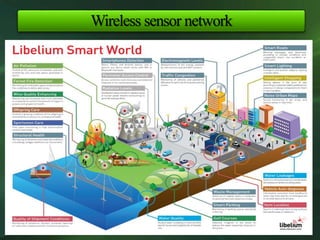
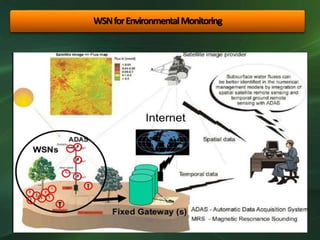
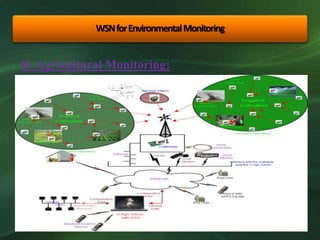
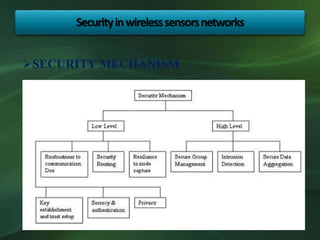
The document discusses the application and importance of wireless sensor networks (WSN) in environmental monitoring, detailing their architecture, advantages, and various applications such as agricultural and climate monitoring. It highlights the need for security measures in WSN due to potential attacks on data transmission. Overall, WSN offers a powerful tool for environmental control and real-time monitoring while facing security challenges.