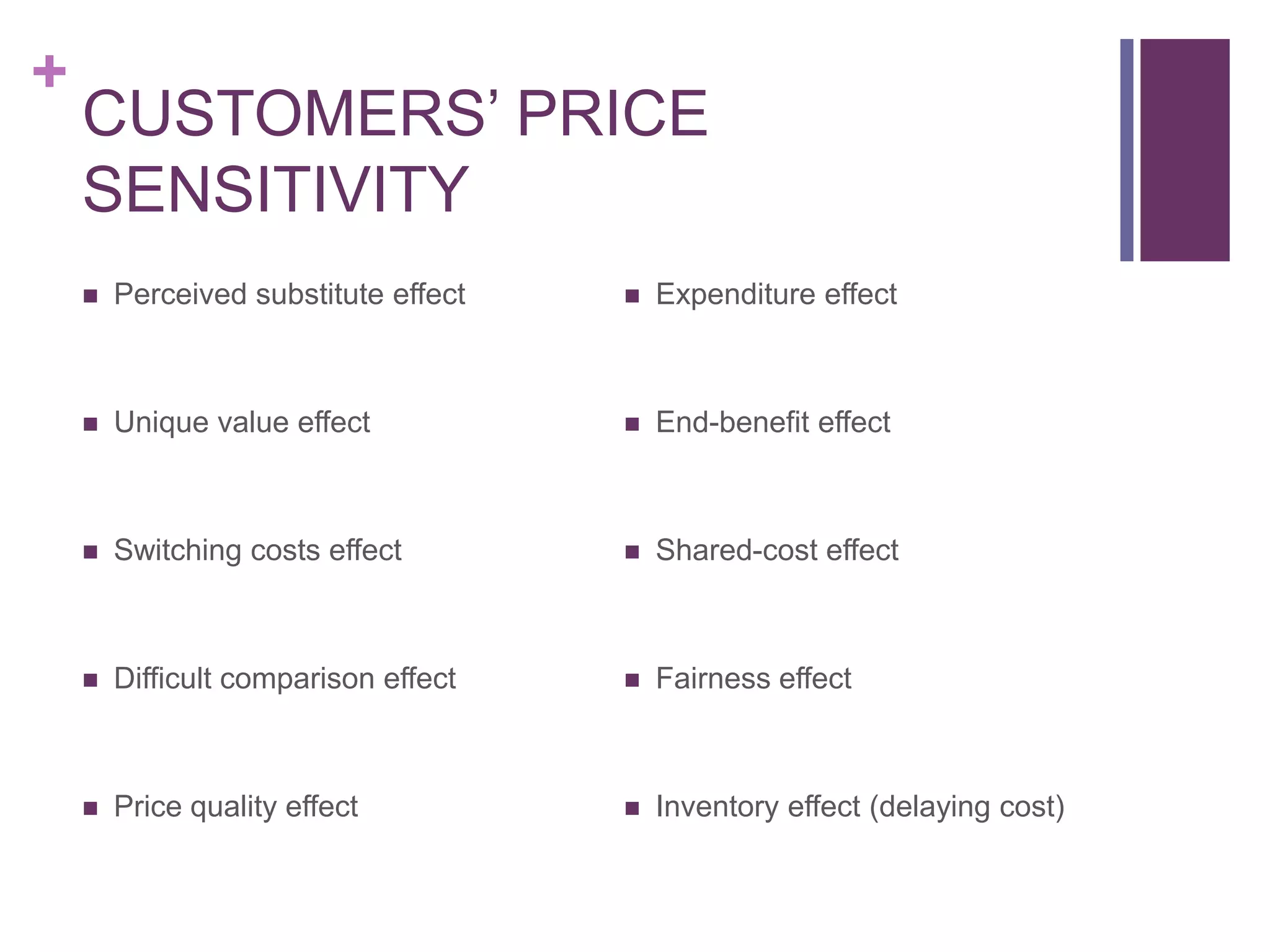
This document discusses pricing strategies for services. It begins by explaining the differences between monetary price and customers' total perceived value of services, which includes additional costs like time and energy. Customers' price sensitivity is influenced by factors like substitute options and quality perceptions. Effective pricing requires understanding costs and competitors as well as market segmentation. Strategies discussed include price leadership, yield management, bundling, and implementing a differentiation premium model where higher prices signal exclusivity and quality. The goal is to set prices that maximize returns through segmentation and consideration of customer value perceptions.