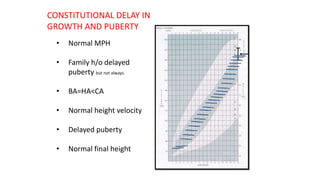
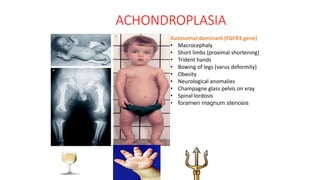
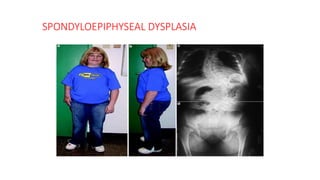
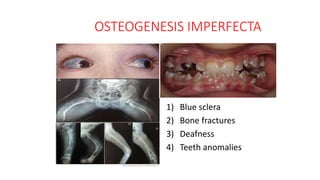
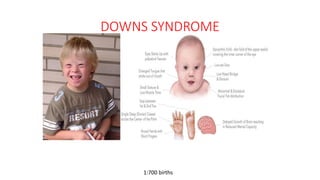
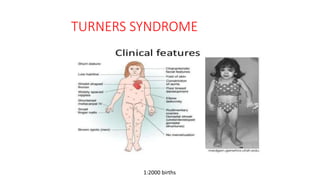
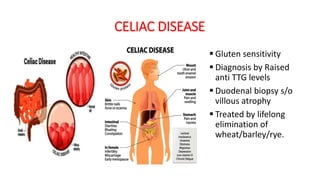
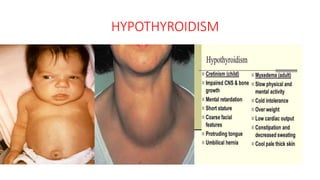
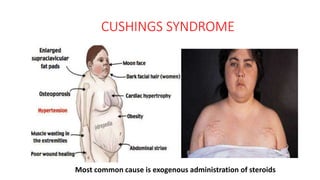
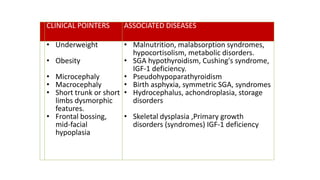
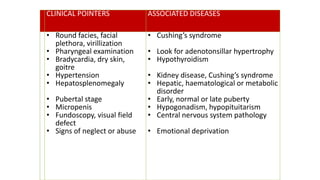
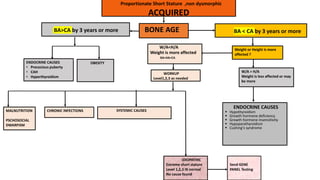
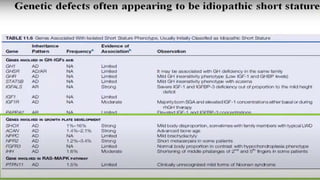
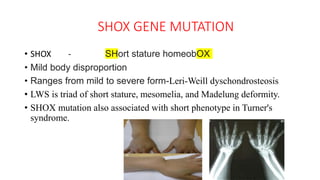
2. Physiological short stature includes familial short stature and constitutional delay of growth and puberty. Pathological short stature can be due to disproportionate short stature from skeletal dysplasias, acquired conditions like malnutrition or genetic syndromes.
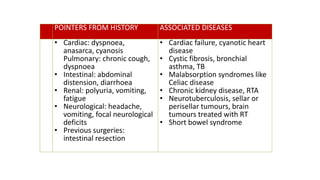
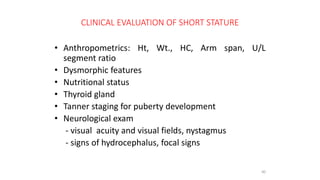
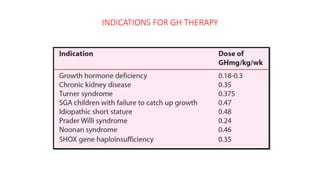
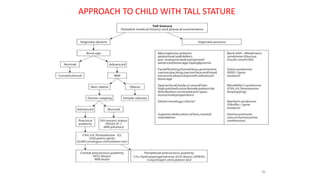
3. Evaluation of short stature involves detailed history, physical exam, bone age assessment and screening for endocrine or systemic illnesses based on three levels of investigation. Management depends on identifying and treating the underlying cause.